Appendix diagnostica – Familial hypercholesterolemia diagnostic criteria
Published in:
Vnitř Lék 2017; 63(1): 49
Category:
Simon Broome system
Definite familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) is defined as follows:
a) cholesterol levels > 6.7 in children under 16 years of age and > 7.5 in adults; or LDL-C levels > 4.9 in adults
and
b) tendinous xanthomas in a patient or a first-/second-degree relative.
Possible familial hypercholesterolemia is defined as follows:
a) cholesterol levels > 6.7 in children under 16 years of age and > 7.5 in adults; or LDL-C levels > 4.9 in adults
and one of the following criteria:
b) family history of myocardial infarction prior to 50 years of age in second-degree relatives, or prior to 60 years in first-degree relatives
c) family history of elevated cholesterol > 7.5 in first-/second-degree relatives.
MedPed criteria used in the United States
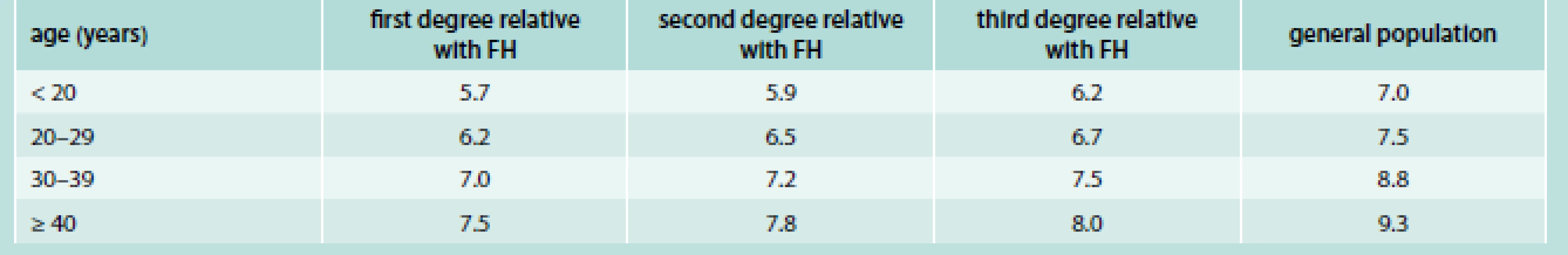
Dutch Lipid Clinic Network criteria for FH
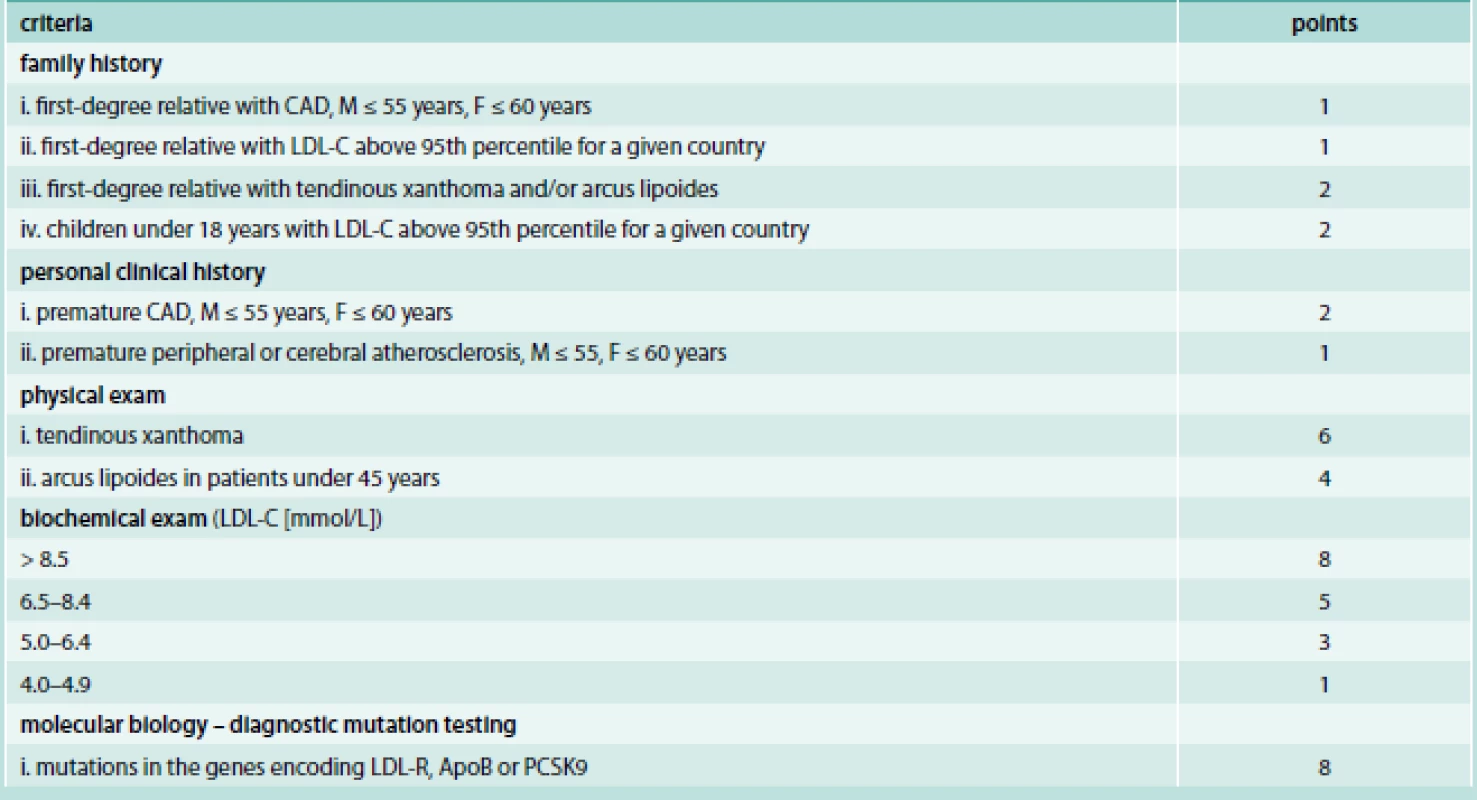
The Dutch criteria are then interpreted as follows: For a definite diagnosis of FH, the subject must have more than 8 points; a probable diagnosis of FH requires 6–8 points; and a possible diagnosis of FH is indicated by 3–5 points. Patients who score 0–2 points most likely do not have FH.
Labels
Diabetology Endocrinology Internal medicineArticle was published in
Internal Medicine

2017 Issue 1
-
All articles in this issue
- Predatory journals: how their publishers operate and how to avoid them
- Closure of the left atrial appendage by means of the AtriClip System
- Treatment of HCV genotype 2 infection
- A contribution to the differential diagnostics of sclerosing cholangitides
- The importance of evaluating the effectiveness of the ventilation VE/VCO2 slope in patients with heart failure
- 2nd Prague European Days of Internal Medicine
- ScreenPro FH – Screening Project for Familial Hypercholesterolemia in Central, Southern and Eastern Europe: Basic Epidemiology
- ScreenPro FH – Screening Project for Familial Hypercholesterolemia in Central, Southern and Eastern Europe: Rationale and Design
- Appendix diagnostica – Familial hypercholesterolemia diagnostic criteria
- Rituximab-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy
- Internal Medicine
- Journal archive
- Current issue
- Online only
- About the journal
Most read in this issue
- Closure of the left atrial appendage by means of the AtriClip System
- The importance of evaluating the effectiveness of the ventilation VE/VCO2 slope in patients with heart failure
- Rituximab-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy
- A contribution to the differential diagnostics of sclerosing cholangitides
