-
Články
- Časopisy
- Kurzy
- Témy
- Kongresy
- Videa
- Podcasty
RNA-seq Brings New Insights to the Intra-Macrophage Transcriptome of Typhimurium
The burden of Salmonellosis remains unacceptably high throughout the world and control measures have had limited success. Because Salmonella bacteria can be transmitted from the wider environment to animals and humans, the bacteria encounter diverse environments that include food, water, plant surfaces and the extracellular and intracellular phases of infection of eukaryotic hosts. An intricate transcriptional network has evolved to respond to a variety of environmental signals and control the “right time/ right place” expression of virulence genes. To understand how transcription is rewired during intracellular infection, we determined the primary transcriptome of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium within murine macrophages. We report the coding genes, sRNAs and transcriptional start sites that are expressed within macrophages at 8 hours after infection, and use these to infer gene function. We identified gene promoters that are specifically expressed within macrophages and could drive the intracellular delivery of antigens by S. Typhimurium vaccine strains. These data contribute to our understanding of the mechanisms used by Salmonella to regulate virulence gene expression whilst replicating inside mammalian cells.
Published in the journal: RNA-seq Brings New Insights to the Intra-Macrophage Transcriptome of Typhimurium. PLoS Pathog 11(11): e32767. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1005262
Category: Research Article
doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1005262Summary
The burden of Salmonellosis remains unacceptably high throughout the world and control measures have had limited success. Because Salmonella bacteria can be transmitted from the wider environment to animals and humans, the bacteria encounter diverse environments that include food, water, plant surfaces and the extracellular and intracellular phases of infection of eukaryotic hosts. An intricate transcriptional network has evolved to respond to a variety of environmental signals and control the “right time/ right place” expression of virulence genes. To understand how transcription is rewired during intracellular infection, we determined the primary transcriptome of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium within murine macrophages. We report the coding genes, sRNAs and transcriptional start sites that are expressed within macrophages at 8 hours after infection, and use these to infer gene function. We identified gene promoters that are specifically expressed within macrophages and could drive the intracellular delivery of antigens by S. Typhimurium vaccine strains. These data contribute to our understanding of the mechanisms used by Salmonella to regulate virulence gene expression whilst replicating inside mammalian cells.
Introduction
Salmonella enterica (S. enterica) is a food and water-borne pathogen responsible for widespread disease in humans and other animals. The serovars responsible for typhoid fever kill more than 250,000 people per year, while an estimated 94 million cases of Salmonella-mediated gastroenteritis cause 155,000 deaths each year [1,2]. Recently, it has been discovered that non-typhoidal serovars are causing an epidemic of invasive disease that is killing 680,000 people each year [3].
Decades of intense research have revealed intricate details of Salmonella pathogenicity [4]. S. enterica initiates infection in the small intestine by penetrating the mucus layer that protects the gut epithelium. During the infection process, S. enterica endures a series of hostile environments within the host, including the acidity of the stomach, antimicrobial peptides and bile in the intestine, and the toxicity of intracellular vacuoles [5]. These challenges are met by physiological and metabolic adaptations that allow the bacterium to resist the innate host defences. Salmonella pathogenicity island (SPI) 1 and SPI4-encoded proteins, and other virulence determinants, mediate the entry into epithelial cells [4,6]. The bacteria subsequently exit from epithelial cells and are taken up by the phagocytic cells of the innate immune system such as macrophages [7,8].
S. enterica responds to the phagosomal environment within macrophages by secreting effector proteins that generate a specialized intracellular compartment, the Salmonella-containing-vacuole (SCV). The SCV allows S. enterica to evade macrophage killing, and infected macrophages become a vehicle for systemic bacterial spread [9,10]. Physiological, metabolic and effector protein-mediated adaptation strategies allow the bacteria to replicate within the SCV, and to form persister cells [10,11]; many of these adaptive processes are regulated at the transcriptional level [12].
Bacterial gene regulation is mediated by a combination of transcription factors, nucleoid-associated proteins and regulatory small non-coding RNAs (sRNAs). Following the publication of the first S. enterica genome, microarray-based transcriptomic approaches were used to define regulons and stimulons of the model pathogen S. enterica serovar Typhimurium (S. Typhimurium) [13]. Because the microarray-derived data only provided a limited view of Salmonella gene expression inside macrophages [14–16], an RNA-seq-based approach was required to gain the information for understanding mechanisms of gene regulation. RNA-seq analysis generates high-resolution transcriptomic data and accurate information on gene expression levels, and provides extensive information concerning the location of Transcriptional Start Sites (TSS), the 5′ and 3′ un-translated regions of genes, antisense transcription, and sRNAs. We recently used this approach to reveal the complete transcriptional network of S. Typhimurium during growth in 22 laboratory conditions [17].
Here, we present the primary transcriptome of intra-macrophage S. Typhimurium strain 4/74. All intra-macrophage gene expression and transcriptional organisation data are presented in our online resource, SalComMac [http://tinyurl.com/SalComMac].
Results and Discussion
The primary transcriptome of intra-macrophage S. Typhimurium
The intra-macrophage transcriptome of S. enterica was determined with S. Typhimurium strain 4/74 (Dataset 1 in S1 Table) within cultured murine RAW 264.7 macrophage-like cells that do not express the Nramp1 (Slc11a1) host resistance cation-efflux pump [18]. Because earlier transcriptomic analyses showed that more than 90% of S. Typhimurium genes were expressed at similar levels during early, middle and late stages of macrophage infection [14], we focused on a single time point. We used eight hours post-infection to coincide with the nitrosative burst in Salmonella-infected murine macrophages [14]. Total bacterial RNA was isolated and analysed by RNA-seq [17] (Materials and Methods) (Fig 1). Overall, 136 million sequence reads were generated from seven cDNA libraries. These represent two biological replicates of intra-macrophage Salmonella RNA-seq, two biological replicates of intra-macrophage Salmonella differential RNA-seq (dRNA-seq) and RNA-seq of the ΔssrA mutant and two biological replicates of wild-type 4/74 grown under in vitro SPI2-inducing conditions. Between 5 and 10 million uniquely-mapped reads were obtained from each library (Dataset 2 in S1 Table), providing sufficient coverage for robust transcriptomic analysis [19]. Gene expression values were calculated by the Transcripts Per Million (TPM) approach [20]. A threshold TPM value of 10 was used as a cut-off to define gene expression (Materials and Methods) [17]. The intra-macrophage transcriptome was compared to our published RNA-seq-based transcriptome for early stationary phase (ESP), an infection-relevant in vitro growth condition that is associated with high expression of S. Typhimurium SPI1 genes [17,21].
Fig. 1. RNA-seq–based strategy to identify promoters, transcribed regions, and small RNAs of S. Typhimurium active during macrophage infection. 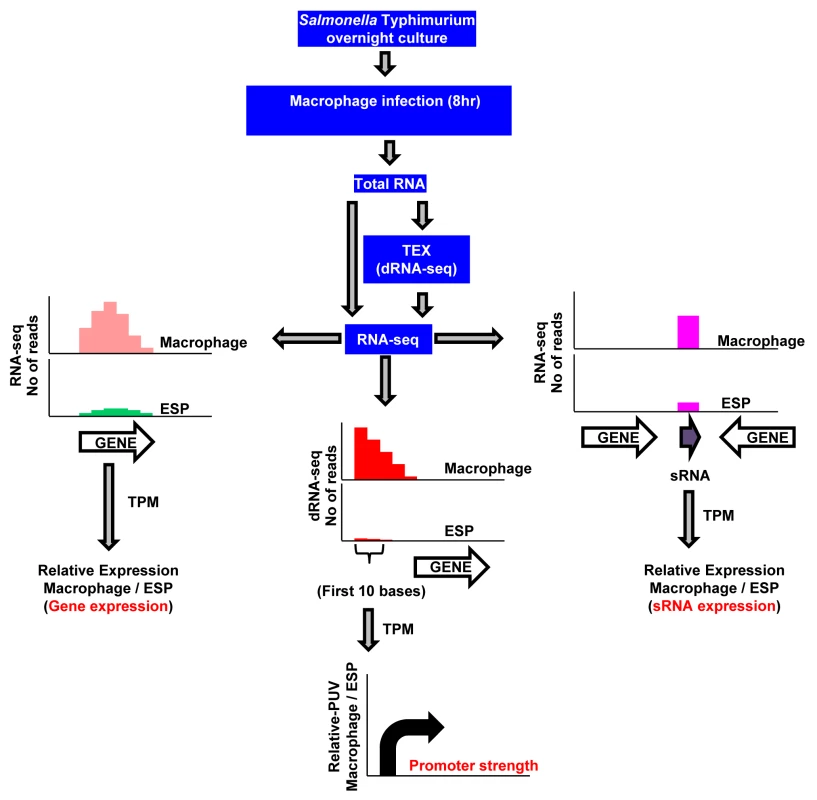
S. Typhimurium strain 4/74 was grown within macrophages for 8 hours using the gentamicin protection assay, and bacterial RNA was isolated using TRIzol (Materials and Methods). The cDNA generated from total RNA was sequenced either directly for gene/sRNA expression analysis (RNA-seq) or after enrichment of primary transcripts (dRNA-seq), and compared with data from 4/74 grown to ESP [17]. The graphs show representations of sequence reads mapped uniquely against the 4/74 genome in different conditions. Transcript per Million (TPM) analysis was used to calculate gene expression values from the number of sequence reads mapped against the 4/74 genome. The promoter usage value (PUV) indicates the TPM value of the first 10 nucleotides from the transcription start sites (TSS) in the direction of transcription, and represents promoter strength. Each curved arrow indicates location of TSS upstream of the respective gene; the width and height of each curved arrow is proportional to TSS expression, based on relative PUV, macrophage versus ESP. The precise nucleotide position of individual TSS was identified on a genome-wide scale by dRNA-seq [22]. In total, 3583 TSS were expressed by S. Typhimurium during infection of macrophages (Dataset 3 in S1 Table). This included 3538 TSS expressed in the ESP condition [17] and 45 TSS which were newly identified in this study. To assign a relative strength to each TSS we determined the expression levels of the first 10 bases of each transcript, designated the promoter usage value (PUV) [17,23]. Because >99% of S. Typhimurium protein coding genes have a 5’ untranslated region (UTR) and 15% of protein-coding genes possess multiple TSS, the PUV allows promoter strength to be quantified independently of gene expression [17]. We used the relative PUV to compare the expression of S. Typhimurium TSS between the intra-macrophage and the ESP in vitro condition, and categorised the TSS as either ‘Macrophage up-regulated’, ‘Macrophage down-regulated’ or ‘Macrophage-independent’ (Materials and Methods). Of the 3583 TSS expressed in macrophages, 883 were macrophage up-regulated and 834 were macrophage down-regulated, compared with ESP (Fig 2A; Dataset 3 in S1 Table). The TSS of the lgl-ripABC (STM3117-3120) SPI13 operon [24,25] was the most highly up-regulated, with a relative PUV of >500 -fold. Other highly up-regulated TSS controlled the expression of genes such as trpE and sseJ. We found that 72% of the promoters reported to be highly expressed in the murine spleen [26] were up-regulated in RAW macrophages.
Fig. 2. The primary transcriptome of intra-macrophage Salmonella. 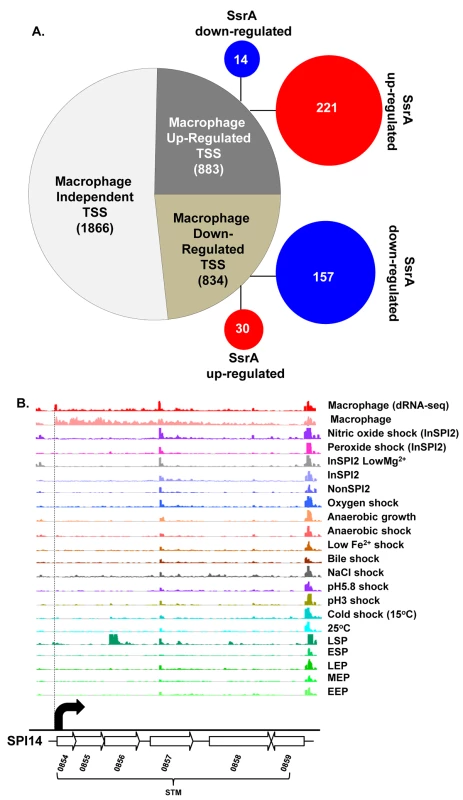
(A) Classification of 3583 Salmonella TSS during intra-macrophage proliferation (Dataset 3 in S1 Table). The TSS were categorized based on their relative-PUV, macrophage versus ESP (Materials and Methods). The red and blue circles represent the TSS that are up/down-regulated in the ∆ssrA versus InSPI2 experiment, respectively (B) The STM0854 TSS (indicated by the dotted vertical line) is a representative of a TSS highly up-regulated in macrophages. Each horizontal arrow represents the gene in scale with the whole island. Each coloured track above the island represents RNA-seq/dRNA-seq reads mapped against the genome in the corresponding conditions, visualized in the IGB browser. Each curved arrow indicates the location of a TSS; the width and height of each curved arrow is proportional to the TSS expression, based on relative PUV, macrophage versus ESP (Dataset 3 in S1 Table) (Materials and Methods). Forty five new TSS were identified in this study, including the TSS of STM0854 that controls intra-macrophage expression of the major polycistronic transcript of SPI14 (Fig 2B). Other novel TSS controlled the expression of genes involved in several core cellular processes including bglA, entB, fliN and nrdE, and a TSS that initiated a transcript antisense to the stfD coding gene.
Of the 834 macrophage down-regulated TSS, the biggest reduction in promoter expression between macrophages and the ESP condition was more than 200-fold and associated with SPI1 genes and the flagellin-encoding fliC gene (Dataset 3 in S1 Table).
The transcriptional organisation of SPI2 during infection of macrophages
Salmonella pathogenicity island 2 (SPI2) is required for Salmonella replication within eukaryotic cells and for systemic infection of mammalian hosts. SPI2 encodes the type III secretion system (T3SS) that delivers many effector proteins responsible for the function of the SCV within macrophages [4,27]. The transcriptional organization of SPI2 is shown in Fig 3. We recently used dRNA-seq to discover a TSS upstream of ssaR [17], which we now confirm by 5’ RACE (S1 Fig). SPI2 is therefore transcribed as six operons inside macrophages (Fig 3).
Fig. 3. The transcriptional organization of SPI2 in intra-macrophage Salmonella. 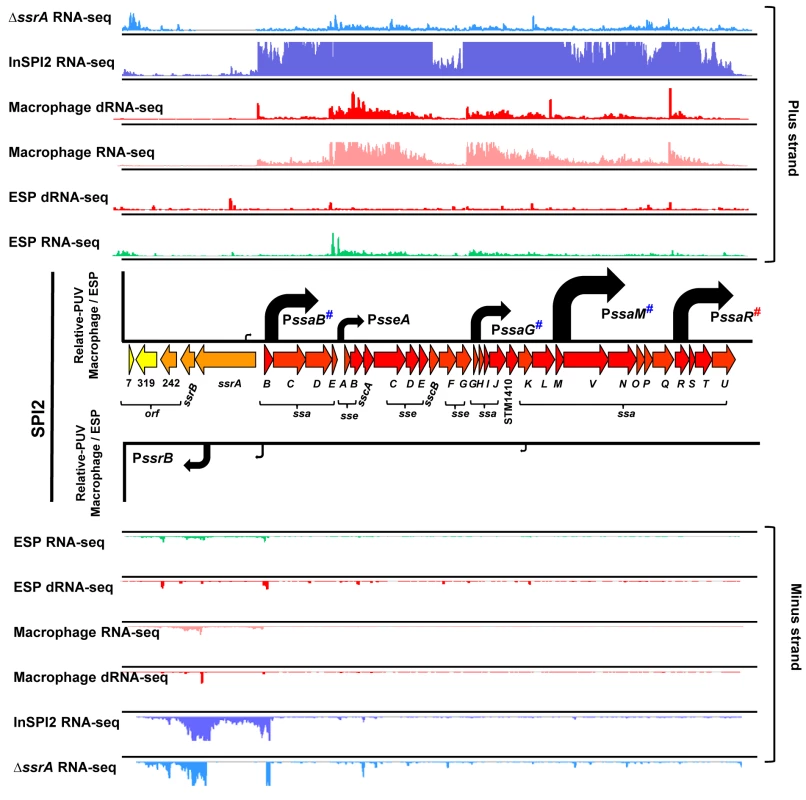
Horizontal arrows represent individual SPI2 genes in scale with the whole Island. The ssrA-B gene products regulate SPI2 expression, the sseA-E genes encode effector proteins, the sscA-B genes encode chaperone proteins and the ssaB-E and ssaG-U loci encode components of the T3SS apparatus. The colour of each gene represents its relative expression, macrophage versus ESP (Dataset 4 in S1 Table) based on the colour scale given in Fig 4. Each track above and below the island shows the mapping of the RNA-seq or dRNA-seq reads against the plus or minus strand of the 4/74 chromosome visualized in IGB. Each curved arrow indicates the location of a TSS upstream of the respective gene; the width and height of each curved arrow is proportional to the TSS expression, based on relative PUV, macrophage versus ESP (Dataset 3 in S1 Table) (Materials and Methods). The red hash on PssaR indicates that the TSS was reported previously [17], and confirmed in this study by 5’RACE (S1 Fig). The blue hashes indicate that the location of promoters PssaB, PsseA, PssaG, PssaM and PssrB that have been confirmed independently by 5’RACE [107] (S1 Fig). All SPI2 genes were up-regulated within macrophages, reflecting the phosphate/magnesium starvation and the acidity of the SCV [28,29]. The RNA-seq data were used to calculate promoter usage values for the different SPI2 promoters, identifying PssaM as the most up-regulated SPI2 promoter, followed by PssaR and PssaB (Dataset 3 in S1 Table). We note that each of the six SPI2 promoters was also transcribed in the “InSPI2” growth condition, confirming that expression of all SPI2 operons occurs in vitro when stimulated by growth in an acidic low-phosphate environment [30].
The SPI2 island and genes that encode SPI2-translocated effectors are activated by the SsrAB two component system [31]. The SsrA sensor kinase phosphorylates the SsrB response regulator to activate gene expression [32–34]. To investigate the role of SsrA in the regulation of macrophage up-regulated TSS, we used RNA-seq to analyse the transcriptome of a ΔssrA mutant and wild-type 4/74 grown in InSPI2 medium. Of the 883 macrophage up-regulated TSS, 221 showed reduced (>2-fold) expression in the absence of SsrA and we infer that these are SsrA-activated (Fig 2A; Dataset 3 in S1 Table). All the genes that encode SPI2-translocated effector proteins were controlled by SsrA-activated promoters. There are 662 macrophage up-regulated TSS that appear to have SsrA-independent regulatory mechanisms, and these merit further study.
Intra-macrophage expression of S. Typhimurium pathogenicity islands and effector-coding genes
S. Typhimurium carries 12 pathogenicity islands on the chromosome of strain 4/74 [17,35,36]. Expression profiles of S. Typhimurium pathogenicity islands (Fig 4; Datasets 4 and 5 in S1 Table) reveal that SPI2 and SPI13 were the most highly up-regulated during infection of macrophages, by an average of 44 and 82-fold, respectively (Dataset 5 in S1 Table). The SPI3, SPI5, SPI11, SPI12 and SPI14 islands showed moderate intra-macrophage up-regulation. SPI6 and SPI9 show macrophage-independent expression, and both SPI1 and SPI4 were significantly down-regulated inside macrophages.
Fig. 4. The relative intra-macrophage expression of the different pathogenicity islands of S. Typhimurium. 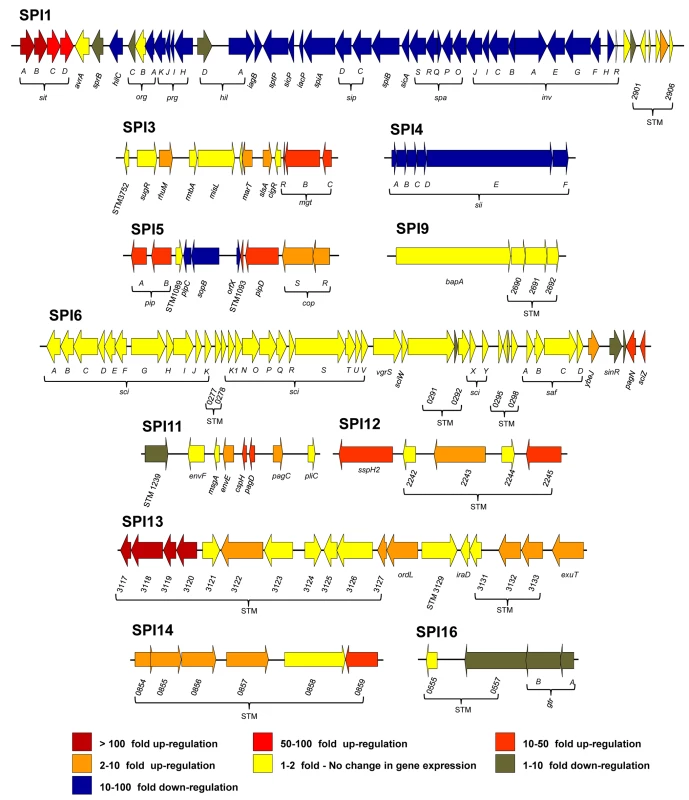
Each horizontal arrow represents individual genes to scale within each SPI Island; the different islands are not scaled against each other. The colour of each arrow represents relative gene expression, macrophage versus ESP (Datasets 4 and 5 in S1 Table) based on the colour scale at the bottom of the figure. SPI2 expression is shown in Fig 3. Effector proteins of S. Typhimurium are secreted via the SPI1 T3SS, the SPI2 T3SS or through both translocation systems. We reported that the genes encoding SPI1-translocated effectors showed a SPI1-like expression pattern, and genes encoding SPI2-translocated effectors showed a SPI2-like expression pattern [17]. Our data show that the genes encoding all SPI2-translocated effectors were highly macrophage up-regulated (Dataset 4 in S1 Table) (up to 70-fold), and the genes that encode the 7 effectors that are secreted by both the SPI1 and SPI2 T3SS were all expressed inside macrophages; the TPM values range from 50 to 230 (Fig 5). In contrast, genes encoding the 9 SPI1-translocated effectors were all macrophage down-regulated, by up to 160-fold, and were not significantly expressed within macrophages. Clearly, the actual intra-macrophage expression level of genes that encode candidate effector proteins has biological relevance.
Fig. 5. The intra-macrophage expression of Salmonella effector genes. 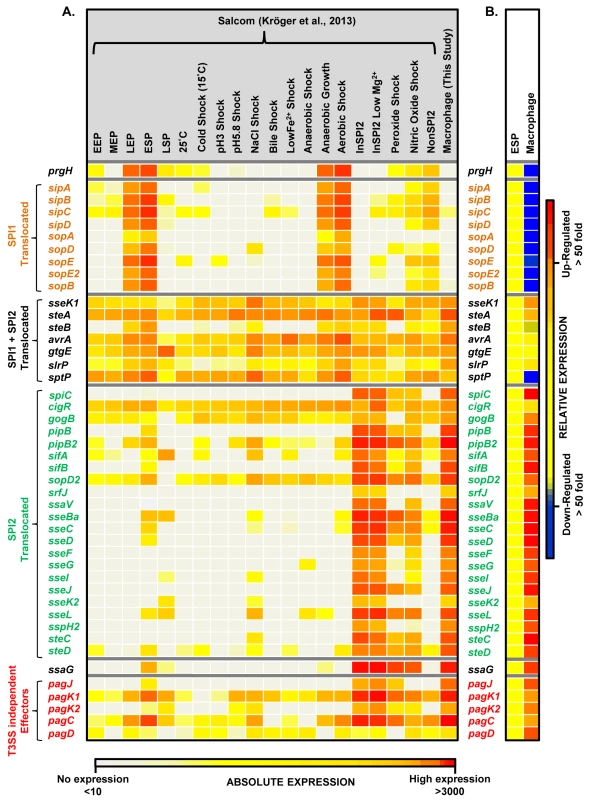
(A) A comparison of absolute expression levels of different S. Typhimurium effector genes within macrophages (Dataset 4 in S1 Table) and in 20 in vitro infection-related conditions [17]. The heatmap colours represent the absolute expression levels (log10 TPM values) based on the colour bar, ranging from TPM values of 49 to 706. (B) The relative expression levels (macrophage versus ESP) of each gene are defined in the colour bar to the right. The genes prgH and ssaG are included to show the SPI1-like and SPI2-like patterns of expression, respectively. The T3SS-independent genes were described by Kidwai et al. (2013) [108]. The transcriptomic data identified two specific SPI13 and SPI14-encoded operons that were highly up-regulated in macrophages (Datasets 4 and 5 in S1 Table) but were not significantly expressed in 20 in vitro conditions [17]. First, the SPI13-associated lgl-ripABC (STM3117-STM3120) operon was >250 fold up-regulated within macrophage. The lgl-ripABC operon is required for Salmonella infection [37,38], encoding enzymes that catabolise itaconate, an anti-microbial metabolite that is synthesised by infected macrophages [25,39]. Second, the SPI14-located STM0854-0857 operon is also required for Salmonella virulence [38], showed moderate (3 to 20-fold) intra-macrophage up-regulation, and was not expressed in in vitro growth conditions [17]. The TSS of the STM0854 and STM0859 transcripts were only expressed in macrophages, and not in any in vitro conditions. Taken together, these data suggest that the STM0854-0857 and lgl-ripABC operons respond to an intra-cellular signal that remains to be identified in macrophages. For ripABC, this signal may be itaconate [25].
For SPI3, the PhoP-activated mgtCBR operon [40] was up-regulated >15 fold within macrophages, while other SPI3 genes (slsA, marT and rhuM) were moderately up-regulated. The role of mgtCBR in virulence involves the long leader of the mgtC transcript that encodes MgtP. The mgtC leader is responsive to ATP levels [41] and inhibits F1Fo ATP synthase to maintain ATP homeostasis in the acidic intra-macrophage environment [42].
SPI5 encodes effectors translocated by both SPI1 and SPI2 T3SS [43,44]. The sopB gene encodes a SPI1-translocated effector and is macrophage down-regulated by 50-fold. In contrast, the gene encoding the SPI2 effector pipB is up-regulated. PipB localizes to the SCV membrane and brings about the formation of tubular extensions, the Salmonella induced filaments (SIFs) [45,46].
The SPI6-encoded Type 6 secretion system [47], is important for the colonization and systemic infections of chickens and mice [48,49]. None of the SPI6 genes were expressed in macrophages or in various in vitro conditions [17]. This is consistent with the reported repression of SPI6 genes by H-NS [50].
During infection of the gastrointestinal tract, the SPI1-encoded T3SS of S. Typhimurium is responsible for inflammatory diarrhoea and the invasion of non-phagocytic epithelial cells [51–53]. Thirty-three SPI1 genes were down-regulated within macrophages (Dataset 4 in S1 Table), and were highly expressed at ESP, confirming earlier reports [17,54]. HilA, the transcriptional activator of SPI1, is controlled by the co-ordinated action of HilC/HilD/RtsA, and consequently up-regulates the SPI1 island & SPI1-translocated genes [55–57]. The transcription of hilA is regulated by HilD, an important activator that controls cross-talk between SPI1 and SPI2 expression [55,58]. The hilA, hilC, hilD and rtsA regulatory genes are down-regulated more than 100-fold within macrophages, consistent with the down-regulation of the SPI1 island.
The siiABCDEF operon of SPI4 encodes a Type 1 secretion system, and was down-regulated within macrophages. SiiE is a non-fimbrial adhesin responsible for the adhesion of Salmonella to epithelial cells and is expressed during the extra-cellular phase of infection [59,60]. Cross talk between SPI1 and 4 can promote tight binding of the bacterium to the epithelial membrane, and facilitate efficient SPI1 translocation [61].
Relating intra-macrophage gene expression to gene function
Intracellular expression of individual bacterial genes or entire regulons can be used to investigate the microenvironment inside the host cell vacuole [62]. Direct comparison between this RNA-seq-based dataset (Dataset 4 in S1 Table) and previous microarray-based transcriptomic results confirm and extend key findings from Eriksson et al. (2003) and Hautefort et al. (2008) [14,15]. The datasets all show that the most highly macrophage up-regulated Salmonella gene is asr (STM1485), required for the intra-cellular replication of Salmonella [63]. The 890-fold up-regulation of asr reflects the acidic conditions within the SCV [64] (Dataset 4 in S1 Table).
To investigate the gene expression network of intra-macrophage Salmonella, we focused on 157 transcriptional regulators (Dataset 6 in S1 Table). The levels of 34 transcription factors were >3-fold macrophage up-regulated, and 7 transcription factors were >3-fold macrophage down-regulated. To determine whether the differential expression of individual regulators was reflected by up - or down-regulation of the associated regulons, we compared the expression of several genes controlled by each transcription factor in ESP and macrophages. We observed that the up-regulation of SPI2 regulators ssrB, ompR and phoP and down-regulation of SPI1 regulators hilD, hilA, hilC, invF and sprB correlates with the expression of their respective regulons (Fig 6A and 6B). The macrophage up-regulation of regulons that detoxify peroxide, detoxify nitric oxide and relieve envelope stress and protein misfolding (soxS, oxyR, marA, marS, rpoE, rpoH and nsrR regulons and genes hmpA, msrA, ycfR, sbp, sodC, katG), reflects the bacterial response to the oxidative and nitrosative bursts that occurred during the infection process.
Fig. 6. Relative intra-macrophage expression of Salmonella transcription factors and selected target genes. 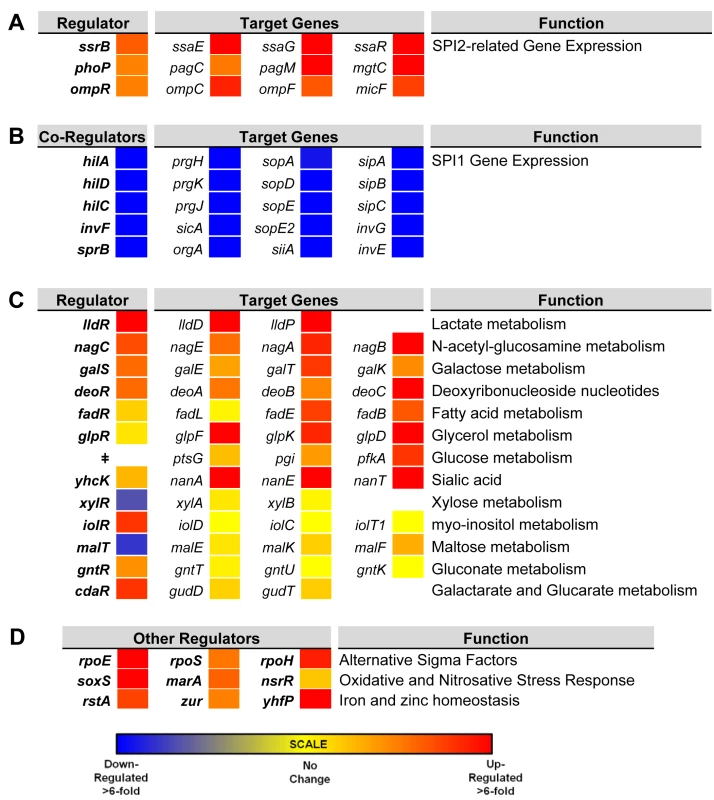
The expression of individual genes is shown as fold change, intra-macrophage versus ESP. Transcription factors are shown in bold. Target genes controlled by individual transcription factors are shown in the same row (A and C). Expression of transcription factors that regulate SPI2-related genes (A). The regulation of SPI1 genes is controlled by a hierarchy, and the transcription factors are depicted as co-regulators, with their combined target genes (B). Relative expression of 13 metabolic systems (C). Relative expression of up-regulated alternative sigma factors and transcription factors that control oxidative stress, and iron and zinc homeostasis (D). ǂNo dedicated transcription factor for glucose metabolism was assigned. Bacterial genes were assigned to functional groups to investigate the metabolic resources of macrophages. The most up-regulated functional categories of S. Typhimurium genes within macrophages are involved in carbohydrate and amino acid metabolism (S2 Fig). The “nutritional immunity” hypothesis posits that the innate immune response of the host reduces the availability of important nutrients for intracellular bacteria [65], which may explain why S. Typhimurium has evolved the ability to utilise a diverse range of host nutrients, including some sugars and amino acids that accumulate in murine macrophages during intracellular infection [66]. It is known that the major carbon sources utilised by S. Typhimurium in macrophages of the mouse spleen are deoxyribonucleotides, fatty acids, glucose, gluconate, glycerol, lactate and N-acetyl-glucosamine [67]. In our study, we observe the concerted up-regulation of multiple metabolic regulons in RAW macrophages that are consistent with the simultaneous degradation of deoxyribonucleotides, fatty acids, galactose, glucose, gluconate, glycerol, lactate, N-acetyl-glucosamine and sialic acid, while regulons controlling gluconate, maltose, myo-inositol and xylose metabolism showed significant macrophage down-regulation (Fig 6). Our current understanding of the intracellular metabolism of Salmonella in cultured macrophages coupled with the comprehensive data available for S. Typhimurium during infection of the murine spleen [66] suggest that cultured macrophages represent a good model for the study of the intracellular metabolism of Salmonella.
Mammalian macrophages reduce intracellular levels of metals such as iron as part of their strategy to limit bacterial replication [68], and S. Typhimurium responds by switching on the expression of metal-uptake systems. These include the intra-macrophage up-regulation of the sitABCD operon, responsible for manganese and iron transport [69] and of genes responsible for iron transport and biogenesis of iron-sulfur cluster containing proteins (ent, fep, fhu, iro, sfb, sit and suf genes, as well as the yhfP (iscR), and rstA regulons), magnesium (mgtCBR) transport and zinc (zur) uptake. We suggest that these expression patterns reflect the relatively low levels of magnesium, manganese, iron and zinc metals within the SCV [70]. Genes encoding the flagella and chemotaxis systems were significantly down-regulated in macrophages (between 50 to 100-fold), consistent with previous reports for both the Typhimurium and Typhi serovars [14,15,71] (Dataset 4 in S1 Table; S2 Fig). Specifically flh, flg, fli, flj, mot, che and aer genes were down-regulated. The flhDC-mediated regulation of flagellar transcription is complex [72], and cross-talk between SPI1 and flagellar genes was recently reported [73]. The flagellar regulator FliZ is a post-transcriptional activator of flhDC that positively regulates SPI1 by activating the hilD-rtsAB cascade [74]. In turn, RtsB represses the flhDC promoter [57]. These regulatory mechanisms probably account for the down-regulation of flagellar genes within macrophages, consistent with the shut-down of flagellar synthesis associated with the non-motile bacteria found in the SCV [75]. This contrasts with the reported up-regulation of SPI1 and flagella that occurs when S. Typhimurium encounters the cytosol of epithelial cells [75].
Thirty one Salmonella genes are specifically up-regulated within macrophages
To find genes that were up-regulated in the intra-macrophage environment but not in standard laboratory conditions, we used a comparative transcriptomic approach to identify genes that showed significantly higher expression in macrophages than in any of 20 in vitro conditions [17] (Materials and Methods). Our analysis identified 31 genes that were specifically up-regulated within macrophages (Dataset 7 in S1 Table; Fig 7A and 7B). These represent an interesting class of bacterial genes that are up-regulated in macrophages due to a factor encountered within macrophages and not in the in vitro growth conditions. The STM3117-STM3120 (lgl-ripABC) genes are a good example, of highly macrophage-induced genes (Fig 7C) that are involved in the detoxification of two SCV-specific metabolites, methylglyoxal and itaconate [24,25]. We propose that comparative transcriptomics will be a useful approach for identifying genes that respond to specific components of the SCV environment. The majority of the genes in Fig 7A have a STM or a yxx prefix and are designated as “FUN” genes, for “function unknown” [76]. Overall, 18 of the 31 genes that were specifically up-regulated within macrophages have previously been shown to be required for virulence (Dataset 7 in S1 Table). We speculate that these FUN genes respond to a specific component of the intra-vacuolar environment of the macrophage and could play important roles in the process of infection.
Fig. 7. Salmonella genes that are specifically up-regulated inside macrophages. 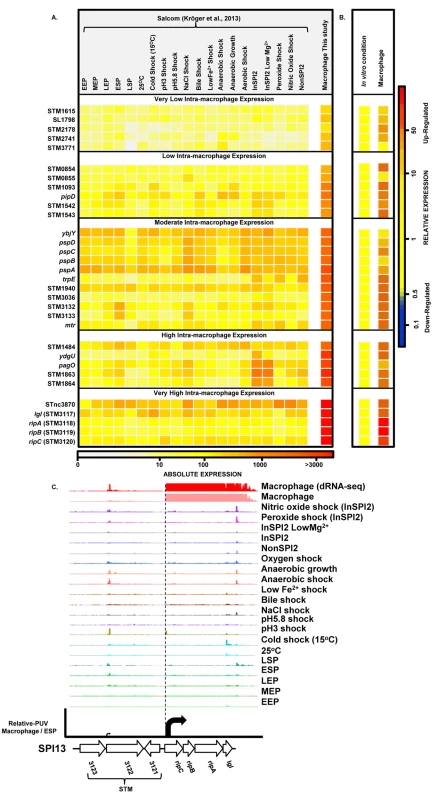
(A) Heatmap showing expression of 31 S. Typhimurium genes that are specifically up-regulated during infection of macrophages, compared to 20 in vitro conditions [17] (Dataset 7 in S1 Table) (Materials and Methods). The heatmap colours represent the absolute expression levels (log10 TPM values) based on the colour bar below. (B) The relative expression level of each gene is the fold-change of macrophage versus [expression in the in vitro condition where the gene in maximally expressed], based on the colour bar to the right. (C) The SPI13 operon (lgl [37] and ripABC [25], or STM3117 and STM3118-STM3120, respectively) is highly induced within macrophages. Salmonella promoters with potential therapeutic applications
The identification of a discrete set of promoters that are up-regulated in macrophages could have therapeutic applications. Attenuated strains of S. Typhimurium have been used extensively as vaccines [77], and for expressing anti-cancer proteins within tumours [78]. These technologies require specific Salmonella gene promoters to drive the production of foreign antigens [79]. For example, the ssaG promoter of SPI2 has been used to express E. coli heat labile toxin in S. Typhimurium [80]. However, the ssaG promoter is active in the gut [81,82], and so may not be the ideal antigen delivery system. We sought to identify candidate promoters with the characteristics required to deliver antigens from attenuated live vaccine strains of S. Typhimurium during intracellular infection.
We screened our intra-macrophage promoter expression data to identify primary TSS that were highly expressed within macrophages, and driving a downstream gene that was highly macrophage up-regulated. Eleven promoters were identified as suitable for antigen delivery during infection (Dataset 8 in S1 Table), controlling the asr, bioB, iroB, sseJ, STM0854 (SPI14) and ripC (SPI13) genes. Of these, sseJ is highly expressed within mouse organs [83]. The ripC promoter may be ideal for antigen delivery as it is highly and specifically induced inside macrophages (Dataset 3 in S1 Table; Fig 7C). However, high-level expression of heterologous antigens does not always generate the optimal stimulation of immune responses [79], and over-expression of certain proteins could compromise bacterial fitness. For this reason, we categorized the macrophage-up-regulated genes from Fig 7A, based on their levels of intra-macrophage expression and identified the promoter of STM0854 as a promising candidate for moderate but specific induction of gene expression within macrophages (Fig 7B). The 11 promoter candidates have the potential to deliver different levels of heterologous antigens and could be used to improve Salmonella-based intracellular vaccine delivery systems.
The sRNA transcriptome of intra-macrophage Salmonella
Bacterial gene expression is controlled by transcription factors, nucleoid-associated proteins and sRNAs. Bacterial sRNAs are roughly 50–300 nucleotides in length, and play regulatory roles in key physiological activities like iron homeostasis, carbon metabolism, anaerobic adaptation, envelope stress and pathogenesis [84–88]. To date, 280 sRNAs have been identified in S. Typhimurium 4/74 [17], but little is known about their role in virulence [5,85]. The fact that 246 of 280 sRNAs were expressed within macrophages (TPM value >10; Dataset 9 in S1 Table) suggests that many could potentially play a regulatory role during infection. In terms of relative expression, we found that 34 sRNAs were macrophage up-regulated and 119 sRNAs were macrophage down-regulated, compared to ESP (Dataset 9 in S1 Table; Fig 8A). The Hfq chaperone protein mediates sRNA-mRNA interactions and binds to at least 115 S. Typhimurium sRNAs [17,89], of which 19 were up-regulated within macrophages (including RyhB-1/2, OxyS, MicF and RybB) and 56 were down-regulated (including ArcZ, DsrA and DapZ), compared to ESP (Dataset 9 in S1 Table; Fig 8B).
Fig. 8. Intra-macrophage expression profile of Salmonella sRNAs. 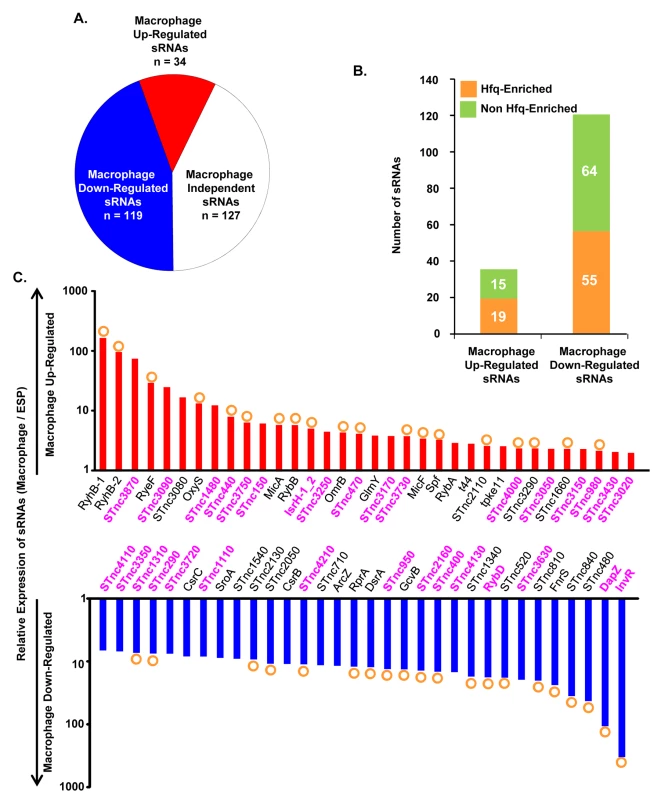
(A) Total number of sRNAs that are up or down-regulated in macrophages, based on the relative TPM value (>2-fold macrophage versus ESP; Dataset 9 in S1 Table). (B) Histograms representing the total number of Hfq-associated sRNAs [109] that are up or down-regulated within macrophages. (C) The relative expression of S. Typhimurium sRNAs in macrophages (TPM values; macrophage versus ESP). The red histograms depict the 34 macrophage up-regulated sRNAs (>2-fold). The blue histograms show sRNAs down-regulated >6-fold within macrophage (Dataset 9 in S1 Table). The orange circles indicate Hfq-bound sRNAs [17]. The names of sRNAs shown as magenta bold text are specific to the Salmonella genus (Dataset 10 in S1 Table). The expression patterns of well-characterised sRNAs provide insight into the conditions experienced by S. Typhimurium bacteria in the SCV. For instance, up-regulation of the RpoE-dependent sRNAs MicA and RybB inside macrophages likely reflects envelope stress of S. Typhimurium during intracellular proliferation [90,91]. Another sRNA that is RpoE-dependent in E. coli, MicL (RyeF) [92] is up-regulated 30-fold within macrophages, but it is not yet known whether this sRNA is controlled by RpoE in Salmonella. The iron-regulated homologs RyhB-1 and RyhB-2 were the most highly up-regulated sRNAs within macrophages compared to ESP (Dataset 9 in S1 Table, Fig 8C), reflecting the iron-limited intra-macrophage environment [14,17,93,94]. RyhB-1 and RyhB-2 (named RfrA and RfrB in S. Typhi) are also known to be important for replication of S. Typhi within macrophages [95]. Our data confirm that the IsrH, RyhB-1 and RyhB-2 (IsrE) sRNAs are up-regulated, as originally reported within J774 macrophages [93]. We analysed the expression of six sRNAs that were up-regulated within fibroblasts, a cell type that does not support the replication of Salmonella [96]. Two of these sRNAs, RyhB-1 and RyhB-2, were also up-regulated in macrophages (Dataset 9 in S1 Table). We identified several uncharacterized Hfq-associated sRNAs that were up-regulated within macrophages, including STnc440, STnc470 and STnc3750 which have an expression pattern consistent with a role in virulence. The function of these sRNAs is currently under investigation.
To determine whether macrophage-regulated sRNAs were phylogenetically conserved between fourteen serovars that represent much of the diversity of the Salmonella genus, we analysed 29 enterobacterial genomes (Dataset 10 in S1 Table). We found that 176 sRNAs were conserved (>90% sequence identity) within the Salmonella genus, but not in other members of the Enterobacteriaceae (<70% sequence identity), and were designated Salmonella-specific. About 10% (17) of the Salmonella-specific sRNAs were up-regulated within macrophages (including STnc440 and IsrH) while 74 were down-regulated in macrophages (including DapZ and InvR), compared to ESP (Fig 8C, Dataset 10 in S1 Table). We propose that some of these 91 macrophage-regulated sRNAs could play important roles in the regulation of gene expression during the intracellular phase of Salmonella infection.
Perspective
Salmonella bacteria are exposed to multiple stressors within the vacuolar compartment of macrophages, including acid pH, reactive oxygen and reactive nitrogen species. Adaptation to this hostile environment has a profound impact upon the transcriptome of S. Typhimurium, and we have now defined the TSS and sRNAs that react to the intra-vacuolar environment during the intracellular phase of the Salmonella infection cycle. Our data provide an overall view of sRNA expression within macrophages, and represent a resource for the investigation of post-transcriptional regulation during the intracellular life of Salmonella.
This study offers new insights into the interaction of Salmonella with mammalian cells, and brings us a step closer to understanding the gene regulatory mechanisms that facilitate the success of this dangerous pathogen. The SalComMac online resource [http://tinyurl.com/SalComMac] is intended to simplify the comparison of the transcriptome of intra-macrophage and in vitro grown S. Typhimurium.
Materials and Methods
Bacterial strains, macrophage cells and growth conditions
Salmonella enterica subspecies enterica serovar Typhimurium strain 4/74 was used for all experiments; 4/74 is the prototrophic parent of strain SL1344; the two strains differ by just eight single nucleotide polymorphisms [21,35,97]. For in vitro RNA isolation, bacterial cells were grown overnight in 5 mL Lennox (L-) Broth (Dataset 1 in S1 Table), diluted 1 : 1000 into 25 mL L-broth, grown at 220 rpm and 37°C in a 250 mL flask until early stationary phase (ESP, OD600 2.0) [17]. InSPI2 minimal media was used to induce expression of SPI2 in vitro [30]. For all intracellular studies, RAW 264.7 (ATCC) murine macrophage cells were maintained in Dulbecco’s Minimal Essential Medium (DMEM) supplemented with 5% fetal bovine serum & L-glutamine (2 mM final concentration) and MEM non-essential amino acids without antibiotics, incubated at 37°C in 5% CO2. All tissue culture reagents were supplied by Lonza.
RNA isolation from intracellular Salmonella
Approximately 109 RAW 264.7 macrophage cells were seeded in 175 cm2 tissue culture flasks and infected with complement-opsonized 4/74 cells at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 100 : 1 (bacteria:macrophages) [14]. Mouse serum (Charles River Laboratories) was used for opsonisation, and was stored at −80°C prior to use. After 30 minutes of infection, extracellular bacteria were killed by media containing 100 μg mL−1 gentamicin and incubated for a further 1h. The medium was then changed to ‘maintenance media’ containing 10 μg mL−1 gentamicin for the rest of the experiment. At 8 hours post infection, the infected macrophages were lysed in ice cold ‘RNA stabilisation solution’ [0.2% SDS, 19% ethanol, 1% acidic phenol in water] and incubated on ice for 30 minutes [14] to prevent RNA degradation [98,99]. The lysates containing intracellular Salmonella were collected, centrifuged and RNA was isolated from the bacterial pellets by a TRIzol-based method that yields both mRNA and sRNA. Briefly, the supernatant was discarded, the pellet was washed three times in 19% ethanol, 1% acidic phenol, re-suspended in the remaining liquid, transferred to a clean 1.5 mL Eppendorf tube and centrifuged at 20,000 × g at 4°C. The cell pellet was dissolved in 1 mL TRIzol (Invitrogen) on ice and transferred into a 2 mL heavy phase lock tube (5 Prime) into which 400 μL of chloroform was added and immediately mixed for 10 seconds. After incubation at room temperature for 2 minutes, the mixture was centrifuged at 20,000 × g for 15 minutes. The RNA present in the upper phase was transferred to a fresh tube, and precipitated by adding 450 μL of isopropanol and incubated at room temperature for 30 minutes. The precipitated RNA was then pelleted by centrifugation at 20,000 × g for 30 minutes. The pellet was washed in 350 μL ethanol (70%) and centrifuged at 20,000 × g for 10 minutes. The washed pellet was air-dried, re-suspended in RNase-free water by shaking (900 rpm) for 5 min in a heating block (65°C) (Peqlab Thriller) and stored at −80°C until cDNA library construction.
The integrity of RNA was verified using an Agilent Bioanalyzer 2100 and RNA concentrations were measured using the nanodrop spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific) and the Qubit fluorometer (Invitrogen). Control RNA was isolated from bacterial cells grown in L - broth in vitro until ESP (see above). The infection process, RNA preparation, sequencing and analysis were conducted in duplicate to provide independent data from biological replicates.
Library preparation and deep sequencing
The cDNA library preparation and Illumina sequencing was done by Vertis Biotechnologie AG (Freising, Germany). The total RNA obtained from the biological replicates of intra-macrophage was digested for 45 minutes with DNase I (Thermo Scientific) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Ribosomal RNA was not depleted. RNA samples were fragmented with ultrasound (4 pulses of 30 sec at 4°C). The 3’ ends of RNA were then subjected to poly (A)-tailing using poly (A) polymerase. The RNA was then treated with TAP (Tobacco acid pyrophosphatase) to remove the pyrophosphate group from the 5’ end, prior to ligation with an RNA adapter. First strand cDNA synthesis was done with an oligo (dT) adapter and M-MLV-RNaseH-reverse transcriptase (Invitrogen), following PCR amplification of cDNA using high-fidelity DNA polymerase to a final concentration of approximately 20–30 ng μL-1. The cDNAs were purified using the Agencourt AMPure XP kit (Beckman Coulter Genomics), and analysed by capillary electrophoresis. The cDNA libraries were sequenced on an Illumina HiSeq 2000 system. For dRNA-seq, prior to cDNA preparation, an aliquot of the RNA samples were enriched for primary transcripts by treating with Terminator 5’-monophosphate dependent exonuclease (Epicentre; TEX) [22].
Mapping of RNA-seq libraries and differential gene expression analysis
The sequence reads obtained from the different cDNA libraries were mapped against the 4/74 reference genome using the Segemehl software, with accuracy set to 100% [35,100]. The mapping coverage was increased by an iterative process that involved the sequential removal of any mismatched nucleotides from the 3’ end, and mapping the read against the 4/74 genome. This process was repeated until the individual sequence reads were accurately mapped to a single location on the chromosome, or until the length dropped below a minimum value of 20 nucleotides [17]. These uniquely-mapped reads were visualised with the Integrated Genome Browser (IGB) [101] and Jbrowse [102]. In total, 6 cDNA libraries (including the biological replicates of RNA-seq, dRNA-seq and RNA-seq of InSPI2 grown ΔssrA & wild type S. Typhimurium 4/74) were generated.
The expression values of each gene were calculated from the uniquely-mapped reads using the Transcript per Million (TPM) approach [20,103]. TPM considers the transcripts to represent a mixture of two distributions of expressed and non-expressed genes, and so is ideal for the analysis of bacterial transcriptomic data. As this approach involves normalization to gene size and the total amount of genome-wide transcription, TPM values can be compared between genes and between growth conditions [20,103,104].
The threshold for expression of a gene was TPM value 10 [17]. Genes with TPM value ≤10 were considered to be “not expressed”. The differential expression of each gene or sRNA within macrophages was calculated against the ESP comparator as a fold change (macrophage versus ESP).
Identification of Salmonella genes specifically up-regulated within macrophage
The average and standard deviation of RNA-seq data (TPM values) was calculated for each gene from the 20 in vitro growth conditions reported earlier [17]. For each gene, the standard deviation was multiplied by five-fold to define a broad expression range that captured all but the most extreme expression levels across the 20 conditions. To identify genes that were specifically up-regulated in macrophage, we selected a strict cut-off of 3-fold more highly expressed than five standard deviations above the mean expression value from the 20 conditions. In other words, macrophage specific gene = TPM > 3 x (average TPM in 20 conditions + 5σ). The genes that passed this cut-off are ‘not significantly expressed’ in any of the 20 in vitro conditions, are up-regulated within macrophages, and are listed in Fig 7A.
The identification of transcriptional start sites (TSS)
A strict criterion was used to identify TSS, after visualization with the IGB browser [17]. Novel TSS were defined when a peak was enriched in the dRNA-seq data compared with the RNA-seq data in two biological replicates, and was located at the beginning of an expressed transcript.
The Promoter Usage Value (PUV) for each TSS was quantified by calculating the TPM for the first 10 nucleotides from the TSS towards the direction of transcription (from +1 to +10). The PUV values were classified as follows: (a) ‘Macrophage independent’ TSS have similar PUV in macrophages and at ESP (less than 2-fold up - or down-regulated); (b) ‘Macrophage up-regulated’ TSS are expressed at least 2-fold higher in macrophages relative to ESP; and (c) ‘Macrophage down-regulated’ TSS are expressed at least 2-fold less in macrophages relative to ESP.
Confirmation of TSS by 5’ RACE
The 5’ RACE (rapid amplification of cDNA ends) was carried out with or without treatment by TAP using DNase I-digested total RNA isolated from the InSPI2 condition [105]. Gene specific amplification was done with the linker-specific primer JVO-0367 and gene specific reverse primers (Dataset 1 in S1 Table). TAP-enriched fragments were excised from an agarose gel, subcloned into a pTOPO vector (Invitrogen) and at least three clones were sequenced to validate individual TSS.
Analysis of conservation of sRNAs between bacterial genomes
The sRNA nucleotide sequences from 4/74 were aligned against a set of bacterial genomes belonging to Enterobacteriaceae using GLSEARCH [106], and identical hits were extracted.
Accession numbers
The RNA-seq data generated from this study are deposited at the NCBI GEO under the accession numbers GSM1462575 to GSM1462579, GSM1914919 and can be accessed at http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE59945.
Supporting Information
Zdroje
1. Majowicz SE, Musto J, Scallan E, Angulo FJ, Kirk M, O'Brien SJ, et al. The global burden of nontyphoidal Salmonella gastroenteritis. Clinical infectious diseases: an official publication of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. 2010;50(6):882–9. doi: 10.1086/650733 20158401.
2. Crump JA, Mintz ED. Global trends in typhoid and paratyphoid Fever. Clinical infectious diseases: an official publication of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. 2010;50(2):241–6. doi: 10.1086/649541 20014951; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2798017.
3. Ao TT, Feasey NA, Gordon MA, Keddy KH, Angulo FJ, Crump JA. Global burden of invasive nontyphoidal Salmonella disease, 2010(1). Emerging infectious diseases. 2015;21(6). doi: 10.3201/eid2106.140999 25860298; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4451910.
4. Fabrega A, Vila J. Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium skills to succeed in the host: virulence and regulation. Clinical microbiology reviews. 2013;26(2):308–41. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00066-12 23554419; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3623383.
5. Hebrard M, Kroger C, Srikumar S, Colgan A, Handler K, Hinton JC. sRNAs and the virulence of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. RNA biology. 2012;9(4):437–45. doi: 10.4161/rna.20480 22546935; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3384567.
6. Hurley D, McCusker MP, Fanning S, Martins M. Salmonella-host interactions—modulation of the host innate immune system. Frontiers in immunology. 2014;5 : 481. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00481 25339955; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4188169.
7. Jones BD, Ghori N, Falkow S. Salmonella typhimurium initiates murine infection by penetrating and destroying the specialized epithelial M cells of the Peyer's patches. The Journal of experimental medicine. 1994;180(1):15–23. 8006579; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2191576.
8. Vazquez-Torres A, Jones-Carson J, Baumler AJ, Falkow S, Valdivia R, Brown W, et al. Extraintestinal dissemination of Salmonella by CD18-expressing phagocytes. Nature. 1999;401(6755):804–8. doi: 10.1038/44593 10548107.
9. Kuhle V, Hensel M. Cellular microbiology of intracellular Salmonella enterica: functions of the type III secretion system encoded by Salmonella pathogenicity island 2. Cellular and molecular life sciences: CMLS. 2004;61(22):2812–26. doi: 10.1007/s00018-004-4248-z 15558211.
10. Haraga A, Ohlson MB, Miller SI. Salmonellae interplay with host cells. Nature reviews Microbiology. 2008;6(1):53–66. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1788 18026123.
11. Helaine S, Holden DW. Heterogeneity of intracellular replication of bacterial pathogens. Current opinion in microbiology. 2013;16(2):184–91. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2012.12.004 23485258.
12. Shen S, Fang FC. Integrated stress responses in Salmonella. International journal of food microbiology. 2012;152(3):75–81. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2011.04.017 21570144; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3164900.
13. Hebrard M, Kroger C, Sivasankaran SK, Handler K, Hinton JC. The challenge of relating gene expression to the virulence of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Current opinion in biotechnology. 2011;22(2):200–10. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2011.02.007 21388802.
14. Eriksson S, Lucchini S, Thompson A, Rhen M, Hinton JC. Unravelling the biology of macrophage infection by gene expression profiling of intracellular Salmonella enterica. Molecular microbiology. 2003;47(1):103–18. 12492857.
15. Hautefort I, Thompson A, Eriksson-Ygberg S, Parker ML, Lucchini S, Danino V, et al. During infection of epithelial cells Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium undergoes a time-dependent transcriptional adaptation that results in simultaneous expression of three type 3 secretion systems. Cellular microbiology. 2008;10(4):958–84. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2007.01099.x 18031307; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2343689.
16. Hammarlof DL, Canals R, Hinton JC. The FUN of identifying gene function in bacterial pathogens; insights from Salmonella functional genomics. Current opinion in microbiology. 2013;16(5):643–51. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2013.07.009 24021902.
17. Kröger C, Colgan A, Srikumar S, Handler K, Sivasankaran SK, Hammarlof DL, et al. An infection-relevant transcriptomic compendium for Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium. Cell host & microbe. 2013;14(6):683–95. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2013.11.010 24331466.
18. Govoni G, Canonne-Hergaux F, Pfeifer CG, Marcus SL, Mills SD, Hackam DJ, et al. Functional expression of Nramp1 in vitro in the murine macrophage line RAW264.7. Infection and immunity. 1999;67(5):2225–32. 10225878; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC115961.
19. Haas BJ, Chin M, Nusbaum C, Birren BW, Livny J. How deep is deep enough for RNA-Seq profiling of bacterial transcriptomes? BMC genomics. 2012;13 : 734. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-734 23270466; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3543199.
20. Wagner GP, Kin K, Lynch VJ. Measurement of mRNA abundance using RNA-seq data: RPKM measure is inconsistent among samples. Theory in biosciences = Theorie in den Biowissenschaften. 2012;131(4):281–5. doi: 10.1007/s12064-012-0162-3 22872506.
21. Kröger C, Dillon SC, Cameron AD, Papenfort K, Sivasankaran SK, Hokamp K, et al. The transcriptional landscape and small RNAs of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2012;109(20):E1277–86. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1201061109 22538806; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3356629.
22. Sharma CM, Hoffmann S, Darfeuille F, Reignier J, Findeiss S, Sittka A, et al. The primary transcriptome of the major human pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Nature. 2010;464(7286):250–5. Epub 2010/02/19. doi: nature08756 [pii] doi: 10.1038/nature08756 20164839.
23. Conway T, Creecy JP, Maddox SM, Grissom JE, Conkle TL, Shadid TM, et al. Unprecedented high-resolution view of bacterial operon architecture revealed by RNA sequencing. mBio. 2014;5(4). doi: 10.1128/mBio.01442-14 25006232.
24. Chakraborty S, Gogoi M, Chakravortty D. Lactoylglutathione lyase, a Critical Enzyme in Methylglyoxal Detoxification, Contributes to Survival of Salmonella in the Nutrient Rich Environment. Virulence. 2014 : 0. doi: 10.4161/21505594.2014.983791 25517857.
25. Sasikaran J, Ziemski M, Zadora PK, Fleig A, Berg IA. Bacterial itaconate degradation promotes pathogenicity. Nature chemical biology. 2014;10(5):371–7. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1482 24657929.
26. Rollenhagen C, Bumann D. Salmonella enterica highly expressed genes are disease specific. Infection and immunity. 2006;74(3):1649–60. doi: 10.1128/IAI.74.3.1649–1660.2006 16495536; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC1418657.
27. Figueira R, Holden DW. Functions of the Salmonella pathogenicity island 2 (SPI-2) type III secretion system effectors. Microbiology. 2012;158(Pt 5):1147–61. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.058115–0 22422755.
28. Beuzon CR, Banks G, Deiwick J, Hensel M, Holden DW. pH-dependent secretion of SseB, a product of the SPI-2 type III secretion system of Salmonella typhimurium. Molecular microbiology. 1999;33(4):806–16. 10447889.
29. Deiwick J, Nikolaus T, Erdogan S, Hensel M. Environmental regulation of Salmonella pathogenicity island 2 gene expression. Molecular microbiology. 1999;31(6):1759–73. 10209748.
30. Lober S, Jackel D, Kaiser N, Hensel M. Regulation of Salmonella pathogenicity island 2 genes by independent environmental signals. International journal of medical microbiology: IJMM. 2006;296(7):435–47. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2006.05.001 16904940.
31. Cirillo DM, Valdivia RH, Monack DM, Falkow S. Macrophage-dependent induction of the Salmonella pathogenicity island 2 type III secretion system and its role in intracellular survival. Molecular microbiology. 1998;30(1):175–88. 9786194.
32. Feng X, Oropeza R, Kenney LJ. Dual regulation by phospho-OmpR of ssrA/B gene expression in Salmonella pathogenicity island 2. Molecular microbiology. 2003;48(4):1131–43. 12753201.
33. Feng X, Walthers D, Oropeza R, Kenney LJ. The response regulator SsrB activates transcription and binds to a region overlapping OmpR binding sites at Salmonella pathogenicity island 2. Molecular microbiology. 2004;54(3):823–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04317.x 15491370.
34. Tomljenovic-Berube AM, Mulder DT, Whiteside MD, Brinkman FS, Coombes BK. Identification of the regulatory logic controlling Salmonella pathoadaptation by the SsrA-SsrB two-component system. PLoS genetics. 2010;6(3):e1000875. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000875 20300643; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2837388.
35. Richardson EJ, Limaye B, Inamdar H, Datta A, Manjari KS, Pullinger GD, et al. Genome sequences of Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium, Choleraesuis, Dublin, and Gallinarum strains of well - defined virulence in food-producing animals. Journal of bacteriology. 2011;193(12):3162–3. doi: 10.1128/JB.00394-11 21478351; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3133203.
36. Sabbagh SC, Lepage C, McClelland M, Daigle F. Selection of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi genes involved during interaction with human macrophages by screening of a transposon mutant library. PloS one. 2012;7(5):e36643. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036643 22574205; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3344905.
37. Chakraborty S, Chaudhuri D, Balakrishnan A, Chakravortty D. Salmonella methylglyoxal detoxification by STM3117-encoded lactoylglutathione lyase affects virulence in coordination with Salmonella pathogenicity island 2 and phagosomal acidification. Microbiology. 2014;160(Pt 9):1999–2017. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.078998–0 24961952.
38. Shah DH, Lee MJ, Park JH, Lee JH, Eo SK, Kwon JT, et al. Identification of Salmonella Gallinarum virulence genes in a chicken infection model using PCR-based signature-tagged mutagenesis. Microbiology. 2005;151(Pt 12):3957–68. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.28126–0 16339940.
39. Jha AK, Huang SC, Sergushichev A, Lampropoulou V, Ivanova Y, Loginicheva E, et al. Network Integration of Parallel Metabolic and Transcriptional Data Reveals Metabolic Modules that Regulate Macrophage Polarization. Immunity. 2015;42(3):419–30. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.02.005 25786174.
40. Blanc-Potard AB, Solomon F, Kayser J, Groisman EA. The SPI-3 pathogenicity island of Salmonella enterica. Journal of bacteriology. 1999;181(3):998–1004. 9922266; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC93469.
41. Lee EJ, Groisman EA. Control of a Salmonella virulence locus by an ATP-sensing leader messenger RNA. Nature. 2012;486(7402):271–5. doi: 10.1038/nature11090 22699622; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3711680.
42. Lee EJ, Pontes MH, Groisman EA. A bacterial virulence protein promotes pathogenicity by inhibiting the bacterium's own F1Fo ATP synthase. Cell. 2013;154(1):146–56. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.06.004 23827679; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC3736803.
43. Wood MW, Jones MA, Watson PR, Hedges S, Wallis TS, Galyov EE. Identification of a pathogenicity island required for Salmonella enteropathogenicity. Molecular microbiology. 1998;29(3):883–91. 9723926.
44. Knodler LA, Celli J, Hardt WD, Vallance BA, Yip C, Finlay BB. Salmonella effectors within a single pathogenicity island are differentially expressed and translocated by separate type III secretion systems. Molecular microbiology. 2002;43(5):1089–103. 11918798.
45. Knodler LA, Vallance BA, Hensel M, Jackel D, Finlay BB, Steele-Mortimer O. Salmonella type III effectors PipB and PipB2 are targeted to detergent-resistant microdomains on internal host cell membranes. Molecular microbiology. 2003;49(3):685–704. 12864852.
46. Knodler LA, Steele-Mortimer O. The Salmonella effector PipB2 affects late endosome/lysosome distribution to mediate Sif extension. Mol Biol Cell. 2005;16(9):4108–23. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E05-04-0367 15987736; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC1196323.
47. Blondel CJ, Jimenez JC, Contreras I, Santiviago CA. Comparative genomic analysis uncovers 3 novel loci encoding type six secretion systems differentially distributed in Salmonella serotypes. BMC genomics. 2009;10 : 354. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-354 19653904; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2907695.
48. Pezoa D, Yang HJ, Blondel CJ, Santiviago CA, Andrews-Polymenis HL, Contreras I. The type VI secretion system encoded in SPI-6 plays a role in gastrointestinal colonization and systemic spread of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium in the chicken. PloS one. 2013;8(5):e63917. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063917 23691117; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3653874.
49. Mulder DT, Cooper CA, Coombes BK. Type VI secretion system-associated gene clusters contribute to pathogenesis of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Infection and immunity. 2012;80(6):1996–2007. doi: 10.1128/IAI.06205-11 22493086; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3370595.
50. Brunet YR, Khodr A, Logger L, Aussel L, Mignot T, Rimsky S, et al. H-NS Silencing of the Salmonella Pathogenicity Island 6-Encoded Type VI Secretion System Limits Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Interbacterial Killing. Infection and immunity. 2015;83(7):2738–50. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00198-15 25916986.
51. Galan JE, Curtiss R 3rd. Cloning and molecular characterization of genes whose products allow Salmonella typhimurium to penetrate tissue culture cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1989;86(16):6383–7. 2548211; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC297844.
52. Watson PR, Galyov EE, Paulin SM, Jones PW, Wallis TS. Mutation of invH, but not stn, reduces Salmonella-induced enteritis in cattle. Infection and immunity. 1998;66(4):1432–8. 9529064; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC108071.
53. Tsolis RM, Adams LG, Ficht TA, Baumler AJ. Contribution of Salmonella typhimurium virulence factors to diarrheal disease in calves. Infection and immunity. 1999;67(9):4879–85. 10456944; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC96822.
54. Bustamante VH, Martinez LC, Santana FJ, Knodler LA, Steele-Mortimer O, Puente JL. HilD-mediated transcriptional cross-talk between SPI-1 and SPI-2. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2008;105(38):14591–6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0801205105 18799744; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2567235.
55. Ellermeier JR, Slauch JM. Adaptation to the host environment: regulation of the SPI1 type III secretion system in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Current opinion in microbiology. 2007;10(1):24–9. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2006.12.002 17208038.
56. Schechter LM, Damrauer SM, Lee CA. Two AraC/XylS family members can independently counteract the effect of repressing sequences upstream of the hilA promoter. Molecular microbiology. 1999;32(3):629–42. 10320584.
57. Ellermeier CD, Slauch JM. RtsA and RtsB Coordinately Regulate Expression of the Invasion and Flagellar Genes in Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium. Journal of bacteriology. 2003;185(17):5096–108. doi: 10.1128/jb.185.17.5096–5108.2003 12923082
58. Petrone BL, Stringer AM, Wade JT. Identification of HilD-Regulated Genes in Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium. Journal of bacteriology. 2014;196(5):1094–101. doi: 10.1128/JB.01449-13 24375101.
59. Gerlach RG, Jackel D, Stecher B, Wagner C, Lupas A, Hardt WD, et al. Salmonella Pathogenicity Island 4 encodes a giant non-fimbrial adhesin and the cognate type 1 secretion system. Cellular microbiology. 2007;9(7):1834–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2007.00919.x 17388786.
60. Wagner C, Barlag B, Gerlach RG, Deiwick J, Hensel M. The Salmonella enterica giant adhesin SiiE binds to polarized epithelial cells in a lectin-like manner. Cellular microbiology. 2014;16(6):962–75. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12253 24345213.
61. Gerlach RG, Claudio N, Rohde M, Jackel D, Wagner C, Hensel M. Cooperation of Salmonella pathogenicity islands 1 and 4 is required to breach epithelial barriers. Cellular microbiology. 2008;10(11):2364–76. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2008.01218.x 18671822.
62. La MV, Raoult D, Renesto P. Regulation of whole bacterial pathogen transcription within infected hosts. FEMS microbiology reviews. 2008;32(3):440–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2008.00103.x 18266740.
63. Allam US, Krishna MG, Sen M, Thomas R, Lahiri A, Gnanadhas DP, et al. Acidic pH induced STM1485 gene is essential for intracellular replication of Salmonella. Virulence. 2012;3(2):122–35. doi: 10.4161/viru.19029 22460643; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3396692.
64. Rathman M, Sjaastad MD, Falkow S. Acidification of phagosomes containing Salmonella Typhimurium in murine macrophages. Infection and immunity. 1996;64(7):2765–73. 8698506; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC174137.
65. Abu Kwaik Y, Bumann D. Host Delivery of Favorite Meals for Intracellular Pathogens. PLoS pathogens. 2015;11(6):e1004866. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004866 26110434; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4482385.
66. Steeb B, Claudi B, Burton NA, Tienz P, Schmidt A, Farhan H, et al. Parallel exploitation of diverse host nutrients enhances Salmonella virulence. PLoS pathogens. 2013;9(4):e1003301. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003301 23633950; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3636032.
67. Mastroeni P, Grant A, Restif O, Maskell D. A dynamic view of the spread and intracellular distribution of Salmonella enterica. Nature reviews Microbiology. 2009;7(1):73–80. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2034 19079353.
68. Nairz M, Haschka D, Demetz E, Weiss G. Iron at the interface of immunity and infection. Front Pharmacol. 2014;5 : 152. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2014.00152 25076907; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4100575.
69. Zaharik ML, Cullen VL, Fung AM, Libby SJ, Kujat Choy SL, Coburn B, et al. The Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium divalent cation transport systems MntH and SitABCD are essential for virulence in an Nramp1G169 murine typhoid model. Infection and immunity. 2004;72(9):5522–5. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.9.5522–5525.2004 15322058; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC517450.
70. Osman D, Cavet JS. Metal sensing in Salmonella: implications for pathogenesis. Advances in microbial physiology. 2011;58 : 175–232. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-381043-4.00005–2 21722794.
71. Faucher SP, Porwollik S, Dozois CM, McClelland M, Daigle F. Transcriptome of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi within macrophages revealed through the selective capture of transcribed sequences. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2006;103(6):1906–11. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0509183103 16443683; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC1413645.
72. Chilcott GS, Hughes KT. Coupling of flagellar gene expression to flagellar assembly in Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium and Escherichia coli. Microbiology and molecular biology reviews: MMBR. 2000;64(4):694–708. 11104815; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC99010.
73. Saini S, Slauch JM, Aldridge PD, Rao CV. Role of cross talk in regulating the dynamic expression of the flagellar Salmonella pathogenicity island 1 and type 1 fimbrial genes. Journal of bacteriology. 2010;192(21):5767–77. doi: 10.1128/JB.00624-10 20833811; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2953706.
74. Saini S, Brown JD, Aldridge PD, Rao CV. FliZ Is a posttranslational activator of FlhD4C2-dependent flagellar gene expression. Journal of bacteriology. 2008;190(14):4979–88. doi: 10.1128/JB.01996-07 18469103; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2447003.
75. Knodler LA, Vallance BA, Celli J, Winfree S, Hansen B, Montero M, et al. Dissemination of invasive Salmonella via bacterial-induced extrusion of mucosal epithelia. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2010;107(41):17733–8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1006098107 20876119; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2955089.
76. Hinton JC. The Escherichia coli genome sequence: the end of an era or the start of the FUN? Molecular microbiology. 1997;26(3):417–22. 9402013.
77. Strugnell RA, Scott TA, Wang N, Yang C, Peres N, Bedoui S, et al. Salmonella vaccines: lessons from the mouse model or bad teaching? Current opinion in microbiology. 2014;17 : 99–105. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2013.12.004 24440968.
78. Toussaint B, Chauchet X, Wang Y, Polack B, Le Gouellec A. Live-attenuated bacteria as a cancer vaccine vector. Expert review of vaccines. 2013;12(10):1139–54. doi: 10.1586/14760584.2013.836914 24124876.
79. Xu X, Husseiny MI, Goldwich A, Hensel M. Efficacy of intracellular activated promoters for generation of Salmonella-based vaccines. Infection and immunity. 2010;78(11):4828–38. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00298-10 20732994; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2976355.
80. McKelvie ND, Stratford R, Wu T, Bellaby T, Aldred E, Hughes NJ, et al. Expression of heterologous antigens in Salmonella Typhimurium vaccine vectors using the in vivo-inducible, SPI-2 promoter, ssaG. Vaccine. 2004;22(25–26):3243–55. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2004.05.014 15308346.
81. Brown NF, Vallance BA, Coombes BK, Valdez Y, Coburn BA, Finlay BB. Salmonella pathogenicity island 2 is expressed prior to penetrating the intestine. PLoS pathogens. 2005;1(3):e32. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0010032 16304611; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC1287911.
82. Osborne SE, Coombes BK. Transcriptional priming of Salmonella Pathogenicity Island-2 precedes cellular invasion. PloS one. 2011;6(6):e21648. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021648 21738750; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3125303.
83. Rollenhagen C, Sorensen M, Rizos K, Hurvitz R, Bumann D. Antigen selection based on expression levels during infection facilitates vaccine development for an intracellular pathogen. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2004;101(23):8739–44. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0401283101 15173591; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC423265.
84. Vogel J. A rough guide to the non-coding RNA world of Salmonella. Molecular microbiology. 2009;71(1):1–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06505.x 19007416.
85. Papenfort K, Vogel J. Small RNA functions in carbon metabolism and virulence of enteric pathogens. Frontiers in cellular and infection microbiology. 2014;4 : 91. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00091 25077072; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4098024.
86. Papenfort K, Vogel J. Regulatory RNA in bacterial pathogens. Cell host & microbe. 2010;8(1):116–27. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2010.06.008 20638647.
87. Storz G, Vogel J, Wassarman KM. Regulation by small RNAs in bacteria: expanding frontiers. Molecular cell. 2011;43(6):880–91. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.08.022 21925377; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3176440.
88. Caldelari I, Chao Y, Romby P, Vogel J. RNA-mediated regulation in pathogenic bacteria. Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in medicine. 2013;3(9):a010298. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a010298 24003243.
89. Vogel J, Luisi BF. Hfq and its constellation of RNA. Nature reviews Microbiology. 2011;9(8):578–89. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2615 21760622.
90. Papenfort K, Pfeiffer V, Mika F, Lucchini S, Hinton JCD, Vogel J. σE-dependent small RNAs of Salmonella respond to membrane stress by accelerating global omp mRNA decay. Molecular microbiology. 2006;62(6):1674–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05524.x 17427289
91. Humphreys S, Stevenson A, Bacon A, Weinhardt AB, Roberts M. The alternative sigma factor, sigmaE, is critically important for the virulence of Salmonella Typhimurium. Infection and immunity. 1999;67(4):1560–8. 10084987; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC96497.
92. Guo MS, Updegrove TB, Gogol EB, Shabalina SA, Gross CA, Storz G. MicL, a new sigmaE-dependent sRNA, combats envelope stress by repressing synthesis of Lpp, the major outer membrane lipoprotein. Genes & development. 2014;28(14):1620–34. doi: 10.1101/gad.243485.114 25030700; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4102768.
93. Padalon-Brauch G, Hershberg R, Elgrably-Weiss M, Baruch K, Rosenshine I, Margalit H, et al. Small RNAs encoded within genetic islands of Salmonella Typhimurium show host-induced expression and role in virulence. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36(6):1913–27. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn050 18267966; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2330248.
94. Calderon IL, Morales EH, Collao B, Calderon PF, Chahuan CA, Acuna LG, et al. Role of Salmonella Typhimurium small RNAs RyhB-1 and RyhB-2 in the oxidative stress response. Res Microbiol. 2014;165(1):30–40. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2013.10.008 24239962.
95. Leclerc JM, Dozois CM, Daigle F. Role of the Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi Fur regulator and small RNAs RfrA and RfrB in iron homeostasis and interaction with host cells. Microbiology. 2013;159(Pt 3):591–602. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.064329–0 23306672.
96. Ortega AD, Gonzalo-Asensio J, Garcia-del Portillo F. Dynamics of Salmonella small RNA expression in non-growing bacteria located inside eukaryotic cells. RNA biology. 2012;9(4):469–88. doi: 10.4161/rna.19317 22336761.
97. Hoiseth SK, Stocker BA. Aromatic-dependent Salmonella Typhimurium are non-virulent and effective as live vaccines. Nature. 1981;291(5812):238–9. 7015147.
98. Tedin K, Blasi U. The RNA chain elongation rate of the lambda late mRNA is unaffected by high levels of ppGpp in the absence of amino acid starvation. The Journal of biological chemistry. 1996;271(30):17675–86. 8663373.
99. Hinton JC, Hautefort I, Eriksson S, Thompson A, Rhen M. Benefits and pitfalls of using microarrays to monitor bacterial gene expression during infection. Current opinion in microbiology. 2004;7(3):277–82. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2004.04.009 15196496.
100. Hoffmann S, Otto C, Kurtz S, Sharma CM, Khaitovich P, Vogel J, et al. Fast mapping of short sequences with mismatches, insertions and deletions using index structures. PLoS computational biology. 2009;5(9):e1000502. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000502 19750212; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2730575.
101. Nicol JW, Helt GA, Blanchard SG Jr., Raja A, Loraine AE. The Integrated Genome Browser: free software for distribution and exploration of genome-scale datasets. Bioinformatics. 2009;25(20):2730–1. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp472 19654113; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2759552.
102. Skinner ME, Uzilov AV, Stein LD, Mungall CJ, Holmes IH. JBrowse: a next-generation genome browser. Genome research. 2009;19(9):1630–8. doi: 10.1101/gr.094607.109 19570905; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2752129.
103. Wagner GP, Kin K, Lynch VJ. A model based criterion for gene expression calls using RNA-seq data. Theory in biosciences = Theorie in den Biowissenschaften. 2013;132(3):159–64. doi: 10.1007/s12064-013-0178-3 23615947.
104. Li B, Ruotti V, Stewart RM, Thomson JA, Dewey CN. RNA-Seq gene expression estimation with read mapping uncertainty. Bioinformatics. 2010;26(4):493–500. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp692 20022975; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2820677.
105. Argaman L, Hershberg R, Vogel J, Bejerano G, Wagner EG, Margalit H, et al. Novel small RNA-encoding genes in the intergenic regions of Escherichia coli. Current biology: CB. 2001;11(12):941–50. 11448770.
106. Pearson WR, Lipman DJ. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1988;85(8):2444–8. 3162770; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC280013.
107. Walthers D, Carroll RK, Navarre WW, Libby SJ, Fang FC, Kenney LJ. The response regulator SsrB activates expression of diverse Salmonella pathogenicity island 2 promoters and counters silencing by the nucleoid-associated protein H-NS. Molecular microbiology. 2007;65(2):477–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.05800.x 17630976.
108. Kidwai AS, Mushamiri I, Niemann GS, Brown RN, Adkins JN, Heffron F. Diverse secreted effectors are required for Salmonella persistence in a mouse infection model. PloS one. 2013;8(8):e70753. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070753 23950998; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3741292.
109. Chao Y, Papenfort K, Reinhardt R, Sharma CM, Vogel J. An atlas of Hfq-bound transcripts reveals 3' UTRs as a genomic reservoir of regulatory small RNAs. EMBO J. 2012;31(20):4005–19. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.229 22922465; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3474919.
Štítky
Hygiena a epidemiológia Infekčné lekárstvo Laboratórium
Článek Increased Susceptibility of Humanized NSG Mice to Panton-Valentine Leukocidin and Skin InfectionČlánek Phosphorylation of a Myosin Motor by TgCDPK3 Facilitates Rapid Initiation of Motility during egress
Článok vyšiel v časopisePLOS Pathogens
Najčítanejšie tento týždeň
2015 Číslo 11- Parazitičtí červi v terapii Crohnovy choroby a dalších zánětlivých autoimunitních onemocnění
- Očkování proti virové hemoragické horečce Ebola experimentální vakcínou rVSVDG-ZEBOV-GP
- Koronavirus hýbe světem: Víte jak se chránit a jak postupovat v případě podezření?
-
Všetky články tohto čísla
- Parasite Glycobiology: A Bittersweet Symphony
- On the Discovery of TOR As the Target of Rapamycin
- Broadening of Virus-Specific CD8 T-Cell Responses Is Indicative of Residual Viral Replication in Aviremic SIV Controllers
- PML/TRIM19-Dependent Inhibition of Retroviral Reverse-Transcription by Daxx
- Cleavage of a Neuroinvasive Human Respiratory Virus Spike Glycoprotein by Proprotein Convertases Modulates Neurovirulence and Virus Spread within the Central Nervous System
- Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus (KSHV) Induces the Oncogenic miR-17-92 Cluster and Down-Regulates TGF-β Signaling
- Interferon-α Subtypes in an Model of Acute HIV-1 Infection: Expression, Potency and Effector Mechanisms
- Perivascular Arrest of CD8 T Cells Is a Signature of Experimental Cerebral Malaria
- Targeting HIV Reservoir in Infected CD4 T Cells by Dual-Affinity Re-targeting Molecules (DARTs) that Bind HIV Envelope and Recruit Cytotoxic T Cells
- Evolution and Emergence of Enteroviruses through Intra- and Inter-species Recombination: Plasticity and Phenotypic Impact of Modular Genetic Exchanges in the 5’ Untranslated Region
- Interferon-γ Inhibits Ebola Virus Infection
- Dengue Virus Non-structural Protein 1 Modulates Infectious Particle Production via Interaction with the Structural Proteins
- P-Type Cyclin CYC3 Modulates Endomitotic Growth during Oocyst Development in Mosquitoes
- Diversity of across Evolutionary Scales
- 50 Years of Disease in Humans: The Dramatic Emergence of a Cluster of Novel Fungal Pathogens
- Worse Comes to Worst: Bananas and Panama Disease—When Plant and Pathogen Clones Meet
- Arenavirus Glycan Shield Promotes Neutralizing Antibody Evasion and Protracted Infection
- Infection-Induced Retrotransposon-Derived Noncoding RNAs Enhance Herpesviral Gene Expression via the NF-κB Pathway
- Structural Insight into Archaic and Alternative Chaperone-Usher Pathways Reveals a Novel Mechanism of Pilus Biogenesis
- Increased Susceptibility of Humanized NSG Mice to Panton-Valentine Leukocidin and Skin Infection
- Global Analysis of the Fungal Microbiome in Cystic Fibrosis Patients Reveals Loss of Function of the Transcriptional Repressor Nrg1 as a Mechanism of Pathogen Adaptation
- The Transcription and Translation Landscapes during Human Cytomegalovirus Infection Reveal Novel Host-Pathogen Interactions
- The N-terminal Helical Region of the Hepatitis C Virus p7 Ion Channel Protein Is Critical for Infectious Virus Production
- Activation of Type I and III Interferon Response by Mitochondrial and Peroxisomal MAVS and Inhibition by Hepatitis C Virus
- Hsp70 Isoforms Are Essential for the Formation of Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Replication and Transcription Compartments
- Distinct Upstream Role of Type I IFN Signaling in Hematopoietic Stem Cell-Derived and Epithelial Resident Cells for Concerted Recruitment of Ly-6C Monocytes and NK Cells via CCL2-CCL3 Cascade
- and Bats: Story of an Emerging Friendship
- Emergence of Pathogenicity in Lagoviruses: Evolution from Pre-existing Nonpathogenic Strains or through a Species Jump?
- Ebolavirus Evolution: Past and Present
- Host and Symbiont Jointly Control Gut Microbiota during Complete Metamorphosis
- Non-Human Primates Harbor Diverse Mammalian and Avian Astroviruses Including Those Associated with Human Infections
- Lactate Dehydrogenase Is Associated with the Parasitophorous Vacuole Membrane and Is a Potential Target for Developing Therapeutics
- Five Questions about Mycoviruses
- Phosphorylation of a Myosin Motor by TgCDPK3 Facilitates Rapid Initiation of Motility during egress
- Ethanolamine Signaling Promotes Niche Recognition and Adaptation during Infection
- Cross-Species Transmission and Differential Fate of an Endogenous Retrovirus in Three Mammal Lineages
- Memory Th1 Cells Are Protective in Invasive Infection
- Transcription Factor SomA Is Required for Adhesion, Development and Virulence of the Human Pathogen
- An -Methyltransferase Is Required for Infection of Tick Cells by
- RNA-seq Brings New Insights to the Intra-Macrophage Transcriptome of Typhimurium
- PLOS Pathogens
- Archív čísel
- Aktuálne číslo
- Informácie o časopise
Najčítanejšie v tomto čísle- Dengue Virus Non-structural Protein 1 Modulates Infectious Particle Production via Interaction with the Structural Proteins
- On the Discovery of TOR As the Target of Rapamycin
- Parasite Glycobiology: A Bittersweet Symphony
- Broadening of Virus-Specific CD8 T-Cell Responses Is Indicative of Residual Viral Replication in Aviremic SIV Controllers
Prihlásenie#ADS_BOTTOM_SCRIPTS#Zabudnuté hesloZadajte e-mailovú adresu, s ktorou ste vytvárali účet. Budú Vám na ňu zasielané informácie k nastaveniu nového hesla.
- Časopisy



