-
Články
- Časopisy
- Kurzy
- Témy
- Kongresy
- Videa
- Podcasty
Deficiency Suppresses Intestinal Tumorigenesis
Conditional deletion of Apc in the murine intestine alters crypt-villus architecture and function. This process is accompanied by multiple changes in gene expression, including upregulation of Cited1, whose role in colorectal carcinogenesis is unknown. Here we explore the relevance of Cited1 to intestinal tumorigenesis. We crossed Cited1 null mice with ApcMin/+ and AhCre+Apcfl/fl mice and determined the impact of Cited1 deficiency on tumour growth/initiation including tumour multiplicity, cell proliferation, apoptosis and the transcriptome. We show that Cited1 is up-regulated in both human and murine tumours, and that constitutive deficiency of Cited1 increases survival in ApcMin/+ mice from 230.5 to 515 days. However, paradoxically, Cited1 deficiency accentuated nearly all aspects of the immediate phenotype 4 days after conditional deletion of Apc, including an increase in cell death and enhanced perturbation of differentiation, including of the stem cell compartment. Transcriptome analysis revealed multiple pathway changes, including p53, PI3K and Wnt. The activation of Wnt through Cited1 deficiency correlated with increased transcription of β-catenin and increased levels of dephosphorylated β-catenin. Hence, immediately following deletion of Apc, Cited1 normally restrains the Wnt pathway at the level of β-catenin. Thus deficiency of Cited1 leads to hyper-activation of Wnt signaling and an exaggerated Wnt phenotype including elevated cell death. Cited1 deficiency decreases intestinal tumourigenesis in ApcMin/+ mice and impacts upon a number of oncogenic signaling pathways, including Wnt. This restraint imposed by Cited1 is consistent with a requirement for Cited1 to constrain Wnt activity to a level commensurate with optimal adenoma formation and maintenance, and provides one mechanism for tumour repression in the absence of Cited1.
Published in the journal: Deficiency Suppresses Intestinal Tumorigenesis. PLoS Genet 9(8): e32767. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1003638
Category: Research Article
doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003638Summary
Conditional deletion of Apc in the murine intestine alters crypt-villus architecture and function. This process is accompanied by multiple changes in gene expression, including upregulation of Cited1, whose role in colorectal carcinogenesis is unknown. Here we explore the relevance of Cited1 to intestinal tumorigenesis. We crossed Cited1 null mice with ApcMin/+ and AhCre+Apcfl/fl mice and determined the impact of Cited1 deficiency on tumour growth/initiation including tumour multiplicity, cell proliferation, apoptosis and the transcriptome. We show that Cited1 is up-regulated in both human and murine tumours, and that constitutive deficiency of Cited1 increases survival in ApcMin/+ mice from 230.5 to 515 days. However, paradoxically, Cited1 deficiency accentuated nearly all aspects of the immediate phenotype 4 days after conditional deletion of Apc, including an increase in cell death and enhanced perturbation of differentiation, including of the stem cell compartment. Transcriptome analysis revealed multiple pathway changes, including p53, PI3K and Wnt. The activation of Wnt through Cited1 deficiency correlated with increased transcription of β-catenin and increased levels of dephosphorylated β-catenin. Hence, immediately following deletion of Apc, Cited1 normally restrains the Wnt pathway at the level of β-catenin. Thus deficiency of Cited1 leads to hyper-activation of Wnt signaling and an exaggerated Wnt phenotype including elevated cell death. Cited1 deficiency decreases intestinal tumourigenesis in ApcMin/+ mice and impacts upon a number of oncogenic signaling pathways, including Wnt. This restraint imposed by Cited1 is consistent with a requirement for Cited1 to constrain Wnt activity to a level commensurate with optimal adenoma formation and maintenance, and provides one mechanism for tumour repression in the absence of Cited1.
Introduction
Inactivation of the APC (adenomatous polyposis coli) gene marks one of the earliest events in colorectal tumourigenesis [1], an observation that has given rise to the concept of Apc as a ‘cellular gatekeeper’ protecting against tumourigenesis [2]. This role in suppressing tumour formation has been closely associated with its ability to regulate the level of β-catenin within cells. Thus, Apc normally forms part of the scaffold of proteins that phosphorylate β-catenin and target it for degradation. In the absence of Apc, β-catenin levels become elevated and translocates to the nucleus, where it drives increased transcription of Wnt target genes associated with cell proliferation and cell death [3].
To investigate the biological consequences of Apc loss and Wnt activation, we and others have previously used a conditional model of Apc loss. In this model, deletion of Apc is achieved through use of an inducible AhCre transgene, which is responsive to exposure to the xenobiotic β-napthoflavone. Following Cre induction and loss of function of Apc, we observe a range of rapid phenotypic changes. These include promiscuous entry of cells into S phase, loss of differentiated cell types, loss of cell polarity and disorganisation of the crypt-villus structure to the point that discrete crypts are no longer discernable. Apc deficiency also reduces the normal migration of cells along the crypt villus axis, leading to the preferential retention of Apc deficient cells. These changes may all be considered pro-tumourigenic, however we also observe a considerable stress signal within Apc deficient cells, most clearly shown by a significant elevation in apoptosis. These phenotypic changes are accompanied by the expected elevation in levels of nuclear β-catenin and marked changes in the transcriptome [3].
One of the changes we observe in the intestinal epithelial cells of AhCre+Apcfl/fl mice is a strong induction of Cited1, a bi-functional transcriptional cofactor which is able to activate or repress transcription in association with other transcription factors [4], [5]. We also found this induction to be dependent upon functional c-Myc as Cited1 expression returns to basal levels in the additional absence of c-Myc, which completely rescues the phenotype of Apc deficiency [6]. These observations suggest that elevation of Cited1 may be directly associated with the preneoplastic phenotype.
Cited1 was originally identified in a mouse melanoma cell line [7]. During vertebrate development, Cited1 is expressed in progenitors of the heart, limb, axial skeleton, kidney, and placenta [8], [9]. It is implicated as a key co-ordinator during renal epithelial morphogenesis [5] and is involved in mammary gland development [10]. Cited1 is required for placental development with effect on embryo growth and survival [9]. However, Cited1 null mice that survive the early postnatal period are otherwise grossly phenotypically normal [9]. Cited1 is also able to enhance TGF-β signaling and inhibit Wnt signaling depending on cellular context [5], [11]. Both activation and inhibition of transcription are dependent on the CBP/p300 binding C-terminal transcription activation domain CR2, which is conserved throughout the Cited family [5], [11]–[13].
Deregulation of CITED1 has been implicated in several human cancers, including melanomas, Wilm's tumours and nephroblastomas [7], [14]–[16]. In the mouse, Cited1 is up-regulated in MMTV-Cre/FloxNeoNeuNT mammary tumours and associates with the transcription factor EGR2 to regulate the expression of the oncogene ErbB2 (HER2, Neu) [17]. Recently it has been shown that Cited1 expression, together with another transcription regulator Six2, specify self-renewing nephron progenitor cells in kidney development and it is suggested that Cited proteins may contribute to the maintenance of the self-renewing capping mesenchyme in the developing kidney [18]–[20]. Thus, although a body of studies have implicated Cited1 in both embryogenesis and carcinogenesis, its potential role in Wnt-induced intestinal tumourigenesis remains unresolved.
Given the data implicating Cited1 as a regulator of the Wnt pathway, we have tested the hypothesis that Cited1 plays a key role in intestinal tumourigenesis. We show that CITED1 is upregulated in human colorectal cancers and that Cited1 deficiency increases the survival of ApcMin/+ mice. When crossed into our acute model of Apc deficiency, we show that loss of Cited1 accentuates nearly all aspects of the Apc deficient phenotype, including the transcription of a range of oncogenic signaling pathways, including the Wnt pathway.
Results
Cited1/CITED1 is up-regulated in the intestine of Apc deficient mouse models and human colorectal tumours
We have previously shown that deletion of Apc in the mouse intestine leads to nuclear β-catenin translocation and up-regulation of Wnt target genes, including Cited1, as scored by microarray analysis [3]. To confirm this upregulation, we analysed mouse intestinal epithelium from AhCre+Apcfl/fl and AhCre+WT (WT: wild type) mice which had been induced by intraperitoneal injection of β-napthoflavone 4 days previously [3]. Quantitative PCR analysis revealed significant upregulation of the Wnt targets c-Myc, Axin2 and Cd44 in the absence of Apc. Similarly, Cited1 showed a 15-fold increase in expression (p<0.05, Figure 1A).
Fig. 1. Cited1 over-expression in ApcMin/+ mice, AhCre+Apcfl/fl mice and human colorectal cancer. 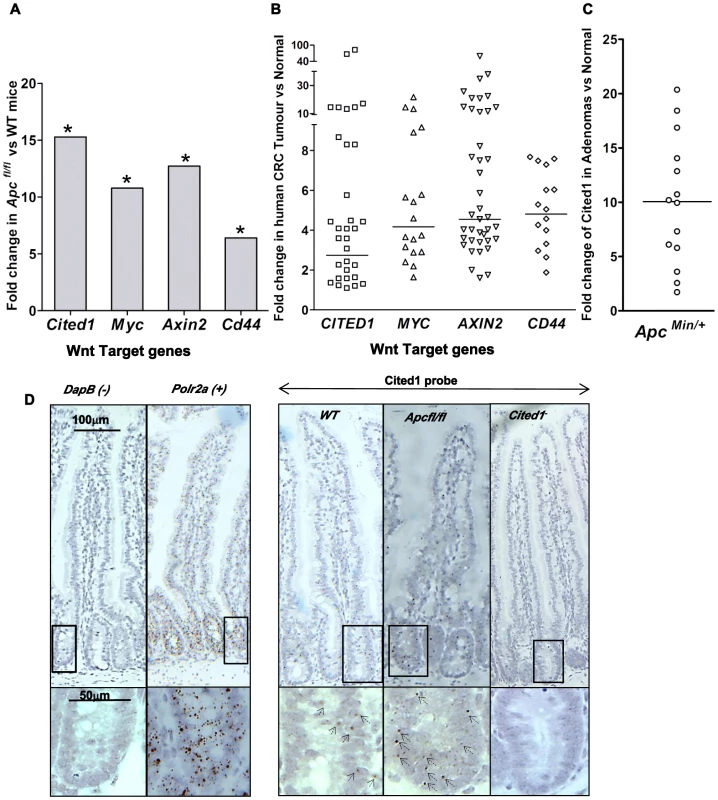
A: QPCR analysis of Wnt target genes 4 days after conditional deletion of Apc in the small intestinal. * p<0.05, Mann-Whitney U test, n = 3. B: Taqman qPCR analysis of gene expression in human CRC tumour tissue presented as fold change relative to adjacent normal tissue. The horizontal line indicates median fold change. p<0.01, Wilcoxon Signed Rank Test. C: Semi-QPCR analysis of Cited1 expression in ApcMin/+ adenomas. Three ApcMin/+ mice were used and 3–6 tumours were taken from each individual, n = 14. (p<0.01, Mann-Whitney U test). D: Cited1 in situ hybridization showing the increase in Cited1 expression in the AhCre+Apcfl/fl compare to AhCre+WT mouse. The staining is represented by single dots which correspond to the Cited1 transcript. The low level of staining (compared to positive control probe Polr2a) of Cited1 probe is distributed throughout the crypt-villus structure in the AhCre+WT mouse and in AhCre+Apcfl/fl mouse with an increase in staining after loss of Apc. Absence of staining is observed in the Cited1− intestinal tissue and in the negative control probe DapB. Inset panels show magnifications of intestine of corresponding zone. To determine if CITED1 was also deregulated in human cancers, we performed a Taqman quantitative PCR on human colorectal tumour tissues. In comparison to paired normal tissues from the same patient, we observed over-expression of the human orthologues of the Wnt target genes c-MYC, AXIN2, CD44 and CITED1 (p<0.01, Figure 1B). These data demonstrate the potential transferability of our data from the acute Apc deletion mouse model to human colorectal carcinogenesis.
We next assessed Cited1 levels in adenomas developing in the ApcMin/+ mouse model of human colorectal cancer, which allows evaluation of the effects of loss of Apc function over the course of polyp development. Again, the level of Cited1 expression was significantly increased in intestinal polyps from ApcMin/+ mice compared to normal tissue from the same mouse (p<0.01, Figure 1C; Figure S1A). Detection of high levels of Cited1/CITED1 expression in both human and murine tumours suggests that Cited1/CITED1 may play a role in intestinal tumourigenesis.
We performed in situ hybridization using a Cited1 probe designed against the deleted sequence in the Cited1− mouse (Figure 1D). We observed low levels of staining (compared to expression of the housekeeping gene Polr2a) throughout the crypt-villus structure in the AhCre+WT mouse intestine (WT) with a trend to higher levels within the crypt. There was no apparent specificity for the stem cell region at the base of the crypt or for any differentiated cell type. Consistent with QPCR data, we observed an increase in the level of staining throughout the crypt-villus structure of the AhCre+Apcfl/fl mouse.
Loss of Cited1 in ApcMin/+ mice increases survival and reduces the number of intestinal adenomas
As Cited1 is upregulated in colonic tumors we next asked whether deficiency of Cited1 could inhibit intestinal adenoma formation in the ApcMin/+ mouse. To achieve this, we crossed Cited1 null (Cited1−) mice onto ApcMin/+. Given that Cited1 is on the X-chromosome, we aged male cohorts of ApcMin/+Cited1− and ApcMin/+ mice until they displayed symptoms of intestinal neoplasia (rectal bleeding and paling feet). The median lifespan of ApcMin/+ mice was 230.5 days, which is increased to 515 days in the ApcMin/+Cited1− mice (Log-Rank p = 0.001, Figure 2A). Cited1− mice had a survival rate that was not significantly different to that of WT mice (Figure 2A).
Fig. 2. Loss of Cited1 extends lifespan of ApcMin/+ mice and reduces the number of intestinal adenomas. 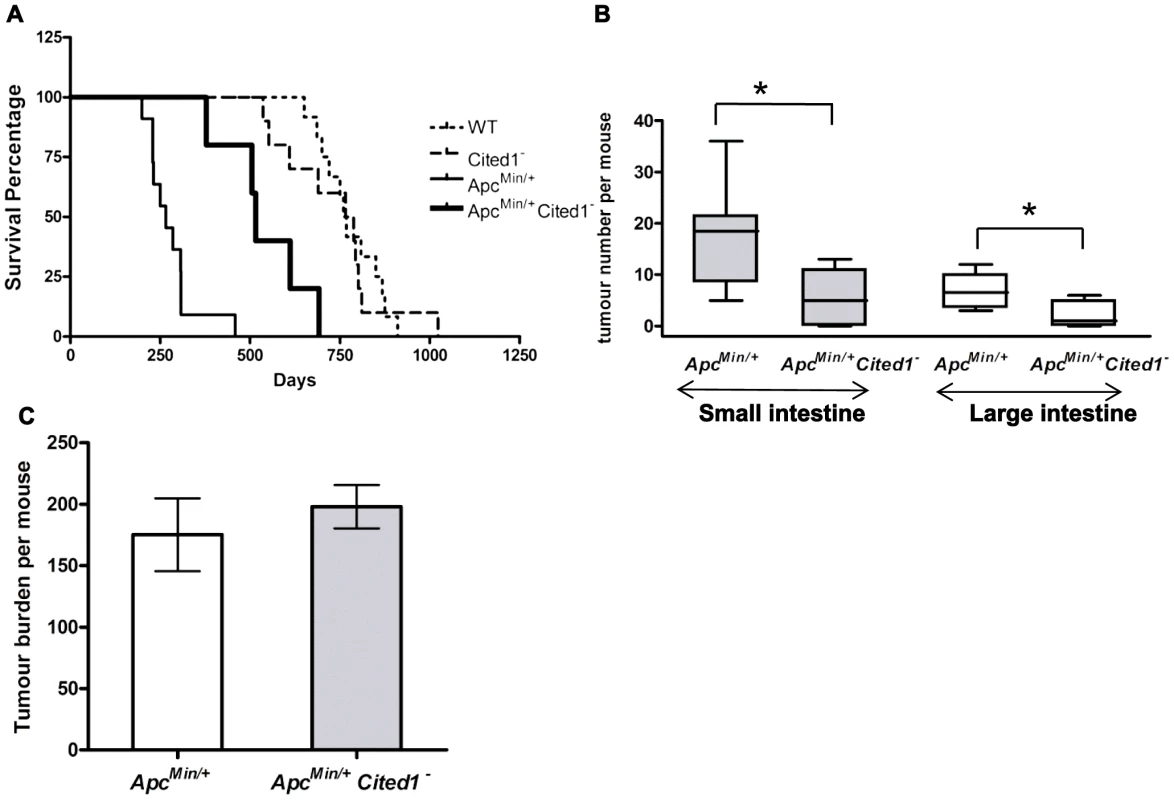
A: Kaplan-Meier plot of survival of ApcMin/+ (thin continuous line), ApcMin/+Cited1− mice (thick continuous line), Cited1− (dashed line) and WT (dotted line). The median lifespan of ApcMin/+ mice cohort was 230.5 days (n = 8), which was increased to 515 days in ApcMin/+Cited1− mice (n = 5) (p = 0.001 Log-Rank test). The median lifespan of Cited1− was 766 days (n = 10) and is similar to WT with a lifespan of 760 days (n = 12) (p = 0.749 Log-Rank test). B: In both small intestine (grey boxes) and large intestine (blank boxes), tumour numbers were reduced in ApcMin/+Cited1− mice (n = 5) compared to ApcMin/+ mice (n = 8) (*p<0.05, Mann-Whitney U test). C: Tumour burden was calculated and represent the total tumour volume per mouse. There is no significant difference between ApcMin/+ (white) and ApcMin/+Cited1− (Grey) (p>0.05, Mann-Whitney U test). We next counted the number of adenomas in the small and large intestine (Figure 2B). ApcMin/+Cited1− mice developed significantly less tumours compared to ApcMin/+ in both the small intestine (5 versus 18.5 adenomas p<0.05) and the large intestine (1 versus 6.5 adenomas, p<0.05). The tumour distribution in the small intestine and the colon was analysed at ill health (Figure S1C). There was no significant difference in the percentage of tumours found in the duodenum or jejunum of the small intestine, or in the large intestine. However, we did observe a significant increase in the percentage of tumours found in the last part of the small intestine which corresponds to the human ileum (Figure S1C). Total tumour burden of ApcMin/+Cited1− mice was not significantly different from that of ApcMin/+ (Figure 2C), and shared the same tubular morphology and degree of invasiveness, as assessed histologically by the frequency of invasion into the submucosa (52.8% High grade +47.16% Low grade in ApcMin/+ vs 42.8% High grade +57.4% Low grade in ApcMin/+Cited1−, Chi-square x2 = 2.1, DF = 1, p>0.05). These data suggest that mice became symptomatic of disease when they had developed an equivalent tumour burden, but that in the Cited1 mutant background this was significantly later and reflected fewer, but larger lesions at these later time points, hence implicating Cited1 in intestinal tumour initiation.
Cited1 deficiency modifies the phenotype observed immediately after Apc loss by increasing the number of Brdu positive cells and the size of the hyperplastic area
To address the mechanism underlying the reduction of adenoma formation in ApcMin/+Cited1− mice, we crossed Cited1− mice with mice conditionally mutant for Apc. We have previously demonstrated that we can achieve almost 100% recombination of the Apcfl/fl allele in the intestine using the β-napthoflavone inducible AhCre transgene to drive recombination [3]. Thus, AhCre+WT, AhCre+Apcfl/fl, AhCre+Cited1−, and AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− mice were induced with β-napthoflavone and culled 4 days after the first injection to determine the role of Cited1 immediately following deletion of Apc. To confirm the level of Apcfl/fl recombination we used quantitative RT-PCR and again found that 100% of the PCR products obtained were from the recombined Apc allele (Figure S1B). We also confirmed Cited1 deficiency in Cited1− mice using RT-PCR. We observed a significant 3.81 fold difference decrease in Cited1 expression in AhCre+Cited1− compare to AhCre+WT. The small difference observed is most likely due to the low level of expression of Cited1 in the intestine [21]. Due to the increased level of Cited1 expression after loss of Apc, Cited1 deficiency is more noticeable in the intestinal epithelial cells of AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− mice which showed a 277.81 fold decrease compared to AhCre+Apcfl/fl mice (p<0.05 Mann-Whitney U test).
We have previously shown that the loss of Apc leads to an increase in proliferation and apoptosis and also to a loss of migration [3]. To analyse the effects of Cited1 deficiency after Apc loss, we first counted the number of cells in S phase within the crypt or hyperplastic areas (formed after Apc loss). On day 4 after β-napthoflavone induction, mice were injected with BrdU to label cells in S-phase and culled 2 hrs later (Figure 3A). In AhCre+WT and AhCre+Cited1− mice the number of proliferating cells was not significantly different (AhCre+WT: 18.97 vs AhCre+Cited1−: 20.65 BrdU positive cells/Crypt; p>0.05. Figure 3B). However, the number of cells in S-phase was significantly increased in the hyperplastic areas of AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− mice compared to AhCre+Apcfl/fl mice (AhCre+Apcfl/fl: 74.13 vs AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1−: 106.4 BrdU positive cells/area, p<0.05, Figure 3B) suggesting a role for Cited1 in controlling cell proliferation in the context of active Wnt signaling.
Fig. 3. Cited1 deficiency increases enterocyte proliferation and decreased cell migration in AhCre+Apcfl/fl mice. 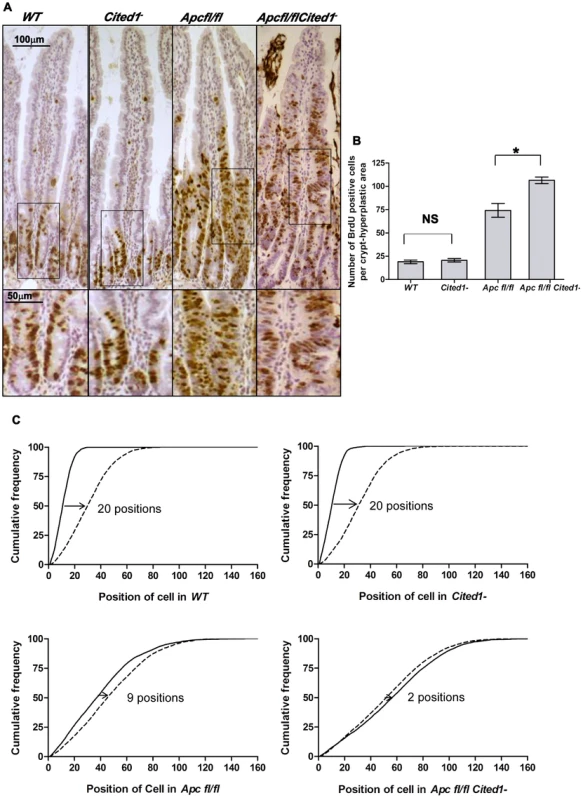
A: Cell proliferation assessed by IHC (immunohistochemistry) in AhCre+WT (WT), AhCre+Cited1−, (Cited1−) AhCre+Apcfl/fl(Apcfl/fl) and AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1−(Apcfl/flCited1−) mice. Bottom panels show magnifications of intestine of corresponding zone. B: Histograms showing the number of BrdU positive cells/crypt or hyperplastic areas. No significant difference in the localisation or number of BrdU positive cells between AhCre+WT and AhCre+Cited1− (p = 0.6625). Significant increase in the number of BrdU positive cell in AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− compared to AhCre+Apcfl/fl (*p = 0.0404). C: Graphs showing the position of BrdU positive cells after 2 hrs (solid line) and 24 hrs (dashed line). The cumulative frequency represents the percentage of BrdU positive cells at a particular position from the bottom of the crypt or hyperplastic areas to the tip of the villus. The difference between the 2 hrs and 24 hrs distributions for a genotype was analysed with the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. The distribution of Brdu positive cells from 2 hrs to 24 hrs varies significantly for all genotypes (p = 0.01) indicating cell migration. The migration of cells from 2 hrs to 24 hrs after Brdu labelling is similar in AhCre+WT compared to AhCre+Cited1− as shown by the distance between the 2 distributions (20 cell positions at the 50% cumulative frequency). In AhCre+Apcfl/fl, the distance is reduced to 9 cell positions indicating reduced migration compared to AhCre+WT (20 positions) and AhCre+Cited1− (20 positions). The migration is further reduced in AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− as the 50% cumulative frequency position moved only 2 positions, compared to AhCre+Apcfl/fl (9 positions). *p<0.05; Statistical tests were done using Mann-Whitney U test (B) or Kolmogorov–Smirnov test (C); NS Non significant. (N = 3/genotype). We next analysed the histology on HE sections of the intestinal tissue from all the genotypes after β-napthoflavone induction. There were no gross changes in the crypt/villus architecture in AhCre+WT compared to AhCre+Cited1− mice, and induced AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− mice had similar large aberrant crypts to those observed in AhCre+Apcfl/fl mice (Figure 4D).
Fig. 4. Cited1 deficiency enhances increased apoptosis in AhCre+Apcfl/fl mice. 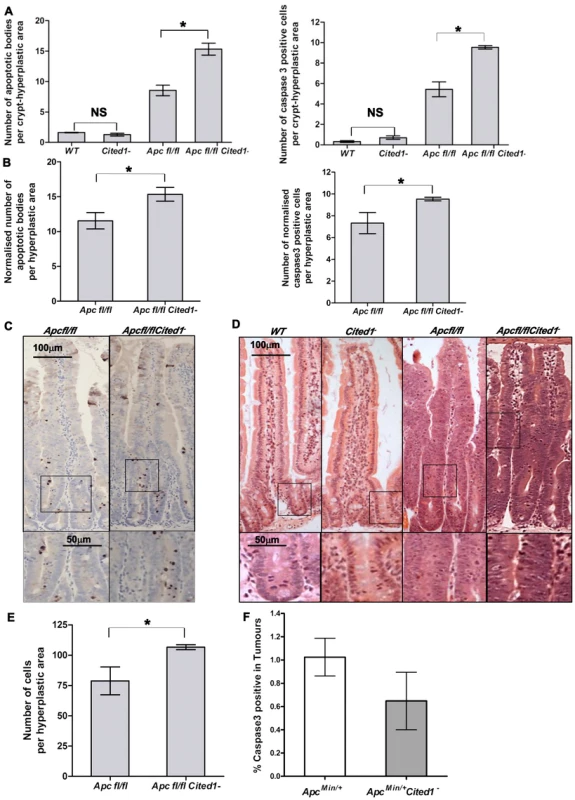
A: Histograms showing the levels of apoptosis in each genotype. Apoptotic cells were scored by H&E staining (left) or cleaved-Caspase3 antibody (right). Both graphs show an increase in the number of apoptotic cells in AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− compared to AhCre+Apcfl/fl (AhCre+Apcfl/fl<AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1−, Left: p = 0.0404; Right: p = 0.0259). No significant difference is observed between AhCre+WT and AhCre+Cited1− (AhCre+WT = AhCre+Cited1−, Left: p = 0.1914; right: p = 0.0952). B: The number of apoptotic cells were normalised to the number of total cells per hyperplastic area in AhCre+Apcfl/fl versus AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1−. After normalisation, the number of apoptotic cells is greater in AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− compared to AhCre+Apcfl/fl (H&E: AhCre+Apcfl/fl<AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1−, p = 0.0404; cleaved-Caspase3: AhCre+Apcfl/fl<AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1−, p = 0.0259). C: cleaved-Caspase3 representative pictures showing an increase in apoptotic bodies in AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− compared to AhCre+Apcfl/fl. D: Histology by H&E stained mouse intestinal sections in each genotype. Bottom panels show magnifications of intestine of corresponding zone. E: Scoring of epithelial cells per hyperplastic areas using the extent of BrdU labelling. Histograms show a significant increase in epithelial cell number in the hyperplastic areas from AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− compared to AhCre+Apcfl/fl mice (p<0.05). *p<0.05; All statistical tests were done using Mann-Whitney U test ; NS Non significant. (n = 3/genotype). F: Histograms showing the levels of apoptosis (cleaved Caspase 3 antibody) in tumours of ApcMin/+ (white) and ApcMin/+Cited1− mice (Grey). There is no significant difference between the 2 genotypes (p>0.05, Mann-Whitney U test). Given our findings of decreased adenoma formation in ApcMin/+ mice, we also examined the extent of the hyperplastic area within the crypts of AhCre+Apcfl/fl mice compared to AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− mice as determined by the extent of BrdU labelling. Surprisingly, the number of cells in the hyperplastic area was greater in AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− mice compared to AhCre+Apcfl/fl mice (AhCre+Apcfl/fl: 78 cells/area vs AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− :106 cells/area, p<0.05, Figure 4E).
We next determined migration rates by comparing the position of cells 2 hrs and 24 hrs after BrdU labelling. The difference between the 2 hrs and 24 hrs distributions for a genotype was analysed with the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. The distribution of Brdu positive cells from 2 hrs to 24 hrs varies significantly for all genotypes (p = 0.01) indicating cell migration. Enterocytes in AhCre+WT mice and AhCre+Cited1− mice migrate at the same rate (20 cell positions at the 50% cumulative frequency) whereas cells in both AhCre+Apcfl/fl mice and AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− mice show greatly reduced migration rates (Figure 3C). Critically, although deletion of Apc in AhCre+Apcfl/fl mice results in strong suppression of migration (9 cell position migration), some movement of cells was detected in these samples (Figure 3C). By comparison, the absence of Cited1 in AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− mice, resulted in even less migration (2 cell position migration) than observed for enterocytes in AhCre+Apcfl/fl mice (Figure 3C). Together, these data demonstrate that Cited1 deficiency further exacerbates both the proliferation and migration phenotypes of Apc loss in the intestine, which is surprising given that ApcMin/+Cited1− mice developed significantly less intestinal tumours than ApcMin/+mice. Consistent with these observations that proliferation is increased in AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− mice, we also observed a decrease in the number of differentiated entoendocrine cells and goblet cells in these mice (Figure S5A–D).
We and others have previously demonstrated that the location and the number of paneth cells in the intestinal crypt are regulated by Wnt signalling [6], [22]–[24]. It is observed by the increased number of paneth cells after loss of Apc (Figure S5F) and the loss of positioning at the bottom of the crypt (Figure S5E–G). Consistent with our observations that the phenotype of AhCre+Apcfl/fl mice is enhanced upon deficiency of Cited1 we also observe a change in position of the paneth cells in the hyperplastic areas of the AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− compared to AhCre+Apcfl/fl (Figure S5G). This is most likely due to the increase in crypt size seen in the double mutant, which gives cells a bigger area to be distributed.
Cited1 deficiency enhances the apoptotic phenotype observed immediately after Apc loss
The increase in proliferation observed in the intestine following deletion of Apc is also associated with a dramatic increase in apoptosis [3]. We therefore examined if Cited1 was regulating apoptosis by counting apoptotic bodies in H&E sections and also scoring Caspase 3 staining. We observed no significant difference in apoptosis between AhCre+WT and AhCre+Cited1− mice, however, there was a significant increase in the number of apoptotic cells in AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− mice compared to AhCre+Apcfl/fl mice, which was verified by both methods (Figure 4A).
As mentioned above, we observed an increase in the number of cells per hyperplastic area in the AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− samples. To verify that the increase in cell death was not an artefact of the difference in the number of cells per area, we corrected for this difference between AhCre+Apcfl/fl and AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− mice. The normalised data confirmed increased cell death in AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− compared to AhCre+Apcfl/fl (p<0.05) after H&E counting (AhCre+Apcfl/fl : 11.53 apoptotic cells/area vs AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1−: 15.33 apoptotic cells/area, p<0.05) and after anti cleaved-Caspase3 staining (AhCre+Apcfl/fl: 7.32 apoptotic cells/area vs AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1−: 9.53 apoptotic cells/area, p<0.05) (Figure 4B–C). These data indicate that the increase in cell death is not proportional to the increase in cell proliferation. Therefore, Cited1 deficiency in a Wnt perturbed background accentuates the apoptotic response.
Scoring of Caspase3 positive cells revealed no change in the number of apoptotic cells in the intestinal tumors of ApcMin/+Cited1− mice compared to ApcMin/+ mice at time of death (Figure 4F). Therefore, the increased apoptosis we observe in the absence of Cited1 is only manifested in the context of acute Wnt activation, which underlines the role of Cited1 in restraining tumour initiation, and also implies that in those tumours that do develop in the absence of Cited1, they have developed alternate mechanisms to restrain the Wnt pathway.
Cited 1 regulates several pathways including the Wnt signaling pathway
We next wished to investigate the mechanism through which Cited1 may be modifying Wnt driven tumorigenesis. One possibility is a direct effect upon Wnt signaling, and in support of this, Cited1 has previously been shown to be able to bind to β-catenin and consequently inhibit Wnt induced transcription during Xenopus development [5]. Two potential TCF-4 sites were identified in the Cited1 promoter region (ctttgt and cattgaa in the 2 kb prior exon1). This implicates Cited1 in the control of the Wnt pathway, however this is not the only pathway known to be altered by Cited1. Cited1 has been shown to bind to the p300/CBP coactivators and also to Smad4, thereby enhancing their transcriptional activity [11], [25]. To analyse the effects of Cited1 deficiency on various transcriptional pathways we performed a microarray analysis using the Affimetrix Chip 430 2.0 and AffylmGUI software [26]. We then submitted our microarray data to ingenuity pathway analysis software (IPA) to identify pathways significantly affected by Cited1 deficiency.
In the AhCre+WT after additional loss of Cited1, a number of signaling pathways identified by IPA analysis were found to be affected, amongst them: P53 (p = 6.87×10−6, ratio = 0.146), PI3K/AKT (p = 6.74×10−6, ratio = 0.114), Pten (p = 7.7×10−4, ratio = 0.097); Wnt (p = 1.08×10−1, ratio = 0.057); and TGFβ (p>0.1, ratio = 0.034). Several targets were analysed by QPCR including c-Myc, Axin2, CD44, Sox4, p53, Pten, Akt1, and Smad4 but none were found to be significantly deregulated (N = 6, p>0.05; Mann-Whitney).
Several signaling pathways identified by IPA analysis were affected in AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− mice compared to AhCre+Apcfl/fl mice, including: P53 (p = 3.5×10−8, ratio = 0.177); PI3K/AKT (p = 2.62×10−5, ratio = 0.107); Pten (p = 7.22×10−4, ratio = 0.097), Wnt (p = 5.4×10−2, ratio = 0.063); and TGFβ (p = 2.22×10−1, ratio 0.056). The validity of the IPA analysis was subsequently verified by QPCR. We analysed several targets from these pathways by QPCR, and found significant upregulation of p53, Runx1, Sox4 (Figure S2C) and a number of Wnt targets known to be deregulated in the intestines of AhCre+Apcfl/fl mice [3] or listed as Wnt target genes in the Nusse webpage (http://www.stanford.edu/group/nusselab/cgi-bin/wnt/target_genes) (Figure 5A–B). 10 Wnt target genes, including c-Myc, Axin2, and CD44 were confirmed by QPCR to be significantly up-regulated in AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− mice compared to AhCre+Apcfl/fl mice (Figure 5A). Three additional transcripts were analysed by microarray analysis that have previously been identified as key players in the Wnt pathway (Nucleophosmin, Nucleolin, and β-catenin respectively: [27]–[29]). These were also found to be upregulated in AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− mice compared to AhCre+Apcfl/fl mice. These data indicate that Cited1 inhibits several signaling pathways, including the Wnt pathway following Apc loss.
Fig. 5. Expression levels of Wnt target genes after loss of Cited. 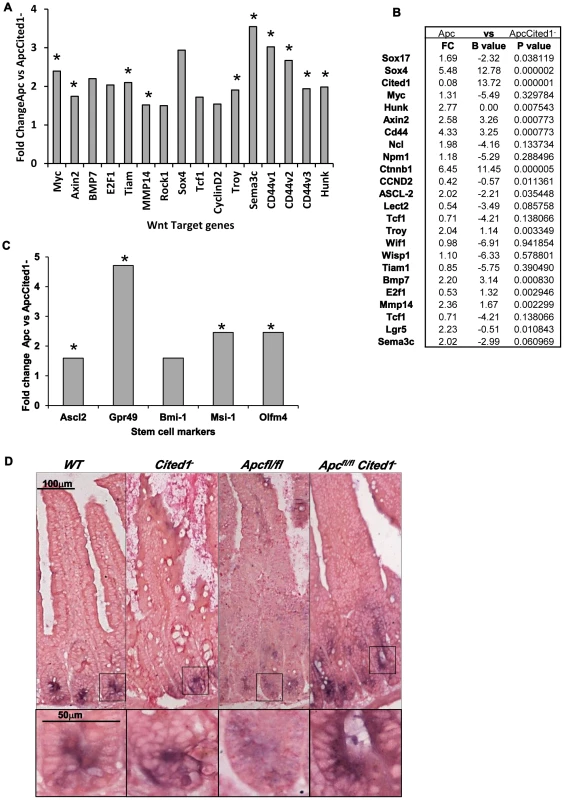
A: Fold change of Wnt target gene expression in the small intestinal epithelium of AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− compared to AhCre+Apcfl/fl mice measured by QRT-PCR, *p<0.05 Mann Whitney U test. B: Microarray analysis showing up-regulation of Wnt target genes with Wnt Key players in AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− compared to AhCre+Apcfl/fl: Fold changes (FC) are presented with correspondent P value and B value (B statistic is lod score). C: Fold change of stem cell markers expression in the small intestinal epithelium of AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− compared to AhCre+Apcfl/fl mice measured by QRT-PCR, *p<0.05 Mann Whitney U test. D: In situ Hybridization (ISH) analysis of Olfm4 in intestinal epithelial cells of all 4 genotypes. Inset panels show magnifications of intestine of corresponding zone. Stem cell markers are upregulated after loss of Cited1
The Wnt signalling pathway has been shown to play a critical role in intestinal homeostasis which includes stem cells maintenance. Because Cited1 loss leads to a deregulation of the Wnt pathway and due to the potential role of Cited1 in the stem cell niche in the cap mesemchyme in the developing kidney [18], we analysed the effect of Cited1 deficiency in the intestine. RT-QPCR analysis revealed a significant upregulation of several stem cell markers (Gpr49, Ascl2, Musashi and Olfm4) in AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− tissues compared to AhCre+Apcfl/fl controls (Figure 5C). We also performed ISH for the surrogate marker of Lgr5, Olfm4 (Figure 5D). In AhCre+Wt and AhCre+Cited1− mice the location of Olfm4 expressing cells is confined to the stem cell niche at the base of the crypts. In AhCre+Apcfl/fl mice, Olfm4 expressing cells were distributed throughout the hyperplastic area. In AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− mice Olfm4 expressing cells are also mislocalised throughout the aberrant crypts but expression is increased, consistent with our RT-QPCR data of the same tissue (Figure 5C).
Cited1 influences the level of the active form of β-catenin in the small intestine
Loss of Apc has been shown to drive an increase in total β-catenin and more importantly a re-localisation of the active form of β-catenin to the nucleus [3]. To test if Cited1 deficiency modified this phenotype, we analysed the localisation of total β-catenin in the small intestine by immuno-histochemistry (Figure 6A). We observed a normal pattern of localisation in both AhCre+WT and AhCre+Cited1− mice consistent with previous findings [30]. Upon deletion of Apc, we observed nuclear translocation of β-catenin in the aberrant crypts of both AhCre+Apcfl/fl and AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− mice (Figure 6A) indicative of de-regulated Wnt signalling.
Fig. 6. Level of the active form of β-catenin in the small intestine. 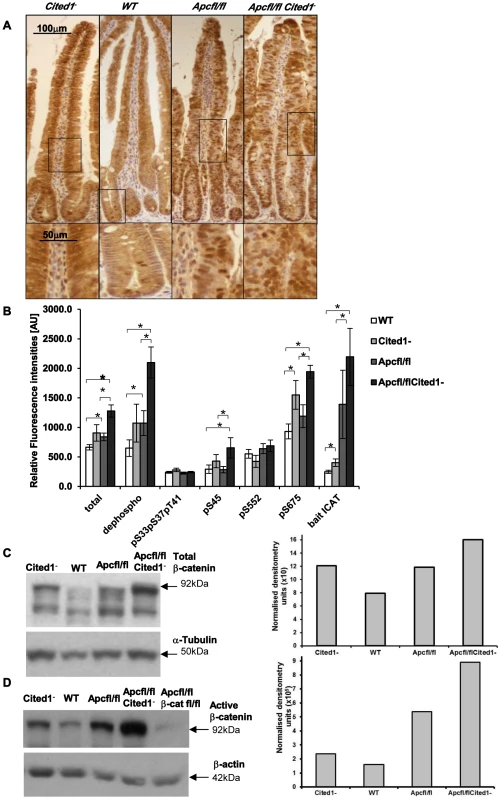
A: Immunohistochemistry for total β-catenin in each genotype. Inset panels show magnifications of intestine of corresponding zone. B: Small intestine epithelial cell extracts from AhCre+WT (WT; n = 14), AhCre+Cited1− (Cited1−; n = 7); AhCre+Apcfl/fl (Apcfl/fl; n = 12); AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− (Apcfl/flCited1−) were analysed for the status of β-catenin using a suspension bead array assay panel. Total β-catenin, dephospho β-catenin (S33, S37 and T41), phosphorylation at S33, S37, and T41, phosphorylation at S45, phosphorylation at S552 and phosphorylation at S675 were analysed by using respective capture antibodies in multiplexed sandwich immunoassays. Free β-catenin (non-complexed) was measured by µGST pull-down assays using GST-ICAT as bait protein. Signal intensities are displayed in relative fluorescence units [AU] (mean+SE). *p<0.05; All statistical tests were done using Mann-Whitney U test. C: Western blot analysis of the Total form of β-catenin in each genotype. The histogram represents the densitometry analysis of the total β-catenin immuno-blot normalised to the internal control α-tubulin, showing an increase in the level of total β-catenin in AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− (Apcfl/flCited1−) compared to AhCre+Apcfl/fl(Apcfl/fl) and AhCre+Cited1− also show an increase compare to AhCre+WT. D: Western blot analysis of the active form of β-catenin using dephospho-β-catenin (dephosphorylated on Ser37/Thr41, Clone 8E7, Millipore) antibody in each genotype. The histogram represents the densitometry analysis of the dephospho-β-catenin immuno-blot normalised to the internal control β-actin, showing an increase in the level of dephos-β-catenin in AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− (Apcfl/flCited1−) compared to AhCre+Apcfl/fl(Apcfl/fl). The sample of each genotype is pooled from 3 to 7 mice in the cohort. AhCre+Apcfl/flβ-catfl/fl (Apcfl/flβ-catfl/fl) is used as a negative control for dephospho-β-catenin. β-catenin regulates important cellular functions such as transcription and adhesion [31], and the cellular concentration and phosphorylation status of β-catenin has been shown to impact on these functions [31], [29]. As we observe an increase in the transcription of several Wnt target genes in AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− mice we examined the level of total β-catenin, the extent of phosphorylation at multiple sites and the ratio of transcriptionally active free β-catenin in purified intestinal epithelial cells (Figure 6B) as previously described [32]. First, we observed a significant increase in total β-catenin accompanied by an increase in the active form of β-catenin (dephosphorylation at pS33, pS37, pT41 sites) in AhCre+Apcfl/fl and AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− mice compared to AhCre+WT and very importantly in AhCre+Apcfl/fl mice compared to AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− mice.
These data were confirmed by western blot analysis using an antibody raised against total β-catenin (Figure 6C) or against the active form of β-catenin (dephosphorylated sites pS33, pS37, pT41) (Figure 6D) and were verified with a second antibody against dephosphorylated β-catenin (Figure S2A–B). There was no significant difference in the phosphorylated (inactive) form of β-catenin (phosphorylated β-catenin at pS33, pS37, pT41 sites is degraded as a mechanism of regulating Wnt signalling) between all genotypes (Figure 6B). β-catenin phosphorylated at pS45 (phosphorylated by casein kinase Iα as part of degradation pathway) is significantly increased in AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− compared to AhCre+WT and AhCre+Apcfl/fl.
Given that β-catenin can also be phosphorylated by Protein Kinase A (PKA) at Ser552 and Ser675 which acts to inhibit ubiquitination and therefore increase levels of active β-catenin [33], we also analysed levels of pS552 and pS675 and found phosphorylation at S675 significantly increased in AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− tissues compared to AhCre+WT and AhCre+Apcfl/fl, demonstrating the ability of Cited1 to regulate β-catenin at multiple sites (Figure 6B).
We also measured the intracellular free β-catenin (active β-catenin) levels by pull-down with a GST-fusion protein of the inhibitor of β-catenin and TCF-4 (ICAT). We observed a significant increase in free β-catenin in AhCre+Apcfl/fl and AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− mice compared to AhCre+WT and noticeably a significant increase in AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− compared to AhCre+Apcfl/fl mice (Figure 6B). These data support our findings above which indicate that Cited1 deficiency increases the levels of active dephosphorylated β-catenin.
These data demonstrated that the active dephosphorylated form of β-catenin in purified intestinal epithelial cells is markedly increased upon Cited1 deficiency. Although the level of dephosphorylated β-catenin is increased in Cited1− intestinal cells compared to WT mice, it is below that observed in the AhCre+Apcfl/fl intestinal cells (Figure 6B, 6D). As Cited1− mice do not develop any intestinal phenotypes such as hyperproliferation this suggests that the level of Wnt activation in Cited1− mice is below the critical threshold required to induce neoplasia [34]. However, when Apc is deleted in Cited1 deficient mice (AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1−) the level of dephosphorylated β-catenin is greater than that observed with Apc loss alone, thus providing an explanation for the increased transcription of Wnt target genes observed in these mice (Figure 5A).
Discussion
Colorectal cancer is driven by a multiplicity of different biochemical pathways, however, key amongst these is the Wnt pathway, which we and others have previously shown to activate a set of c-Myc dependent genes which are critical for the early stages of colorectal cancer [6], [35]. One of these genes is Cited1, which has been found to interact at the protein level with β-catenin and thereby negatively regulate β-catenin transcription [5]. Its relevance to carcinogenesis has already been described as Cited1 up-regulation has been observed in various cancers [14], [36], [37]. Here, we have extended those observations and find that CITED1 is significantly up-regulated in colorectal tumours from patients and in intestinal adenomas developing in the ApcMin/+ mouse model [38]. We also previously found Cited1 to be over-expressed in intestinal epithelial cells immediately following deletion of the Wnt regulator gene Apc in AhCre+Apcfl/fl mice in a c-Myc dependent manner [6]. These data establish Cited1 as an immediate Wnt target gene in the intestine.
On the basis of these data we hypothesised that Cited1 might control β-catenin activity and thereby modulate Wnt signaling activation and its effects on colorectal tumorigenesis. To investigate this, we used microarray analysis and quantitative PCR studies to show that loss of Cited1 on an Apc deficient background does indeed impact upon a range of oncogenic signaling pathways, including Wnt. Our array data therefore show multiple effects of Cited1 deficiency including negative regulation of the Wnt-pathway.
To investigate the requirement of Cited1 during Wnt induced tumourigenesis, we analysed the effects of deletion of Cited1 in two well characterised mouse models of Wnt signaling activation; the ApcMin/+ mouse model of colorectal tumourigenesis and the AhCre+Apcfl/fl mouse, a conditional model of Apc loss in which the immediate phenotypic consequences of Apc deletion can be studied [3]. Surprisingly, we obtained the apparently paradoxical result that although ApcMin/+Cited1− mice developed fewer intestinal tumours (associated with an increased life-span) than ApcMin/+ mice, the phenotypes induced upon conditional loss of Apc (including perturbed cell proliferation, apoptosis, differentiation and migration) were enhanced, rather than diminished, with additional loss of Cited1. Of note, we observed reduced capacity to differentiate (reflected by a reduced number of goblet cells and enteroendocrine cells), but no difference in total paneth cell numbers, although we did observe a difference in the positioning of paneth cells, which may well reflect differences in the Wnt signalling environment.
Our studies, suggest that a possible explanation for this apparent paradox is that the hyper-activated Wnt phenotype that occurs in the absence of Cited1 includes increased apoptosis. Several studies in cell culture systems already support such a model. For example, it has been reported that overexpression of β-catenin when transfected into cell lines leads to a 3–4 fold increase in cell death [39]. In addition, it has been demonstrated that high levels of c-Myc induce apoptosis in vivo [40]. This is consistent with our observations that c-Myc is overexpressed immediately following deletion of Apc in the intestine and that levels are significantly increased further with additional absence of Cited1. We interpret our data to indicate that the increase in apoptosis may counteract the increase in proliferation to the extent that the overall effect is reduced development of Wnt transformed cells and consequently inhibition of tumourigenesis.
The mechanism underlying such hyper-activation of Wnt signaling appears to be at least in part mediated through increased levels of dephosphorylated β-catenin, which we found to be up-regulated in AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− tissue compared to comparable AhCre+Apcfl/fl tissue at both the transcriptional and protein levels. Thus, we found increased levels of the dephosphorylated forms of β-catenin (T41, S33, S37). These sites when phosphorylated are involved in the degradation of β-catenin by the proteasome pathway [31]. This is accompanied by an increase in the levels of phosphorylation at serine 675 which has been shown to be phosphorylated by protein kinase A (PKA) and which has been shown to lead to inhibiting of ubiquitination of β-catenin causing its accumulation and subsequent Wnt signalling activation. We therefore show that Cited deficiency increases the pool of active β-catenin, consistent with the enhanced Wnt pathway activation we observe. It does however remain possible that Cited1 may in addition be mediating its effects downstream of β-catenin.
We cannot rule out the possibility that the other pathway changes we observe are responsible for the reduction in tumourigenesis in ApcMin/+Cited1− mice, as the effects of loss of Cited1 are not exclusive to the Wnt pathway. We also cannot rule out that the effects we observe may be secondary to Cited1 deletion. For example, it is possible that some of the changes we observe may be due directly to the upregulation of c-Myc rather than a direct consequence of Cited1 loss. Functional delineation of the precise relevance of all the changes we observe requires multiple crosses onto the relevant pathways to probe such dependency. Finally, AhCre+WT, AhCre+Apcfl/fl, AhCre+Cited1−, and AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− mice were maintained on an outbred background, and because the comparisons of genotypes within the same littermates was restricted due to the small number of litter size, we cannot completely rule out the effect of gene modifiers on the Cited1 loss phenotype.
Our current primary hypothesis is that Cited1 deficiency mediates its effects upon adenoma formation primarily through the apparently paradoxical derepression of the Wnt pathway. This result is however consistent with a “just right model” wherein a specific level of Wnt signaling activity is required for maximal tumour development and those levels of Wnt signaling above or below this level compromise tumour growth [41]. This model is further supported by recent studies on a novel mutant Apc mouse (Apc1322T), which has reduced Wnt signaling compared to ApcMin/+ littermates, but surprisingly develops significantly more intestinal tumours [42]. Recently it was shown by Leedham et al [43] that in normal mouse intestine, stem cell markers and Wnt target genes are expressed in a physiological gradient compatible with normal intestinal homeostasis. Pathological activation of Wnt activity using the Ctnnb1Δex3 mouse model led to variable gradients in stem cell number and Wnt signalling activity which influenced tumour susceptibility, with regional differences in tumour predisposition throughout the length of the intestinal tract. This data, which supports the just right model hypothesis, may explain the variation we observe in the tumour distribution in the ileum between the ApcMin/+ and ApcMin/+Cited1− mice models. These observations clearly show that there is not a simple linear relationship between Wnt pathway activity and tumour burden. Our data is consistent with another version of this “just right” concept where perturbation of Cited1 leads to increased dephosphorylated β-catenin and hyper-activation of the Wnt pathway to a level that is incompatible with maximum tumour growth (Figure 7). Notably, this relationship appears specific to the intestine as similar analysis of kidney tumorigenesis in these mice showed no effect of Cited deficiency (Figure S3). Furthermore, to define the precise relationship between Wnt levels and tumourigenicity will require mouse modelling experiments in which Wnt activity is precisely regulated at numerous levels.
Fig. 7. Schematic diagram of a “just right” model of Cited1 action on colorectal tumourigenesis. 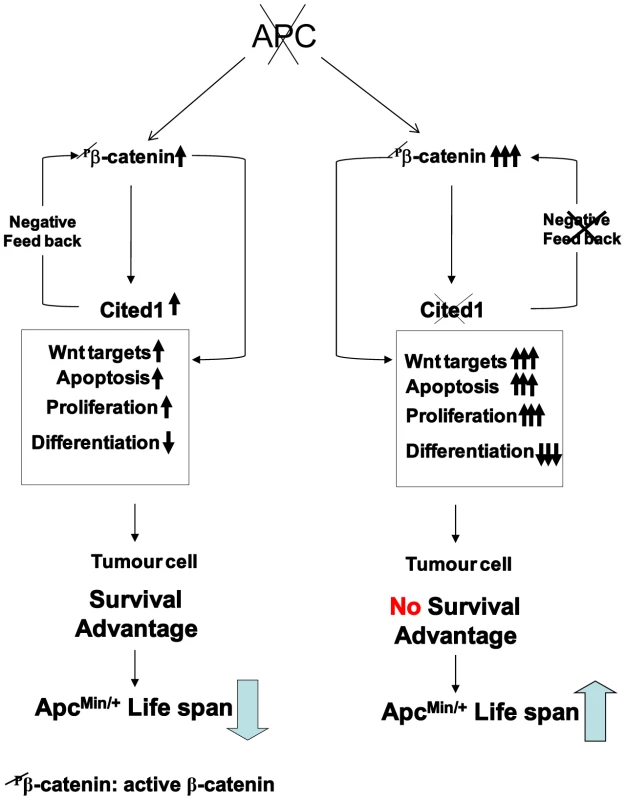
Loss of function of Apc is accompanied by multiple changes in gene expression, including upregulation of active β-catenin (dephospho-β-catenin), activation of Wnt and Cited1. Hence, immediately following deletion of Apc, Cited1 normally restrains the Wnt pathway at the level of β-catenin. We observe a range of rapid phenotypic changes. These include increase in proliferation and apoptosis and loss of differentiated cell types, also reduced migration, leading to the preferential retention of Apc deficient cells. These changes may all be considered pro-tumourigenic, leading to survival advantage of the tumour cell and decreased survival of the ApcMin/+ mouse compared to WT. Additional Cited1 deficiency leads to hyper-activation of Wnt signaling including upregulation of active β-catenin and an exaggerated Wnt phenotype including elevated proliferation, a further loss of cell differentiation, and most importantly increased cell death. The net effect of these changes is an increase in ApcMin/+ survival. This restraint imposed by Cited1 is consistent with a requirement for Cited1 to constrain Wnt activity to a level commensurate with optimal adenoma formation and maintenance, and provides one mechanism for tumour repression in the absence of Cited1. Wnt/beta-catenin signalling plays a key role in the homeostasis of the intestinal epithelium and its role in the fate and maintenance of the stem cell compartment have been clearly demonstrated [44]. Our data clearly show that Cited1 is an immediate target of Wnt signalling and is an important regulator of the Wnt pathway. The loss of Cited1 has a direct impact on stem cell status in the small intestine as we have found several stem cell markers to be upregulated including Lgr5 (Gpr49), Musashi and Olfm4. These alterations in expression could be a direct consequence of the ‘hyper’ activation of the Wnt pathway we observe after combined loss of Apc and Cited1. This would implicate Cited1 as an important player in Wnt dependant stem cell maintenance in the small intestine. This has been already suggested in the developing kidney where Cited1 may contribute to the maintenance of the self-renewing capping mesenchyme [18]. By regulating the Wnt pathway, Cited1 may be an important regulator of the self-renewal compartment in the crypt of the small intestine.
Our data show that Cited1 deficiency represses tumourigenesis. The consequences of Cited1 deficiency are diverse, but in particular impact upon Wnt pathway activity. We propose a model whereby loss of Cited1, in the context of deregulated Wnt signaling, hyper-activates the Wnt pathway resulting in apoptosis of Wnt induced transformed cells and thus inhibits tumourigenesis. As Cited1 mice are fertile and viable this suggests that Cited1 represents a possible target for therapeutic intervention, where Cited1 inhibition induces cytotoxic effects due to very high Wnt signalling.
Materials and Methods
Human colorectal cancer tissue RNA samples
Total RNA samples from patient colorectal tumour tissues were obtained from the Cancer Tissue Bank Research Centre (CTBRC). All colorectal cancer tissues and adjacent uninvolved colonic mucosa were obtained from surgically removed specimens with informed patient consent. Uninvolved colonic mucosa was generally 5–10 cm away from the malignant tissue.
Mouse colonies
All experiments were performed under the UK Home Office guidelines. Mice were obtained and genotyped as follows: Cited1 null (Cited1−) [9]; ApcMin/+ [38]; AhCre transgene (AhCre+) [45]; Apc580S allele [46]; β-catfl/fl [47]; ApcMin/+ and ApcMin+Cited1− mice were maintained on an inbred C57BL/6J background and were confirmed as congenic for the C57BL/6 Mom-1 allele via PCR analysis. Mice were sacrificed at ill-health. Intestine were fixed in Methacarn (methanol-chloroform-glacial acetic acid [4∶2∶1]), and the lesion numbers were scored macroscopically.
To study the role of Cited1 after the early loss of Apc, AhCre+WT, AhCre+Apcfl/fl, AhCre+Cited1− and AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− mice were generated and maintained on an outbred background. Cre activity was induced by three intraperitoneal injections of 80 mg/kg β-naphthoflavone within 24 h and mice were taken Day4 or Day5 later. Tissues analysed were from age (8–12 weeks), sex (males), background and genotype matched animals, however these were not always littermates.
Assaying apoptosis, number of cells per crypt, S-phase labelling in vivo and migration
Apoptosis was scored from H&E or after anti cleaved-Caspase3 immuno-staining as previously described [3]. For proliferation analysis, mice were injected with 0.25 ml of BrdU (Amersham) before culling and were taken either 2 hrs (day4) or 24 hrs (day5) after BrdU injection. Staining was performed as previously described [3]. The number of cells in AhCre+Apcfl/fl and AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1− hyperplastic area was scored using the position of the last BrdU positive cells in the hyperplastic area. For each analysis, 25 full crypts or areas were scored from at least 3 mice of each genotype and time point.
In situ hybridization (ISH)
In situ hybridization of Olfm4 and Cited1 in the small intestine was performed for all genotypes using sections embedded in paraffin sectioned at 5 µm. Olfm4 hybridization was performed as described in Gregorieff et al., 2005. [48]. Cited1 hybridization was performed using a probe against the sequence deleted in the Cited1− allele designed by Advanced cell Diagnostics inc (ACD). RNAscope 2.0 FFPE Reagent Kit – Brown kit was used according manufacturer instructions. Negative control Probe-DapB was used together with a positive control probe Polr2a from the ACD manufacturer.
Microarray data analysis
The DNA microarray were performed from three mice of each genotype using Mouse Genome 430 2.0 Affymetrix chips at Liverpool Microarray Facility according to the manufacturer's instructions. The Microarray data were analyzed using AffylmGUI (Affymetrix linear modeling Graphical User Interface; http://bioinf.wehi.edu.au/affylmGUI/#citation) [26]. The p values presented have been corrected for multiple testing using the BH method to control the false discovery rate. The B statistic is the log odds that the gene is differentially expressed and is adjusted for multiple testing using the assumption that 1% of genes are expected to be differentially expressed [26], [49]–[51]. Microarray data were deposited in MIAME format at www.ebi.ac.uk/arrayexpress/ (Accession Number: E-MEXP-3202)
QPCR protocols, routine methods and a description of the statistical analyses used are provided in Protocol S1. List of primers for Taqman RT-QPCR, Sybr green RT-QPCR, and Cited1 semi quantitative RT-PCR are provided in Figure S4.
Analysis of signaling pathways
Ingenuity pathway analysis (IPA) software (www.ingenuity.com) was used to determine which signaling pathways were affected by the loss of Cited1 in AhCre+WT or AhCre+Apcfl/fl mice. The comparative (AhCre+WT vs AhCre+Cited1− and AhCre+Apcfl/fl vs AhCre+Apcfl/flCited1−) data from the microarray analysis were filtered for a p value of less than 0.05 and imported into the IPA software. The significance of the association between the data set and the pathway was measured in 2 ways: by the ratio and by a p value. The ratio corresponds to the number of genes from our data set that map to the ingenuity pathway divided by the total number of genes that map to the Ingenuity canonical pathway. The p value is calculated by a right tailed Fischer's exact test. The p-value associated with a pathway is a measure of the likelihood that the association between a set of focus genes in your experiment and a pathway is due to random chance.
β-catenin suspension bead array based assay
Analysis of biological function, localization, and posttranslational modification of the different forms of β-catenin were carried out as previously described [32]. Two additional assays were included in the analysis. Anti-dephospho S33/S37 and T41 (Cell Signalling Technologies) was used as an additional capture antibody to measure dephosphorylated β-catenin and GST-ICAT was employed as an additional bait protein to study free β-catenin.
Supporting Information
Zdroje
1. GryfeR, SwallowC, BapatB, RedstonM, GallingerS, et al. (1997) Molecular biology of colorectal cancer. Curr Probl Cancer 21 : 233–300.
2. ClarkeAR (2005) Studying the consequences of immediate loss of gene function in the intestine: APC. Biochem Soc Trans 33 : 665–666.
3. SansomOJ, ReedKR, HayesAJ, IrelandH, BrinkmannH, et al. (2004) Loss of Apc in vivo immediately perturbs Wnt signaling, differentiation, and migration. Genes Dev 18 : 1385–1390.
4. YahataT, ShaoW, EndohH, HurJ, CoserKR, et al. (2001) Selective coactivation of estrogen-dependent transcription by CITED1 CBP/p300-binding protein. Genes Dev 15 : 2598–2612.
5. PlisovS, TsangM, ShiG, BoyleS, YoshinoK, et al. (2005) Cited1 is a bifunctional transcriptional cofactor that regulates early nephronic patterning. J Am Soc Nephrol 16 : 1632–1644.
6. SansomOJ, MenielVS, MuncanV, PhesseTJ, WilkinsJA, et al. (2007) Myc deletion rescues Apc deficiency in the small intestine. Nature 446 : 676–679.
7. ShiodaT, FennerMH, IsselbacherKJ (1996) msg1, a novel melanocyte-specific gene, encodes a nuclear protein and is associated with pigmentation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93 : 12298–12303.
8. DunwoodieSL, RodriguezTA, BeddingtonRS (1998) Msg1 and Mrg1, founding members of a gene family, show distinct patterns of gene expression during mouse embryogenesis. Mech Dev 72 : 27–40.
9. RodriguezTA, SparrowDB, ScottAN, WithingtonSL, PreisJI, et al. (2004) Cited1 is required in trophoblasts for placental development and for embryo growth and survival. Mol Cell Biol 24 : 228–244.
10. HowlinJ, McBryanJ, NapoletanoS, LambeT, McArdleE, et al. (2006) CITED1 homozygous null mice display aberrant pubertal mammary ductal morphogenesis. Oncogene 25 : 1532–1542.
11. YahataT, de CaesteckerMP, LechleiderRJ, AndrioleS, RobertsAB, et al. (2000) The MSG1 non-DNA-binding transactivator binds to the p300/CBP coactivators, enhancing their functional link to the Smad transcription factors. J Biol Chem 275 : 8825–8834.
12. ShiodaT, FennerMH, IsselbacherKJ (1997) MSG1 and its related protein MRG1 share a transcription activating domain. Gene 204 : 235–241.
13. FreedmanSJ, SunZY, KungAL, FranceDS, WagnerG, et al. (2003) Structural basis for negative regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha by CITED2. Nat Struct Biol 10 : 504–512.
14. NairSS, ChaubalVA, ShiodaT, CoserKR, MojamdarM (2001) Over-expression of MSG1 transcriptional co-activator increases melanin in B16 melanoma cells: a possible role for MSG1 in melanogenesis. Pigment Cell Res 14 : 206–209.
15. LovvornHN3rd, BoyleS, ShiG, ShyrY, WillsML, et al. (2007a) Wilms' tumorigenesis is altered by misexpression of the transcriptional co-activator, CITED1. J Pediatr Surg 42 : 474–481.
16. LovvornHN, WestrupJ, OppermanS, BoyleS, ShiG, et al. (2007b) CITED1 expression in Wilms' tumor and embryonic kidney. Neoplasia 9 : 589–600.
17. DillonRL, BrownST, LingC, Shioda, T.MullerWJ (2007) An EGR2/CITED1 transcription factor complex and the 14-3-3sigma tumor suppressor are involved in regulating ErbB2 expression in a transgenic-mouse model of human breast cancer. Mol Cell Biol 27 : 8648–8657.
18. MugfordJW, YuJ, KobayashiA, McMahonAP (2009) High-resolution gene expression analysis of the developing mouse kidney defines novel cellular compartments within the nephron progenitor population. Dev Biol September 15; 333(2): 312–323.
19. HendryC, RumballeB, MoritzK, LittleMH (2011) Defining and redefining the nephron progenitor population. Pediatr Nephrol Sep;26(9): 1395–406 Epub 2011 Jan 14. Review.
20. MurphyAJ, PierceJ, de CaesteckerC, TaylorC, AndersonJR, et al. (2012) SIX2 and CITED1, markers of nephronic progenitor self-renewal, remain active in primitive elements of Wilms' tumor. J Pediatr Surg Jun;47(6): 1239–49.
21. SuAI, WiltshireT, BatalovS, LappH, ChingKA, et al. (2004) A gene atlas of the mouse and human protein-encoding transcriptomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A Apr 20;101(16): 6062–7.
22. AndreuP, ColnotS, GodardC, GadS, ChafeyP, et al. (2005) Crypt-restricted proliferation and commitment to the Paneth cell lineage following Apc loss in the mouse intestine. Development Mar;132(6): 1443–51.
23. BatlleE, HendersonJT, BeghtelH, van den BornMM, SanchoE, et al. (2002) Beta-catenin and TCF mediate cell positioning in the intestinal epithelium by controlling the expression of EphB/ephrinB. Cell 18;111(2): 251–63.
24. PhesseTJ, ParryL, ReedKR, EwanKB, DaleTC, et al. (2008) Deficiency of Mbd2 attenuates Wnt signaling. Mol Cell Biol 28 : 196094–103.
25. ShiodaT, LechleiderRJ, DunwoodieSL, LiH, YahataT, et al. (1998) Transcriptional activating activity of Smad4: roles of SMAD hetero-oligomerization and enhancement by an associating transactivator. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95 : 9785–90.
26. SmythGK (2004) Linear models and empirical bayes methods for assessing differential expression in microarray experiments. Stat Appl Genet Mol Biol 3: Article3.
27. WillertJ, EppingM, PollackJR, BrownPO, NusseR (2002) A transcriptional response to Wnt protein in human embryonic carcinoma cells. BMC Dev Biol Jul 2;2 : 8.
28. GonzálezV, HurleyLH (2010) The C-terminus of nucleolin promotes the formation of the c-MYC G-quadruplex and inhibits c-MYC promoter activity. Biochemistry Nov 16;49(45): 9706–14.
29. CleversH, NusseR (2012) Wnt/β-catenin signaling and disease. Cell Jun 8;149(6): 1192–205.
30. van de WeteringM, SanchoE, VerweijC, de LauW, OvingI, et al. (2002) The beta-catenin/TCF-4 complex imposes a crypt progenitor phenotype on colorectal cancer cells. Cell 111 : 241–250.
31. ValentaT, HausmannG, BaslerK (2012) The many faces and functions of beta-catenin. Embo J 31(12): 2714–2736.
32. LuckertK, GötschelF, SorgerPK, HechtA, JoosTO, PötzO (2011) Snapshots of protein dynamics and post-translational modifications in one experiment–beta-catenin and its functions. Mol Cell Proteomics 10(5): M110.007377.
33. HinoS, TanjiC, NakayamaKI, KikuchiA (2005) Phosphorylation of beta-catenin by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase stabilizes beta-catenin through inhibition of its ubiquitination. Mol Cell Biol 25 : 9063–72.
34. BuchertM, AthineosD, AbudHE, BurkeZD, FauxMC, et al. (2010) Genetic dissection of differential signaling threshold requirements for the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in vivo. PLoS Genet 15;6(1): e1000816.
35. FevrT, RobineS, LouvardD, HuelskenJ (2007) Wnt/beta-catenin is essential for intestinal homeostasis and maintenance of intestinal stem cells. Mol Cell Biol 27 : 7551–9.
36. LiH, AhmedNU, FennerMH, UedaM, IsselbacherKJ, et al. (1998) Regulation of expression of MSG1 melanocyte-specific nuclear protein in human melanocytes and melanoma cells. Exp Cell Res 242 : 478–486.
37. ScognamiglioT, HyjekE, KaoJ, ChenYT (2006) Diagnostic usefulness of HBME1, galectin-3, CK19, and CITED1 and evaluation of their expression in encapsulated lesions with questionable features of papillary thyroid carcinoma. Am J Clin Pathol 126 : 700–708.
38. SuLK, KinzlerKW, VogelsteinB, PreisingerAC, MoserAR, et al. (1992) Multiple intestinal neoplasia caused by a mutation in the murine homolog of the APC gene. Science 256 : 668–670.
39. KimK, PangKM, EvansM, HayED (2000) Overexpression of beta-catenin induces apoptosis independent of its transactivation function with LEF-1 or the involvement of major G1 cell cycle regulators. Mol Biol Cell 11 : 3509–3523.
40. MurphyDJ, JunttilaMR, PouyetL, KarnezisA, ShchorsK, et al. (2008) Murphy Distinct thresholds govern Myc's biological output in vivo. Cancer Cell 14 : 447–457.
41. AlbuquerqueC, BreukelC, van der LuijtR, FidalgoP, LageP, et al. (2002) The ‘just-right’ signaling model: APC somatic mutations are selected based on a specific level of activation of the beta-catenin signaling cascade. Hum Mol Genet 11 : 1549–1560.
42. PollardP, DeheragodaM, SegditsasS, LewisA, RowanA, et al. (2009) The Apc 1322T mouse develops severe polyposis associated with submaximal nuclear beta-catenin expression. Gastroenterology 136 : 2204–2213.
43. LeedhamSJ, Rodenas-CuadradoP, HowarthK, LewisA, MallappaS, et al. (2013) A basal gradient of Wnt and stem-cell number influences regional tumour distribution in human and mouse intestinal tracts. Gut Jan;62(1): 83–93.
44. BarkerN, van de WeteringM, CleversH 14. The intestinal stem cell. Genes Dev 2008 Jul 15;22(14): 1856–64 Review.
45. IrelandH, KempR, HoughtonC, HowardL, ClarkeAR, et al. (2004) Inducible Cre-mediated control of gene expression in the murine gastrointestinal tract: effect of loss of beta-catenin. Gastroenterology 126 : 1236–1246.
46. ShibataH, ToyamaK, ShioyaH, ItoM, HirotaM, et al. (1997) Rapid colorectal adenoma formation initiated by conditional targeting of the Apc gene. Science 278 : 120–123.
47. BraultV, MooreR, KutschS, IshibashiM, RowitchDH, et al. (2001) Inactivation of the beta-catenin gene by Wnt1-Cre-mediated deletion results in dramatic brain malformation and failure of craniofacial development. Development 128 : 1253–1264.
48. GregorieffA, PintoD, BegthelH, DestréeO, KielmanM, CleversH (2005) Expression pattern of Wnt signaling components in the adult intestine. Gastroenterology 129(2): 626–38.
49. Smyth GK. (2005) Limma: linear models for microarray data. In: Bioinformatics and Computational Biology Solutions using R and Bioconductor, RGentleman, VCarey, SDudoit, RIrizarry, WHuber (eds.), Springer, New York, pages 397–420.
50. WettenhallJM, SimpsonKM, SatterleyK, SmythGK (2006) AffylmGUI: a graphical user interface for linear modeling of single channel microarray data. Bioinformatics (7): 897–9.
51. BenjaminiY, HochbergY (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series B (57): 289–300.
Štítky
Genetika Reprodukčná medicína
Článek Re-Ranking Sequencing Variants in the Post-GWAS Era for Accurate Causal Variant IdentificationČlánek Bypass of 8-oxodGČlánek Integrated Model of and Inherited Genetic Variants Yields Greater Power to Identify Risk GenesČlánek Comparative Genomic and Functional Analysis of 100 Strains and Their Comparison with Strain GGČlánek A Nuclear Calcium-Sensing Pathway Is Critical for Gene Regulation and Salt Stress Tolerance inČlánek Computational Identification of Diverse Mechanisms Underlying Transcription Factor-DNA OccupancyČlánek Reversible and Rapid Transfer-RNA Deactivation as a Mechanism of Translational Repression in StressČlánek Genome-Wide Association of Body Fat Distribution in African Ancestry Populations Suggests New Loci
Článok vyšiel v časopisePLOS Genetics
Najčítanejšie tento týždeň
2013 Číslo 8- Gynekologové a odborníci na reprodukční medicínu se sejdou na prvním virtuálním summitu
- Je „freeze-all“ pro všechny? Odborníci na fertilitu diskutovali na virtuálním summitu
-
Všetky články tohto čísla
- Genome-Wide DNA Methylation Analysis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Reveals Persistent Hypomethylation of Interferon Genes and Compositional Changes to CD4+ T-cell Populations
- Re-Ranking Sequencing Variants in the Post-GWAS Era for Accurate Causal Variant Identification
- Histone Variant HTZ1 Shows Extensive Epistasis with, but Does Not Increase Robustness to, New Mutations
- Past Visits Present: TCF/LEFs Partner with ATFs for β-Catenin–Independent Activity
- Functional Characterisation of Alpha-Galactosidase A Mutations as a Basis for a New Classification System in Fabry Disease
- A Flexible Approach for the Analysis of Rare Variants Allowing for a Mixture of Effects on Binary or Quantitative Traits
- Masculinization of Gene Expression Is Associated with Exaggeration of Male Sexual Dimorphism
- Genic Intolerance to Functional Variation and the Interpretation of Personal Genomes
- Endogenous Stress Caused by Faulty Oxidation Reactions Fosters Evolution of 2,4-Dinitrotoluene-Degrading Bacteria
- Transposon Domestication versus Mutualism in Ciliate Genome Rearrangements
- Comparative Anatomy of Chromosomal Domains with Imprinted and Non-Imprinted Allele-Specific DNA Methylation
- An Essential Function for the ATR-Activation-Domain (AAD) of TopBP1 in Mouse Development and Cellular Senescence
- Depletion of Retinoic Acid Receptors Initiates a Novel Positive Feedback Mechanism that Promotes Teratogenic Increases in Retinoic Acid
- Bypass of 8-oxodG
- Calpain-6 Deficiency Promotes Skeletal Muscle Development and Regeneration
- ATM Release at Resected Double-Strand Breaks Provides Heterochromatin Reconstitution to Facilitate Homologous Recombination
- Generation of Tandem Direct Duplications by Reversed-Ends Transposition of Maize Elements
- Loss of a Conserved tRNA Anticodon Modification Perturbs Cellular Signaling
- Integrated Model of and Inherited Genetic Variants Yields Greater Power to Identify Risk Genes
- High-Throughput Genetic and Gene Expression Analysis of the RNAPII-CTD Reveals Unexpected Connections to SRB10/CDK8
- Dynamic Rewiring of the Retinal Determination Network Switches Its Function from Selector to Differentiation
- β-Catenin-Independent Activation of TCF1/LEF1 in Human Hematopoietic Tumor Cells through Interaction with ATF2 Transcription Factors
- Genetic Mapping of Specific Interactions between Mosquitoes and Dengue Viruses
- A Highly Redundant Gene Network Controls Assembly of the Outer Spore Wall in
- Origin and Functional Diversification of an Amphibian Defense Peptide Arsenal
- Myc-Driven Overgrowth Requires Unfolded Protein Response-Mediated Induction of Autophagy and Antioxidant Responses in
- Integrative Modeling of eQTLs and Cis-Regulatory Elements Suggests Mechanisms Underlying Cell Type Specificity of eQTLs
- Species and Population Level Molecular Profiling Reveals Cryptic Recombination and Emergent Asymmetry in the Dimorphic Mating Locus of
- Ras-Induced Changes in H3K27me3 Occur after Those in Transcriptional Activity
- Characterization of the p53 Cistrome – DNA Binding Cooperativity Dissects p53's Tumor Suppressor Functions
- Global Analysis of Fission Yeast Mating Genes Reveals New Autophagy Factors
- Deficiency Suppresses Intestinal Tumorigenesis
- Introns Regulate Gene Expression in in a Pab2p Dependent Pathway
- Meiotic Recombination Initiation in and around Retrotransposable Elements in
- Comparative Oncogenomic Analysis of Copy Number Alterations in Human and Zebrafish Tumors Enables Cancer Driver Discovery
- Comparative Genomic and Functional Analysis of 100 Strains and Their Comparison with Strain GG
- A Model-Based Analysis of GC-Biased Gene Conversion in the Human and Chimpanzee Genomes
- Masculinization of the X Chromosome in the Pea Aphid
- The Architecture of a Prototypical Bacterial Signaling Circuit Enables a Single Point Mutation to Confer Novel Network Properties
- Distinct SUMO Ligases Cooperate with Esc2 and Slx5 to Suppress Duplication-Mediated Genome Rearrangements
- The Yeast Environmental Stress Response Regulates Mutagenesis Induced by Proteotoxic Stress
- Mediator Directs Co-transcriptional Heterochromatin Assembly by RNA Interference-Dependent and -Independent Pathways
- The Genome of and the Basis of Host-Microsporidian Interactions
- Regulation of Sister Chromosome Cohesion by the Replication Fork Tracking Protein SeqA
- Neuronal Reprograming of Protein Homeostasis by Calcium-Dependent Regulation of the Heat Shock Response
- A Nuclear Calcium-Sensing Pathway Is Critical for Gene Regulation and Salt Stress Tolerance in
- Cross-Species Array Comparative Genomic Hybridization Identifies Novel Oncogenic Events in Zebrafish and Human Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma
- : A Mouse Strain with an Ift140 Mutation That Results in a Skeletal Ciliopathy Modelling Jeune Syndrome
- The Relative Contribution of Proximal 5′ Flanking Sequence and Microsatellite Variation on Brain Vasopressin 1a Receptor () Gene Expression and Behavior
- Combining Quantitative Genetic Footprinting and Trait Enrichment Analysis to Identify Fitness Determinants of a Bacterial Pathogen
- The Innocence Project at Twenty: An Interview with Barry Scheck
- Computational Identification of Diverse Mechanisms Underlying Transcription Factor-DNA Occupancy
- GUESS-ing Polygenic Associations with Multiple Phenotypes Using a GPU-Based Evolutionary Stochastic Search Algorithm
- H2A.Z Acidic Patch Couples Chromatin Dynamics to Regulation of Gene Expression Programs during ESC Differentiation
- Identification of DSB-1, a Protein Required for Initiation of Meiotic Recombination in , Illuminates a Crossover Assurance Checkpoint
- Binding of TFIIIC to SINE Elements Controls the Relocation of Activity-Dependent Neuronal Genes to Transcription Factories
- Global Analysis of the Sporulation Pathway of
- Genetic Circuits that Govern Bisexual and Unisexual Reproduction in
- Deletion of microRNA-80 Activates Dietary Restriction to Extend Healthspan and Lifespan
- Fifty Years On: GWAS Confirms the Role of a Rare Variant in Lung Disease
- The Enhancer Landscape during Early Neocortical Development Reveals Patterns of Dense Regulation and Co-option
- Gene Expression Regulation by Upstream Open Reading Frames and Human Disease
- Sociogenomics of Cooperation and Conflict during Colony Founding in the Fire Ant
- The Intronic Long Noncoding RNA Recruits PRC2 to the Promoter, Reducing the Expression of and Increasing Cell Proliferation
- The , p.E318G Variant Increases the Risk of Alzheimer's Disease in -ε4 Carriers
- The Wilms Tumor Gene, , Is Critical for Mouse Spermatogenesis via Regulation of Sertoli Cell Polarity and Is Associated with Non-Obstructive Azoospermia in Humans
- Reversible and Rapid Transfer-RNA Deactivation as a Mechanism of Translational Repression in Stress
- QTL Analysis of High Thermotolerance with Superior and Downgraded Parental Yeast Strains Reveals New Minor QTLs and Converges on Novel Causative Alleles Involved in RNA Processing
- Genome Wide Association Identifies Novel Loci Involved in Fungal Communication
- Chromatin Sampling—An Emerging Perspective on Targeting Polycomb Repressor Proteins
- A Recessive Founder Mutation in Regulator of Telomere Elongation Helicase 1, , Underlies Severe Immunodeficiency and Features of Hoyeraal Hreidarsson Syndrome
- Genome-Wide Association of Body Fat Distribution in African Ancestry Populations Suggests New Loci
- Causal and Synthetic Associations of Variants in the Gene Cluster with Alpha1-antitrypsin Serum Levels
- Hard Selective Sweep and Ectopic Gene Conversion in a Gene Cluster Affording Environmental Adaptation
- Brittle Culm1, a COBRA-Like Protein, Functions in Cellulose Assembly through Binding Cellulose Microfibrils
- Chromosomal Copy Number Variation, Selection and Uneven Rates of Recombination Reveal Cryptic Genome Diversity Linked to Pathogenicity
- The Ribosomal Protein Rpl22 Controls Ribosome Composition by Directly Repressing Expression of Its Own Paralog, Rpl22l1
- Ras1 Acts through Duplicated Cdc42 and Rac Proteins to Regulate Morphogenesis and Pathogenesis in the Human Fungal Pathogen
- The DSB-2 Protein Reveals a Regulatory Network that Controls Competence for Meiotic DSB Formation and Promotes Crossover Assurance
- Recurrent Modification of a Conserved -Regulatory Element Underlies Fruit Fly Pigmentation Diversity
- Associations of Mitochondrial Haplogroups B4 and E with Biliary Atresia and Differential Susceptibility to Hydrophobic Bile Acid
- The Conditional Nature of Genetic Interactions: The Consequences of Wild-Type Backgrounds on Mutational Interactions in a Genome-Wide Modifier Screen
- A Critical Function of Mad2l2 in Primordial Germ Cell Development of Mice
- A Role for CF1A 3′ End Processing Complex in Promoter-Associated Transcription
- Vitellogenin Underwent Subfunctionalization to Acquire Caste and Behavioral Specific Expression in the Harvester Ant
- PLOS Genetics
- Archív čísel
- Aktuálne číslo
- Informácie o časopise
Najčítanejšie v tomto čísle- Chromosomal Copy Number Variation, Selection and Uneven Rates of Recombination Reveal Cryptic Genome Diversity Linked to Pathogenicity
- Genome-Wide DNA Methylation Analysis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Reveals Persistent Hypomethylation of Interferon Genes and Compositional Changes to CD4+ T-cell Populations
- Associations of Mitochondrial Haplogroups B4 and E with Biliary Atresia and Differential Susceptibility to Hydrophobic Bile Acid
- A Role for CF1A 3′ End Processing Complex in Promoter-Associated Transcription
Prihlásenie#ADS_BOTTOM_SCRIPTS#Zabudnuté hesloZadajte e-mailovú adresu, s ktorou ste vytvárali účet. Budú Vám na ňu zasielané informácie k nastaveniu nového hesla.
- Časopisy



