-
Články
- Časopisy
- Kurzy
- Témy
- Kongresy
- Videa
- Podcasty
Two Coregulated Efflux Transporters Modulate Intracellular Heme and Protoporphyrin IX Availability in
Streptococcus agalactiae is a major neonatal pathogen whose infectious route involves septicemia. This pathogen does not synthesize heme, but scavenges it from blood to activate a respiration metabolism, which increases bacterial cell density and is required for full virulence. Factors that regulate heme pools in S. agalactiae are unknown. Here we report that one main strategy of heme and protoporphyrin IX (PPIX) homeostasis in S. agalactiae is based on a regulated system of efflux using two newly characterized operons, gbs1753 gbs1752 (called pefA pefB), and gbs1402 gbs1401 gbs1400 (called pefR pefC pefD), where pef stands for ‘porphyrin-regulated efflux’. In vitro and in vivo data show that PefR, a MarR-superfamily protein, is a repressor of both operons. Heme or PPIX both alleviate PefR-mediated repression. We show that bacteria inactivated for both Pef efflux systems display accrued sensitivity to these porphyrins, and give evidence that they accumulate intracellularly. The ΔpefR mutant, in which both pef operons are up-regulated, is defective for heme-dependent respiration, and attenuated for virulence. We conclude that this new efflux regulon controls intracellular heme and PPIX availability in S. agalactiae, and is needed for its capacity to undergo respiration metabolism, and to infect the host.
Published in the journal: Two Coregulated Efflux Transporters Modulate Intracellular Heme and Protoporphyrin IX Availability in. PLoS Pathog 6(4): e32767. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1000860
Category: Research Article
doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1000860Summary
Streptococcus agalactiae is a major neonatal pathogen whose infectious route involves septicemia. This pathogen does not synthesize heme, but scavenges it from blood to activate a respiration metabolism, which increases bacterial cell density and is required for full virulence. Factors that regulate heme pools in S. agalactiae are unknown. Here we report that one main strategy of heme and protoporphyrin IX (PPIX) homeostasis in S. agalactiae is based on a regulated system of efflux using two newly characterized operons, gbs1753 gbs1752 (called pefA pefB), and gbs1402 gbs1401 gbs1400 (called pefR pefC pefD), where pef stands for ‘porphyrin-regulated efflux’. In vitro and in vivo data show that PefR, a MarR-superfamily protein, is a repressor of both operons. Heme or PPIX both alleviate PefR-mediated repression. We show that bacteria inactivated for both Pef efflux systems display accrued sensitivity to these porphyrins, and give evidence that they accumulate intracellularly. The ΔpefR mutant, in which both pef operons are up-regulated, is defective for heme-dependent respiration, and attenuated for virulence. We conclude that this new efflux regulon controls intracellular heme and PPIX availability in S. agalactiae, and is needed for its capacity to undergo respiration metabolism, and to infect the host.
Introduction
Heme (iron protoporphyrin IX) is a redox-active molecule, and a cofactor for numerous cell functions used in oxygen sensing and signal transmission, metabolism, and metal homeostasis [1][–][3]. In addition to its varied activities as a cofactor, heme promotes toxic oxygen radical production [4]. The duality between heme as a multifunctional cofactor, and a potentially toxic molecule, suggests the need for strict limitation of its intracellular levels. Metal-free protoporphyrin IX (PPIX) is also found intracellularly, as a heme precursor in bacteria that synthesize heme, and as an intermediate during iron recovery from heme, as shown in Escherichia coli [5]. Thus, cells might have to deal with both heme and PPIX intracellular pools.
While most studied organisms synthesize heme to ensure activity of hemoproteins under the appropriate conditions, numerous bacteria lack heme biosynthesis genes, making heme-catalyzed processes fully dependent upon external heme supplies. For example, Haemophilus influenzae, Bacteroides sp., and several Firmicutes, including Lactococcus lactis, Enterococcus faecalis, Streptococcus agalactiae, and numerous Lactobacillus sp., require heme to activate a respiration metabolic pathway [6][18]. Some of these bacteria (e.g., H. influenzae, E. faecalis, Bacteroides sp., Lactobacillus brevis and Lactobacillus plantarum) also encode heme-dependent catalases, which rely on exogenous heme for both their stability and activity [19]. Thus, heme supplied by the environment can have a determining effect on the metabolic and enzymatic capacities in organisms lacking the heme biosynthetic pathway.
All bacteria, regardless of their heme biosynthesis capacities, need to manage their intracellular heme pools. Regulation may be exerted at the levels of biosynthesis, uptake, degradation, and possibly efflux, which is in some cases coordinated with the cell iron status [20][25]. The use of efflux as a means of heme homeostasis remains in question. The sole candidate, HrtAB, a heme-regulated transporter, was first reported as having a role in heme toxicity in Staphylococcus aureus; orthologs of this system were also described in L. lactis and Bacillus anthracis [12], [26][–][28]. HrtAB in S. aureus, B. anthracis, and likely several Gram-positive pathogens responds to an extracytoplasmic heme sensor, HssS (part of HssSR two-component system) to activate expression [27], [28].
S. agalactiae is an important human pathogen that does not synthesize its own heme. Nevertheless, infection by this bacterium involves compulsory passage through the bloodstream, causing septicemia and subsequent meningitis [29], [30]. We showed previously that although S. agalactiae generally grows by a fermentation metabolism, it can also use heme, present in blood, to activate the terminal cytochrome bd quinol oxidase for respiration metabolism. Thus, beyond the potential use of heme uptake to acquire iron, the use of heme to activate the energetically favorable respiration metabolism confers a significant gain in cell density, and is required for full bacterial virulence in a septicemia model [17], [18].
Despite the importance of growth in heme-rich blood as an initial step of S. agalactiae infection, the functions involved in regulating intracellular heme levels are unknown. Homologs of HrtAB and HssSR exist in S. agalactiae, and might participate in modulating heme toxicity upon sensing of extracellular heme. However, the mechanism by which HrtAB modulates heme toxicity is unknown, and the question remains whether other systems are needed to regulate heme pools. Here we report the existence of a novel regulon comprising two efflux operons and a single repressor that senses intracellular heme and PPIX, and is needed to maintain their homeostasis. This newly described system is shown to impact on S. agalactiae respiration capacity and virulence.
Results
Identification of gbs1753 gbs1752 as a putative heme - and PPIX - induced locus in S. agalactiae
Transcriptome studies, comparing S. agalactiae gene expression under respiration (i.e., aerobic growth in the presence of exogenous heme and menaquinone) versus aerobic fermentation (i.e., no addition) conditions, initially revealed that gbs1753 gbs1752 was 2.4 to 5.1 fold higher under respiration conditions (AD, PG, EC, and P. Glaser [Pasteur Institute]; Table S1). The gbs1753 ORF encodes an integral membrane protein of the drug:H+ antiporter family, belonging to the major facilitator superfamily (MFS) [31]. The gbs1752 ORF encodes an unknown protein with 2 transmembrane domains. We chose this locus for study, as it was conserved among Gram-positive bacteria that lack a complete heme biosynthesis pathway, but encode cytochrome bd quinol oxidases, indicating a capacity for respiration metabolism (Fig. 1 and Table S2).
Fig. 1. Genetic context of two loci for which expression is heme-induced. 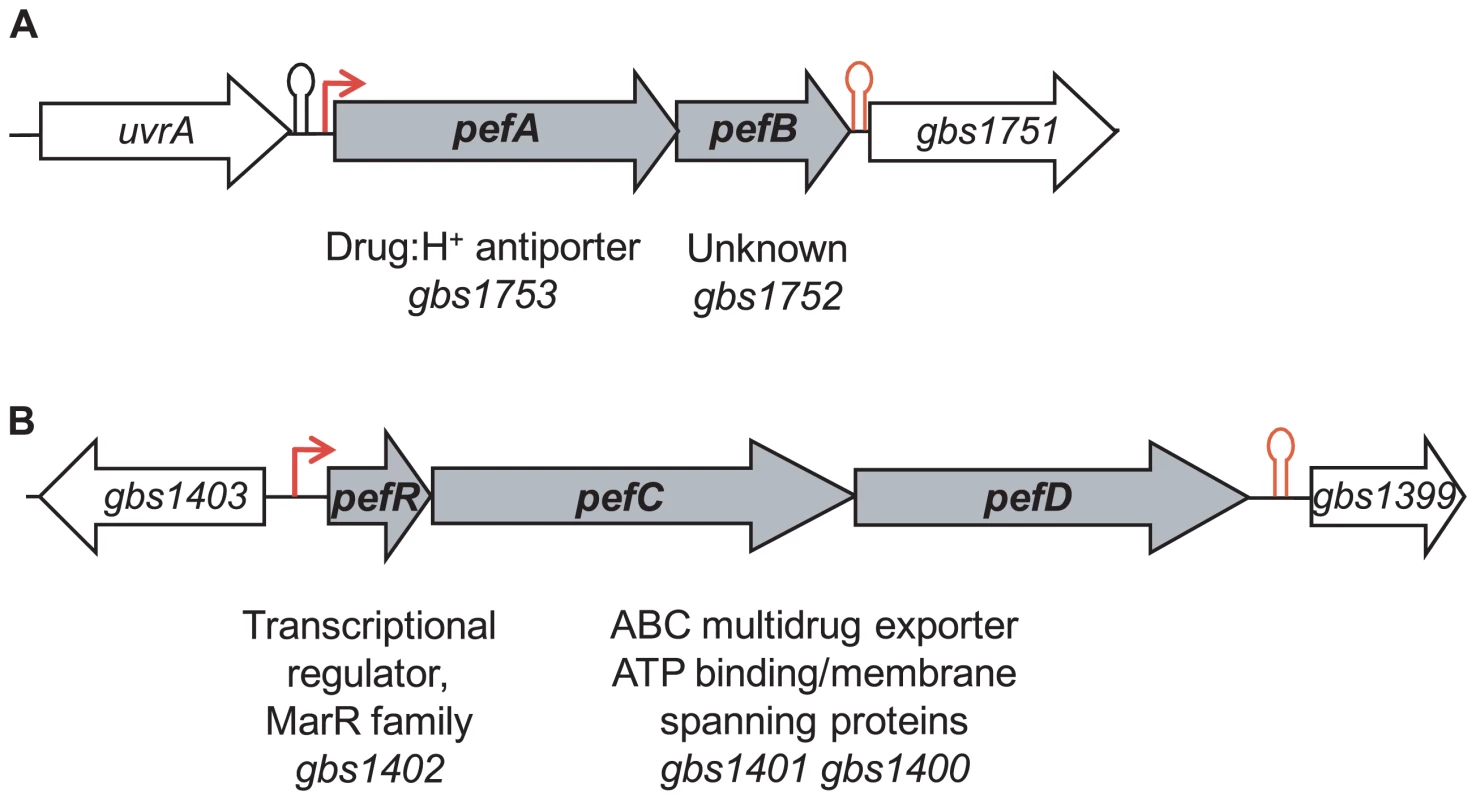
A, gbs1753 gbs1752 (pefA pefB) and B, gbs1402 gbs1401 gbs1400 (pefR pefC pefD) loci. Bent arrows and lollipops indicate the mapped or putative promoters, and rho-independent terminators, respectively. The +1 transcriptional start of gbs1753 gbs1752 was located by 5′-RACE PCR mapping at 134 nucleotides upstream of the gbs1753 start codon at a cytosine (Fig. 2A). The gbs1753 promoter region was fused to a lacZ reporter, referred to as Pgbs1753-lacZ, and expressed on a low copy number plasmid (Fig. 2A) [32]. In the absence of added heme, Pgbs1753-lacZ displayed basal level expression in static and aerobic growth conditions (possibly reflecting trace amounts of heme in BHI medium). Cultures grown with added heme (from 0.1 µM to 10 µM) displayed up to 9-fold higher Pgbs1753-lacZ expression compared to controls without heme, even in non-respiration-permissive conditions (Fig. 2B), indicating that heme, and not the state of respiration, was the inducing factor for the gbs1753 promoter. Significant Pgbs1753-lacZ induction was observed at heme concentrations of 0.3 µM and above. Similarly, PPIX, gallium protoporphyrin (GaPPIX), and zinc mesoporphyrin (ZnMPIX) also induced Pgbs1753-lacZ, while free iron had no inducing effect. These initial results indicate that gbs1753 expression is induced by different porphyrin molecules, regardless of their metal core status.
Fig. 2. The pefAB locus is induced by porphyrin molecules: heme, PPIX, GaPPIX and ZnMPIX. 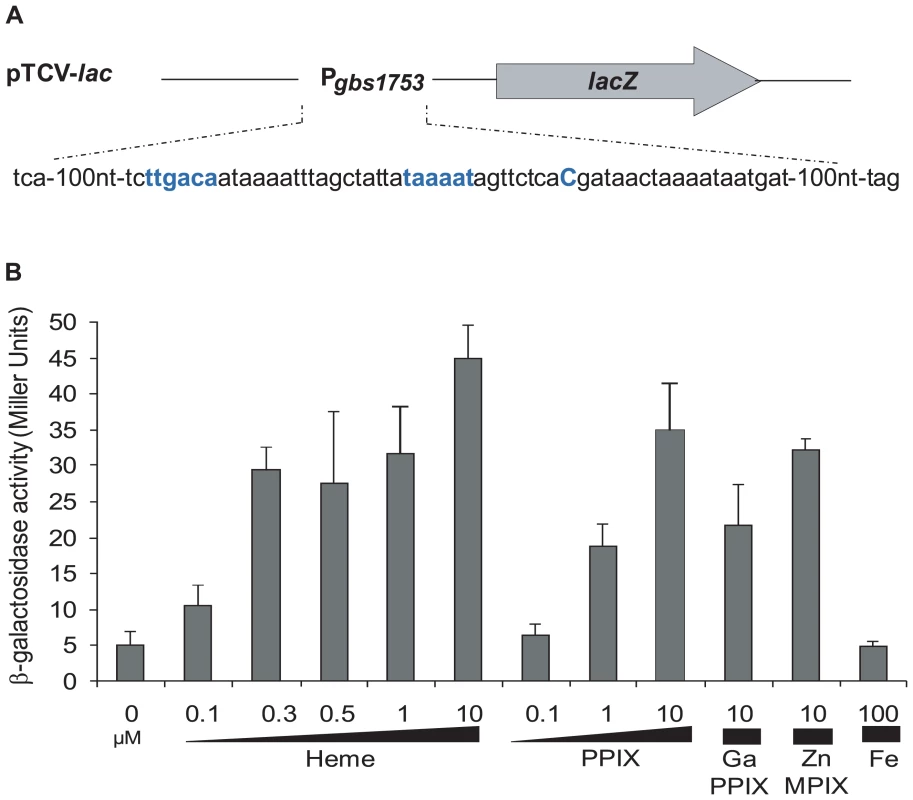
A. Schematic map of the transcriptional fusion PpefA-lacZ (same as Pgbs1753-lacZ). Sequence of the pefAB promoter region is displayed. The +1 transcriptional start and −10 and −35 motifs are in bold blue characters. B. Expression analysis of PpefA-lacZ by determination of β-galactosidase activity in early stationary phase. S. agalactiae was grown in BHI liquid medium in the presence of the indicated amount of candidate inducers. Strains harboring the pTCV-lac vector (promoterless negative control) did not show β-galactosidase activity during growth (0.4±0.1 Miller Units). Measurements were performed at least three times. Identification of Gbs1402 as a putative regulator of gbs1753 gbs1752 expression
A random mutagenesis approach was used to identify genetic factors that affect gbs1753 gbs1752 expression. A transposon-generated mutant library was screened for clones in which expression of the Pgbs1753-lacZ fusion was up-regulated, as detected by deep blue colony color. Several mutations mapped in a single ORF, gbs1402. The gbs1402 gene encodes a multiple antibiotic resistance MarR-like regulator (for review see [33]), and is located just upstream of gbs1401 gbs1400, encoding a putative ABC-type multidrug transport complex (Fig. 1B). Sequence analysis predicted that the Gbs1401 and Gbs1400 proteins both contain a transmembrane domain and an ATPase signature. These observations led us to formulate a working hypothesis that both gbs1753 gbs1752 and gbs1401 gbs1400 loci are involved in PPIX and metalloporphyrin efflux, and are regulated by a single protein, Gbs1402. The genes were renamed as pef genes, for porphyrin-regulated efflux. gbs1753 gbs1752 are renamed pefA pefB; gbs1401 gbs1400 are renamed pefC pefD; and the gbs1402 gene for the potential regulator is renamed pefR (Fig. 1).
PefR binds specifically to pefAB and pefRCD promoter regions and represses their transcription
Proteins of the MarR family characteristically bind to DNA inverted repeat motifs (IR) [33]. Sequence analysis revealed the presence of a near-perfect 18-nucleotide IR within a 23 bp consensus, (5′-TAAAATAGTTCTCACGATAACTA-3′) present once upstream of pefA pefB, and twice (one identical sequence, and one inexact copy with 3 nucleotide substitutions in italics) upstream of pefR pefC pefD (Fig. 3A). The IR is not present elsewhere on the S. agalactiae genome. This 23-nucleotide sequence contains the −10 region (TAAAAT) of a putative promoter and constituted a candidate target site for PefR binding to pefAB and pefRCD promoter regions. Mobility shift assays were performed using a purified PefR His-fusion protein, in combination with DNA fragments comprising the IRs of pefAB or pefRCD promoter regions, plus a fragment without an IR as negative internal control (Fig. 3B). PefR caused a mobility shift of both the pefAB and pefRCD fragments in a protein concentration-dependent manner. No shift was observed with the control DNA fragment.
Fig. 3. PefR is a repressor of pefAB and pefRCD loci. 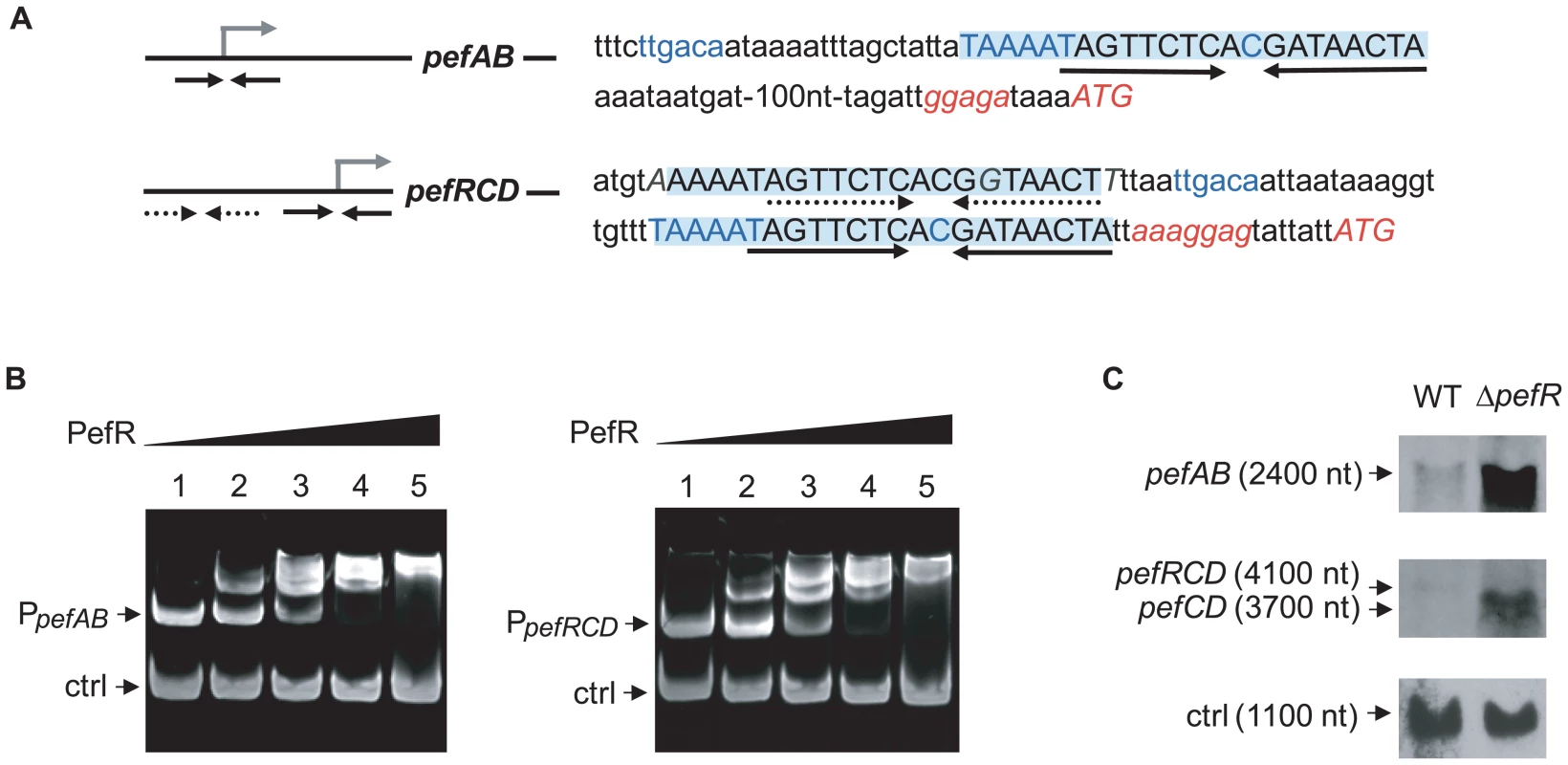
A. A conserved 23-nucleotide motif is present once upstream of pefAB, and twice upstream of pefRCD and is highlighted. The IR present in each of the motifs is marked by arrows. The −10 and −35 motifs, and the mRNA pefAB and putative pefRCD start sites are in blue. Start codons and RBS sequence are in italics. One motif upstream of pefRCD (dotted arrows) differs from the other motifs by 3 nucleotides, which are in gray italics. B. PefR binds the pefAB and pefRCD promoter regions in gel shift assays. Two pmoles of pefAB or pefRCD promoter fragment were incubated in the presence of 0, 4, 17, 34, 63 pmoles of PefR (lanes 1 to 5) and 4.6 pmoles control fragment, corresponding to an 116-bp fragment of the pefA gene. C. Northern blot analyses of pefAB and pefRCD mRNA in the WT and pefR strains, using locus-specific probes (see Materials and Methods). As probe efficiencies and times of exposure differ for each target RNA, differences between pefAB and pefRCD levels are not comparable. ldhL mRNA (‘ctrl’) was used to control for RNA quantity. To determine whether PefR impacts on pefA pefB and pefR pefC pefD expression in vivo, Northern blot experiments were performed on the WT strain and an in-frame ΔpefR mutant, using pefAB and pefC as probes (Fig. 3C). The deduced transcript sizes were compatible with organization of the pefA and pefB genes as one operon, and of pefR, pefC, and pefD genes as another. Compared to the WT strain, expression of both pefAB and pefRCD operons was strongly increased in the ΔpefR mutant. We also evaluated expression of the PpefA-lacZ transcriptional fusion in the WT and ΔpefR mutant strains. β-galactosidase expression in the ΔpefR background was 12 times higher than in the WT strain (Miller Units were 62.9±9.2 in ΔpefR versus 5.1±1.7 in the WT strain).
The above in vitro and in vivo results indicate that PefR is a transcriptional repressor of both the pefAB and the pefRCD operons, by binding directly to the operator regions.
PefR is an intracellular heme and PPIX sensor and regulator of pef expression
A characteristic of MarR family regulators is their binding to effector molecules, which leads to induction or repression of their target genes [34]–[36]. Transcriptional fusions showed that the pefAB operon was induced in the presence of metalloporphyrins or PPIX (Fig. 2B). As PefR binds the two pef promoter regions, and appears to repress transcription, we hypothesized that PefR binding and repression are modulated by heme and PPIX. To test this in vitro, mobility shift assays between PefR and the pefAB or pefRCD promoter region DNA fragments were performed with and without heme or PPIX. For both DNA targets, PefR–DNA binding was alleviated in a heme or PPIX concentration-dependent manner (Fig. 4A, Fig. S1A). Iron had no effect on PefR-DNA binding (Fig. S1B).
Fig. 4. PefR is a heme- and PPIX-modulated repressor of pefAB and pefRCD loci. 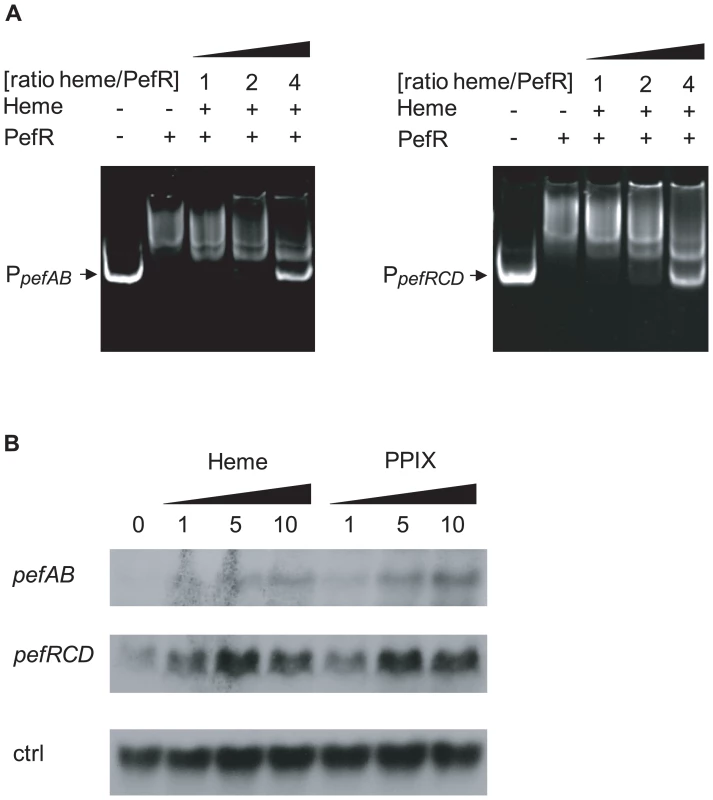
A. Gel mobility shift analysis of the effect of heme on PefR binding to pefAB (right) and pefRCD (left) promoter regions. 2 pmoles of PpefAB or PpefRCD fragments and 30 pmoles of PefR were mixed. Increased concentrations of heme were added in ratios indicated (keeping PefR constant). Assays were also performed with PPIX (Fig. S1A), giving similar results. On the two top panels, lanes 1–3 were juxtaposed to lanes 4–5, which were separated on the initial same gel. B. Northern blot analyses of pefAB and pefRCD expression in the presence of heme or PPIX in WT NEM316. Cultures were grown in the presence of 0, 1, 5 and 10 µM heme or PPIX, and harvested for total RNA extraction in early stationary phase. As probe efficiencies and times of exposure differ for each target RNA, differences between pefAB and pefRCD levels are not comparable. ldhL (gbs0947; ‘ctrl’) mRNA was used to control for RNA quantities. Transcriptional fusion data showed that heme and PPIX up-regulate pefAB expression. To further confirm these results, we performed Northern blot experiments in the absence and presence of these molecules, using pefAB and pefC DNA as probes. Both heme and PPIX induced expression of the two pef operons (Fig. 4B). These in vivo results are in keeping with in vitro gel shift data showing that PefR repression is alleviated in the presence of these porphyrins. We conclude that heme and PPIX both modulate PefR repression of the pefAB and pefRCD operons.
Expression of hrtAB as a function of heme and PPIX levels in S. agalactiae
Genomic studies of S. agalactiae revealed the existence of an analog of HrtAB, a heme-regulated transport system initially characterized in S. aureus and shown to be involved in heme toxicity [37]. Gbs0119 and Gbs0120 showed 45% and 29% identity with HrtB and HrtA of S. aureus respectively. We used Northern blot experiments (Fig. 5A) and a lacZ promoter fusion, Pgbs0119-lacZ (Fig. 5B), to assess the heme and PPIX concentrations needed to induce the hrtAB locus. Interestingly, hrtAB expression was low at heme concentrations below 1 µM, with strong induction at 10 µM; PPIX did not induce its expression, as was observed in S. aureus. Importantly, no hrtAB induction was observed at heme levels where pefAB was induced, i.e., between 0.1 and 0.5 µM heme (Fig. 2B). We conclude that the pef regulon is induced at heme concentrations below those needed for hrtAB induction, indicating that these functions are active under different conditions.
Fig. 5. The hrtAB locus is induced by higher heme concentrations than pefAB or pefRCD, and is not induced by PPIX. 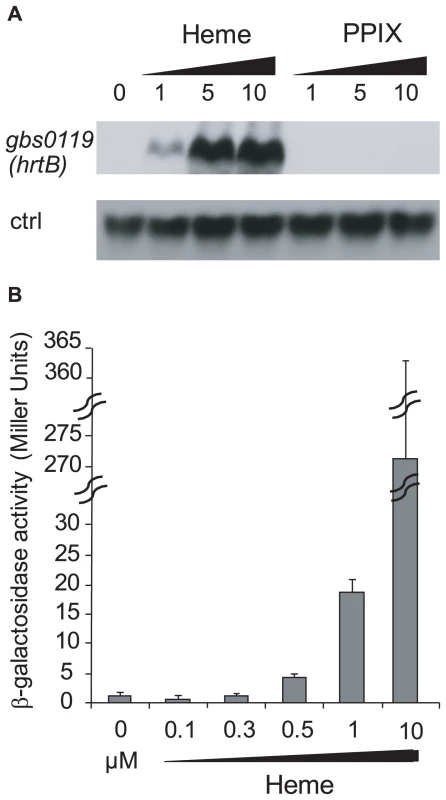
A. Northern blot analyses of gbs0119 expression in the presence of heme or PPIX in WT NEM316. Cultures were grown in the presence of 0, 1, 5 and 10 µM heme or PPIX, and harvested for total RNA extraction in early stationary phase. ldhL (gbs0947; ‘crtl’) mRNA was used as RNA quantity control. The hybridization was performed on the same membrane as that used in Fig. 4B. B. Expression analysis of Pgbs0119-lacZ by determination of β-galactosidase activity in early stationary phase. S. agalactiae was grown in BHI liquid medium in the presence of different heme concentrations. Measurements were performed three or more times. Role of pefAB and pefRCD operons in porphyrin sensitivity
The above results led us to ask whether pefAB and pefRCD loci are involved in porphyrin efflux. Several in vivo approaches were developed to explore this question. We constructed in-frame pefA (encoding a putative drug:H+ antiporter) and pefB (encoding a membrane protein of unknown function) deletion mutants; as the two components of pefCD are predicted to encode a single ATP-dependent transporter, we generated a deletion removing both ORFs. Mutations were combined to inactivate both pef operons. Tests were also performed with the ΔpefR deletion mutant, in which expression of both pef loci were highly induced (Fig. 3C).
Sensitivity of ΔpefR, ΔpefA ΔpefCD, and ΔpefB ΔpefCD mutants to metalloporphyrins was evaluated by plate inhibition tests (Fig. S2). Both ΔpefA ΔpefCD and ΔpefB ΔpefCD mutants showed greater sensitivity than the WT strain to 1 nmole heme (Fig. S2A). Similar results were obtained using Gallium PPIX (GaPPIX; tested at 50 nmoles, Fig. S2B). We noted that ΔpefA ΔpefCD was more sensitive than ΔpefB ΔpefCD; this phenotypic difference might suggest an accessory role of PefB in PefA PefB function. The single ΔpefA, ΔpefB, ΔpefC or ΔpefD mutants gave little or no inhibition by these porphyrins (data not shown), suggesting a functional redundancy between the efflux systems encoded by these loci. Sensitivity of the ΔpefR mutant to heme and GaPPIX did not differ significantly from the WT. We further tested heme-mediated inhibition in liquid medium by growing WT and pef single and double mutants, and the ΔpefR mutant, in 0 or 1 µM heme (Fig. 6A and data not shown). The ΔpefA ΔpefCD and ΔpefB ΔpefCD mutants, but not the other tested strains, displayed a slight growth inhibition in the presence of heme. Addition of 2 µM or 4 µM heme exacerbates growth retardation of these mutants (data not shown). These results indicate the need for at least one of the Pef efflux systems to avoid heme toxicity.
Fig. 6. ΔpefAB and ΔpefCD mutants are affected in PPIX and heme sensitivity. 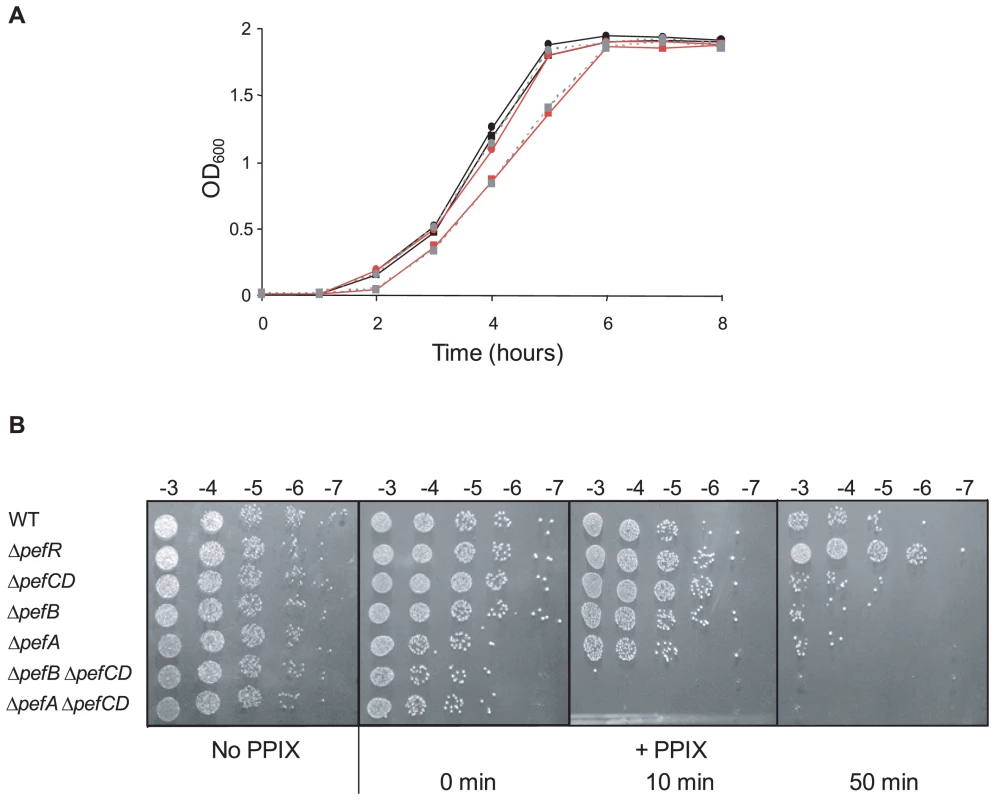
A. Growth curves of WT and mutant strains in the presence of heme. Cells were grown aerobically in M17G medium supplemented with 0 or 1 µM heme. WT (black circle), WT +1 µM heme (black square), ΔpefA ΔpefCD (red circle), ΔpefA ΔpefCD +1 µM heme (red square), ΔpefB ΔpefCD (gray circle, dashed line) and ΔpefB ΔpefCD +1 µM heme (gray square, dashed line). Results shown are representative of 3 experiments. Growth retardation of ΔpefA ΔpefCD or ΔpefB ΔpefCD was more pronounced with 2 and 4 µM heme. B. Photosensitivity of WT and mutant S. agalactiae strains grown in the presence of PPIX. Cells were grown until early stationary phase in M17G medium supplemented or not with 10 µM PPIX. Serial 10-fold dilutions (exponent is indicated) were exposed to 0, 10, or 50 minutes visible light. Plates were photographed after 24 h incubation. To evaluate PPIX accumulation in S. agalactiae WT and mutant cells, we exploited its reactivity upon exposure to visible light; when excited by light, PPIX generates reactive oxygen species [38],[39]. The WT strain, and ΔpefAB ΔpefCD single and combined mutants, and the ΔpefR mutant, were grown with 10 µM PPIX and exposed to visible light for 0, 10 or 50 minutes. Viability of cells grown without PPIX and exposed to light was equivalent for all strains (Fig. 6B). Strikingly, inactivation of both putative pumps led to total mortality upon short light exposure (Fig. 6B). These results suggested that PPIX accumulates in S. agalactiae when pefAB and pefCD systems are inactivated. There were also marked differences between WT and ΔpefR sensitivity to PPIX after a longer (50 minute) light treatment. The ΔpefR mutant, which is up-regulated for pefAB and pefCD expression, showed essentially full viability, compared to a >10-fold drop for the WT strain. These data, showing heme and PPIX sensitivities of ΔpefAB ΔpefCD mutants, and lower PPIX sensitivity of the ΔpefR mutant give strong evidence for a role of the pef regulon in porphyrin efflux and intracellular homeostasis.
Intracellular porphyrin availability in S. agalactiae WT and ΔpefA ΔpefCD strains
We used two approaches to evaluate differences in intracellular porphyrin in the WT versus ΔpefA ΔpefCD strain. First, we exploited the fact that heme - and PPIX - induce PpefA-lacZ (same as Pgbs1753-lacZ above), to compare induction levels in the WT and ΔpefA ΔpefCD double mutant strains (Fig. 7A). In response to heme and PPIX addition, β-galactosidase activity was respectively about 2-fold and 3-fold increased in the ΔpefA ΔpefCD mutant compared to WT, suggesting that more heme and PPIX are available to activate the pefA (gbs1753) promoter in this mutant.
Fig. 7. PPIX intracellular accumulation in vivo. 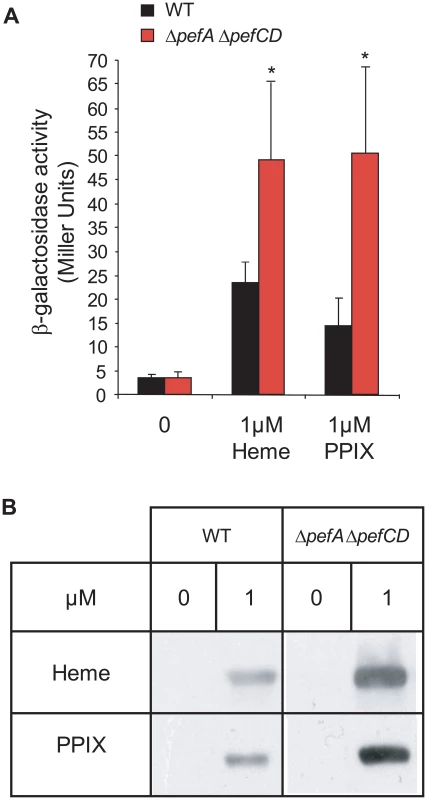
A. Expression analysis of PpefA-lacZ by β-galactosidase activity determinations was performed in early stationary phase cells of WT and ΔpefA ΔpefCD strains. S. agalactiae and derivatives were grown in BHI liquid medium. Results represent the mean ± standard deviation from triplicate experiments. Asterisks denote statistically significant differences as determined by Student's t-test (p≤0.05). B. PPIX- or heme-dependent production of the E. faecalis catalase KatA in S. agalactiae WT, and ΔpefA ΔpefCD mutant strains. Cells were grown in M17G supplemented or not with 1 µM of PPIX or heme. The loading of equivalent amounts of protein was verified by Coomassie stained gels performed in parallel. KatA was detected in total S. agalactiae protein extracts by immunoblot assays. Results shown are representative of 3 experiments. Second, we used an in vivo “heme and PPIX sensor”: the E. faecalis catalase KatA is degraded if not bound to a porphyrin molecule [19]. Intracellular availability of heme or PPIX was evaluated by comparing the relative stability of the E. faecalis KatA expressed in the WT strain and ΔpefA ΔpefCD and ΔpefR mutants (Fig. 7B and data not shown). Cells were grown without porphyrins or in 1 µM heme or PPIX, and KatA levels were followed in Western blots on cell lysates. Amounts of KatA in the WT and ΔpefR mutant strains were not significantly different (data not shown), which might reflect the limits of this reporter system. However, in the ΔpefA ΔpefCD mutant to which heme or PPIX was added, KatA showed pronounced stabilization, as expected for higher intracellular porphyrin levels in that strain. Results of both in vivo systems used above point to greater availability of porphyrins in the ΔpefA ΔpefCD mutant.
Physiological impact of pefAB and pefRCD activities on S. agalactiae respiration and virulence
S. agalactiae takes up exogenous heme, which activates its membrane cytochrome bd quinol oxidase, and is needed for respiration metabolism; the shift to respiration increases cell density by at least 20% compared to aerobic fermentation growth [17]. We compared WT, ΔpefR, ΔpefA ΔpefCD, ΔpefB ΔpefCD, and the ΔpefR strain complemented by a plasmid-carried pefR gene (ppefR) for their capacity to grow in respiration conditions (Fig. 8A). The WT, ΔpefA ΔpefCD, ΔpefB ΔpefCD, and the complemented ΔpefR strain showed increased growth densities, indicative of respiration growth in these conditions. In contrast, the ΔpefR mutant was not augmented, suggesting a respiration defect of this strain. The pefR::ISS1 insertional mutant gave the same results as the ΔpefR deletion strain (data not shown).
Fig. 8. Physiological consequences of pef mutations. 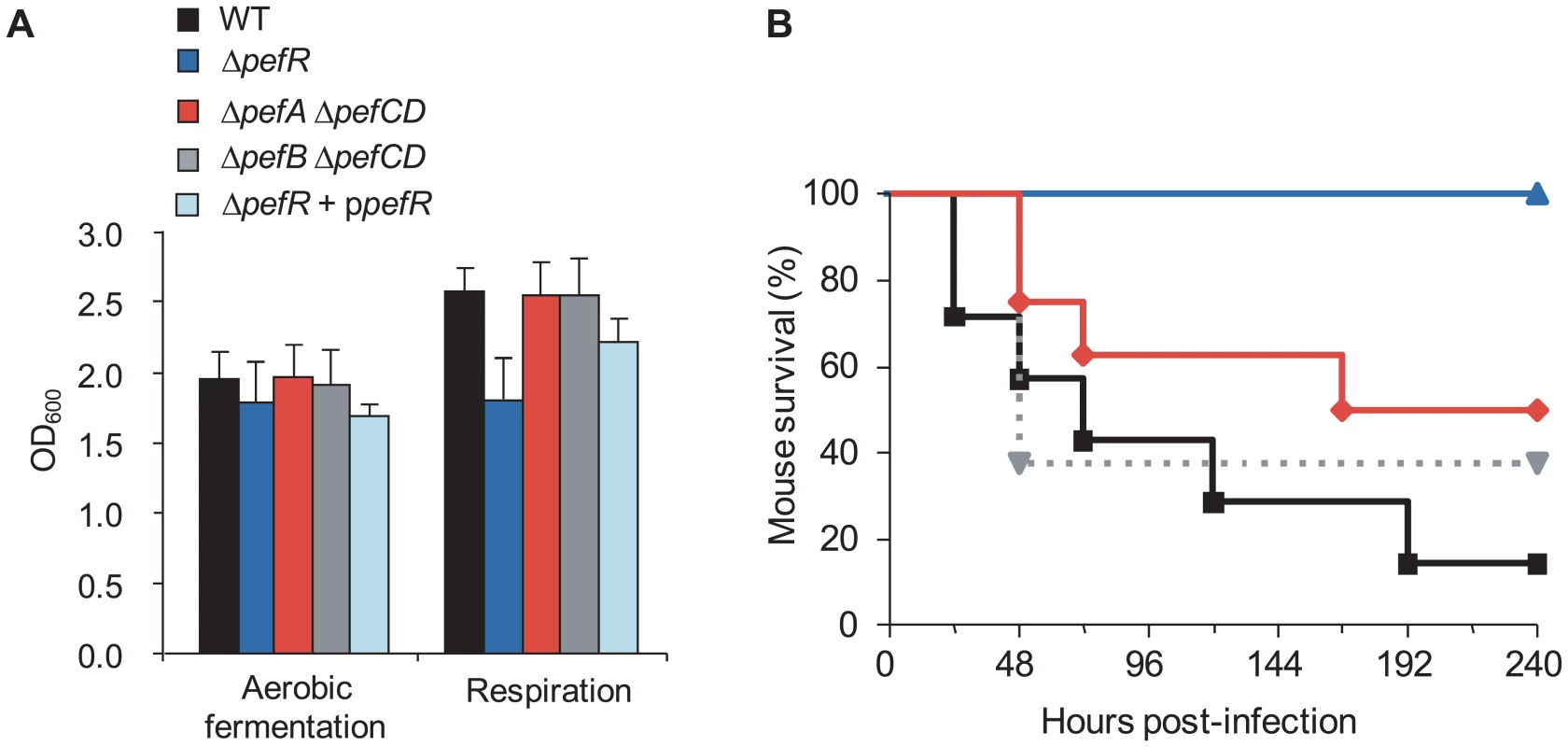
A. Impact on respiration metabolism of deregulating pefAB pefCD expression by pefR inactivation. S. agalactiae WT, ΔpefA ΔpefCD, ΔpefB ΔpefCD, ΔpefR and ΔpefR transformed with vector containing a wild-type copy of pefR (ΔpefR + ppefR) strains were grown in respiration-permissive conditions (i.e., 1 µM heme and 10 µM menaquinone). S. agalactiae respiration growth is characterized by a gain in cell density [17]. Absorbance (OD600) is shown on cultures after 22 h growth. Errors bars represent the standard deviation of three independent experiments. B. Impact on virulence of deregulating pefAB pefCD expression by pefR inactivation. Survival curves in adult mice infected with S. agalactiae WT (black square), ΔpefA ΔpefCD (red diamond), ΔpefB ΔpefCD (gray triangle, dashed line) or ΔpefR (blue triangle) strains. Differences in mortality between mice infected with the WT versus the ΔpefR mutant were statistically significant (p<0.001). To confirm that the growth difference observed above was due to respiration metabolism, we performed the same growth experiments in the presence of 2-n-heptyl-4-hydroxyquinoline N-oxide (HQNO), which inhibits respiration but allows fermentation growth (data not shown; [17]). All tested strains except ΔpefR displayed lower growth densities in HQNO, which were comparable to those in aerobic fermentation; HQNO had no effect on cell density of the ΔpefR mutant. These results confirm that all strains tested above (Fig. 8A), except ΔpefR, activated respiration growth.
Respiration growth provokes an increase in oxygen consumption [17]. This property was examined to confirm the respiration-defect of ΔpefR. Oxygen consumption in aerobic fermentation growth by the WT, ΔpefR, and ΔpefR (ppefR) strains was measured as 20.3, 21.0, and 31.1 µM.min−1 per OD600 = 1 cells (Table 1), which in these conditions reflects cytoplasmic NADH oxidase activity [17]. In respiration-permissive conditions, oxygen consumption by the WT and ΔpefR (ppefR) strain was markedly higher (44.2 and 51.6 µM.min−1 respectively), but only moderately higher for the ΔpefR mutant (30.2 µM.min−1) (Table 1), further indicating the respiration-defect in the ΔpefR mutant. These results, together with the above studies, indicate that high PefAB and PefCD efflux activities impact on respiration by diminishing heme availability.
Tab. 1. Measurement of oxygen consumption according to metabolism in WT and ΔpefR strains. 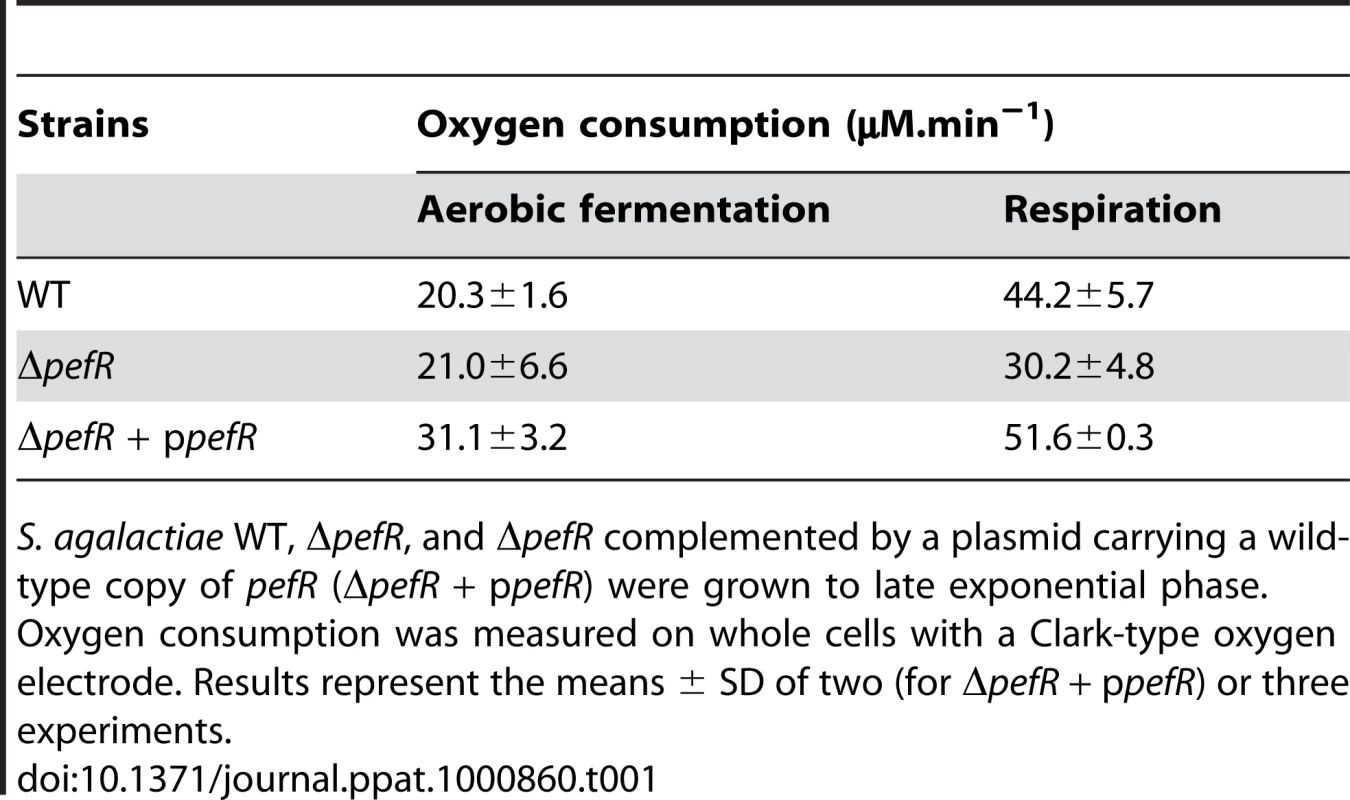
S. agalactiae WT, ΔpefR, and ΔpefR complemented by a plasmid carrying a wild-type copy of pefR (ΔpefR + ppefR) were grown to late exponential phase. Oxygen consumption was measured on whole cells with a Clark-type oxygen electrode. Results represent the means ± SD of two (for ΔpefR + ppefR) or three experiments. WT, ΔpefAB ΔpefCD and ΔpefR strains were tested in a mouse infection model (Fig. 8B). Virulence of the parental strain, and the ΔpefA ΔpefCD or ΔpefB ΔpefCD mutants was essentially the same. In contrast, the ΔpefR mutant (as well as the pefR::ISS1 insertional mutant; data not shown) showed markedly attenuated virulence. Earlier findings showed that a S. agalactiae respiration-defective mutant is attenuated for virulence [17]. Reduced intracellular heme of pefR leads to a respiration deficiency, which can explain virulence attenuation of this mutant.
Discussion
The present study uncovers a previously unknown system of porphyrin homeostasis in S. agalactiae, comprising two operons encoding distinct efflux pumps, controlled by a single intracellular regulator. Our results indicate that PefR, like numerous MarR-type proteins, acts as an intracellular sensor to regulate efflux of its ligands [40], [33], in this case, porphyrins. The range of PefR regulation is confined to the pefAB and pefRCD operons, as deduced from the presence of an IR within a 23 bp sequence uniquely upstream of these operons. This configuration is typical of MarR binding sites [33], [41], [42]. Expression of the pefAB and pefCD efflux loci limits S. agalactiae intracellular porphyrin availability; at high pef expression levels, S. agalactiae may be unable to activate respiration metabolism, and to cause septicemic infection in the animal host. The management of intracellular porphyrin levels by efflux pumps, and regulation by an intracellular sensor in S. agalactiae constitutes new information on heme and PPIX homeostasis strategies.
Homology searches revealed that 9 out of 10 species carrying pefAB genes also encode cytochrome bd quinol oxidases, and thus are genetically equipped (like S. agalactiae) to activate a respiration metabolism in the presence of heme, or heme and a menaquinone (Table S2). In contrast, the pefRCD operon seems to be specific to the Streptococcus genus, and is also present in species lacking the respiration genes. Among conditionally respiring bacteria, most characterized S. agalactiae isolates [43], and Streptococcus uberis encode the complete pef regulon. Since members of both these species share the same ecological niche (both are responsible for bovine intramammary infection [44], [45]), the presence of the complete pef regulon might conceivably arise from a genetic transfer event. However, this possibility is unlikely, as the identity between their pef ORFs (73% to 49%) is not higher than the 72% identity between these species at the genome level (Average Nucleotide Identity; calculated as in [46]). Conservation of the pef regulon may indicate a role in survival and/or infection in the particular biotopes of both these species.
Results of this study add heme and PPIX to the inventory of MarR interactants. Several MarR proteins were previously shown to bind to, and regulate efflux of lipophilic and planar molecules, such as antibiotics, aromatic aldehydes or fatty acids, usually as a means to limit cellular toxicity [47][51]. PefR activity would expectedly be tuned to retain sufficient intracellular heme for functions such as respiration. Indeed, pefAB expression in cells grown with porphyrins is induced to only half the levels compared to a fully induced ΔpefR mutant (data not shown). This, and the fact that the ΔpefR mutant is respiration defective, supports the need for basal levels of intracellular heme. Moreover, the presence of two putative PefR binding sites upstream of pefRCD (versus one upstream of pefAB) might influence the differential regulation of the two loci; possibly, lower levels of pefCD expression could participate in limiting intracellular heme depletion.
PefAB and PefCD add to a handful of other systems described as being involved in porphyrin efflux. The PefAB and PefCD systems share common features with two efflux systems in eukaryotes that control porphyrin pools: Feline leukemia virus receptor C, FLVRC, is an MFS-family protein (like PefA) that exports cytoplasmic metalloporphyrins across an ion-proton gradient [52], [53]. The breast cancer resistance protein Bcrp/ABCG2 in humans is an ABC family transporter (like PefCD) that regulates eukaryotic intracellular heme levels under hypoxic conditions [54], [55]. Just two possible porphyrin efflux systems were described in bacteria, neither of which is an analog of PefAB or PefCD: In E. coli, TolC effluxes PPIX, possibly to facilitate its turnover after iron extraction from heme; neither its regulation, nor its capacity to efflux heme have been reported [5], [56]. In S. aureus, the hrtAB locus is regulated by heme, but not PPIX, and its inactivation provokes accrued heme sensitivity [28], [27]. The S. agalactiae hrtAB homologous system (gbs0120 gbs0119) is likely to have a similar role in limiting heme toxicity. In contrast, the pef regulon is activated by PPIX, and at heme concentrations that do not induce hrtAB.
As PefAB efflux relies on proton motive force (PMF) to export substrates, we speculate that activity would be stimulated by the greater PMF generated under respiration conditions, as shown in L. lactis [57], [17], [58]. Indeed, the PefAB system is conserved in streptococci and lactobacilli having the capacity to activate a respiration metabolism. As PefCD requires ATPase activity, its activity likely varies according to growth conditions [59], [60]. The need for both PefAB and PefCD activities in S. agalactiae may accommodate the different metabolic states encountered in vivo, e.g., anaerobic fermentation in abscess, aerobic fermentation in lungs, and respiration in sepsis.
A model for heme and PPIX homeostasis in S. agalactiae, based on the newly characterized Pef operons, is proposed (Fig. 9): PefR represses expression of pefAB and pefRCD operons. Heme and PPIX are assimilated by unknown mechanisms. Once intracellular, these molecules interact with PefR, which detaches from its binding sites to activate PefAB and PefCD efflux pumps. Activities of the two Pef systems may assure rapid adjustment of intracellular heme levels under different cell physiological conditions. Whether PPIX efflux by pefAB pefCD has a biological role in S. agalactiae as an enzymatic byproduct of iron capture as in E. coli [5] remains to be determined. At higher heme concentrations, HrtAB homologs Gbs0120 and Gbs0119 could be activated via the putative two-component system Gbs0122 (heme sensor) and Gbs0121 (regulator), as was demonstrated for HssRS in S. aureus [27]. This system would have a dominant role in protecting cells in a heme-rich environment, e.g., in conditions of massive degradation of host red blood cells; such a role is consistent with the strong induction of hrtAB (>200-fold) when heme levels are high (Fig. 5). Inactivation of pefAB and pefCD loci results in increased intracellular heme and PPIX pools, with consequences on growth and on heme-dependent enzyme activities; constitutive activity of these operons by pefR inactivation depletes these intracellular pools, resulting in respiration and virulence defects.
Fig. 9. Model for pefAB and pefCD functions regulated by an intracellular sensor in S. agalactiae. 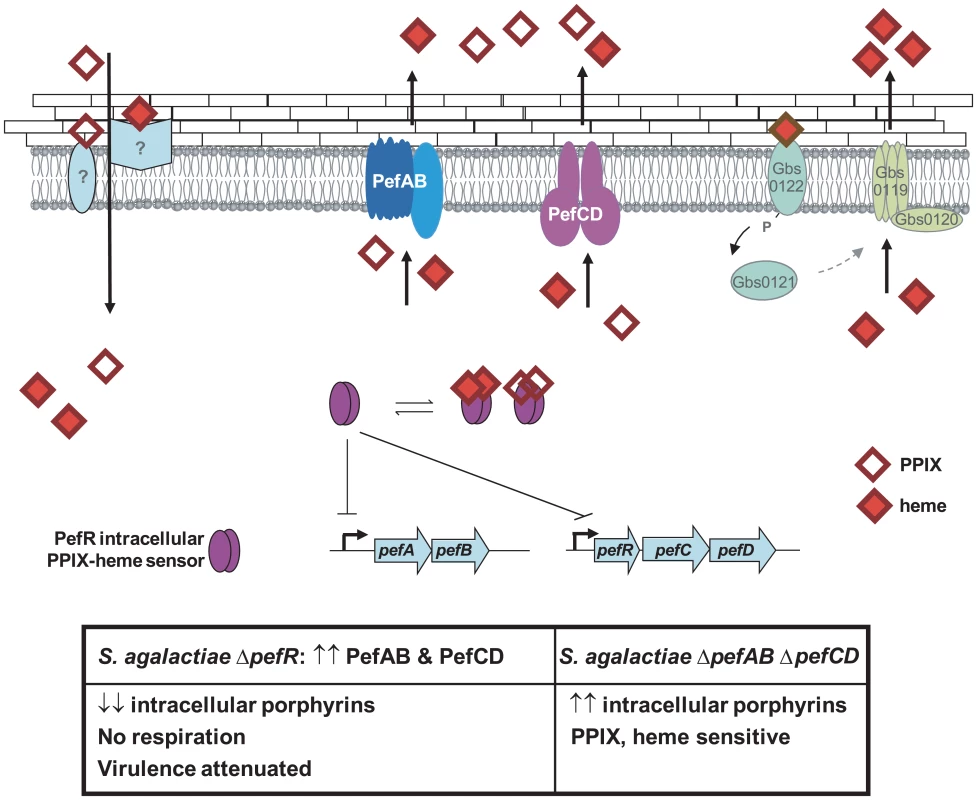
Extracellular heme and PPIX may be internalized by as yet unknown transporters. By homology with a recently described system in S. aureus [27], heme, but not PPIX, may bind to a putative external two-component receptor protein Gbs0122, the homolog of S. aureus HssS, resulting in gbs0119 gbs0120 (hrtAB) induction. Once inside the cell, free porphyrin molecules may encounter different binding proteins, including PefR. Apo-PefR binds to pefAB and pefRCD promoter regions to repress their expression. PefR-porphyrin binding releases PefR from DNA, to enable pefAB and pefRCD expression. The PefAB and PefCD loci mediate efflux of free heme and PPIX to avoid toxicity. Overexpression of PefAB and PefCD leads to heme depletion and respiration and virulence defects. Phenotypes of ΔpefR versus ΔpefAB ΔpefCD mutants are shown in the Table below. A role for respiration functions in virulence has been reported for diverse bacterial pathogens, including Brucella abortus, Shigella flexnei, S. aureus and Mycobacterium tuberculosis; unlike S. agalactiae, these bacteria biosynthesize heme and are autonomous for respiration [61][64]. In S. agalactiae, respiration is part of the metabolic reprogramming that occurs during the requisite septicemic phase of infection, in heme-rich blood [17]. We suggest that a correlation between unavailability of heme due to high pefAB and pefCD activity, and the respiration defect explains virulence attenuation in the ΔpefR mutant. The use of efflux to regulate metabolic activity of a major bacterial pathogen has not been previously reported, and will lead to a better understanding of how bacteria deal with heme and other porphyrins in the variable conditions they encounter during infection.
Materials and Methods
Ethics statement
All animal experiments were performed in strict accordance with INRA institutional guidelines of good animal practice (Jouy-en-Josas, France), and approved by the Direction des Services Vétérinaires (accreditation number 78-63).
Bacterial strains, growth conditions and plasmids
Strains and plasmids used in this study are described in Tables 2 and 3. NEM316, a S. agalactiae capsular serotype III strain was used as wild type (referred to as WT) and was isolated from a fatal case of septicemia [65]. S. agalactiae and its derivatives were cultivated at 37°C in M17 medium (Oxoid) supplemented with glucose (0.2% for pre-cultures and 1% for test cultures [referred to as M17G]). For β-galactosidase assays, S. agalactiae was grown in BHI (brain heart infusion, Difco Laboratories) supplemented with 0.8% glucose. Aerated cultures were grown under agitation at 200 rpm in a ratio of air space to liquid of approximately 5/1. Respiring cultures were grown under agitation in the presence of 1 µM hemin (from a stock solution of 10 mM hemin chloride, Fluka) and 10 µM vitamin K2 (a menaquinone; Sigma). E. coli was cultivated in LB medium (Luria-Bertani, Difco Laboratories) at 37°C with aeration by shaking at 180 rpm. Antibiotics were used as needed at the following concentrations: for S. agalactiae, 5 µg/ml erythromycin, 1000 µg/ml kanamycin, 4 µg/ml chloramphenicol, 5 µg/ml tetracycline; for E. coli, 100 µg/ml erythromycin, 20 µg/ml chloramphenicol.
Tab. 2. Strains used in this study. 
Tab. 3. Plasmids used in this study. 
RNA extraction, Northern blot and RACE PCR
RNA was extracted from S. agalactiae cultures as described [66]. Cells from 20 ml culture with an OD600 of 0.5∼0.8 (exponential growth phase) or OD600∼1.5 were harvested by centrifugation at 6000×g during 10 min. Total RNA was extracted with a guanidine isothycionate and phenol-chloroform step [67], using the TRIzol Reagent (Invitrogen).
For Northern blot analysis, RNA samples (30 µg) were mixed with an equal volume of glyoxal load dye (Ambion) and were electrophoretically separated on a 0.9% agarose glyoxal gel [68]. RNA samples were transferred to a Biodyne B membrane (Pall) according to manufacturer's instructions. Hybridization and detection were performed using ECL direct nucleic acid labeling and detection systems (Amersham). A ∼500 base pair (bp) DNA labeled fragment of each ORF tested was used as probe. Primers used for probe generation are shown in Table S3.
The pefA transcriptional start was mapped using a 5′/3′ rapid amplification cDNA ends (RACE) kit, second generation (Roche Applied Science) according to supplier's instructions. Mapping was realized with RNA extracted from respiring cells, using primers: 5′TAGATGTAGGTGCTAACGTCG3′ and 5′CTTGTTGAGCCGTTGACAACG3′.
β-galactosidase assays
Plasmid pTCV-lac is a low copy number plasmid used to evaluate promoter activities in S. agalactiae [32]. A DNA fragment containing gbs1753 promoter was PCR-amplified with primers 5′GCGTAGAATTCATTAAATGGAG3′, containing an EcoRI site (underlined) and 5′TATCTCGGATCCCTATTTCTGAT3′, containing a BamHI site (underlined). After digestion of the amplified fragment by EcoRI and BamHI, the gbs1753 promoter was cloned into plasmid pTCV-lac, resulting in plasmid pTCV-J11 carrying the Pgbs1753-lacZ (or PpefA-lacZ) fusion. The plasmids pTCV-lac and pTCV-J11 were subsequently transformed into S. agalactiae by electroporation and recombinant clones were obtained by erythromycin selection. The same strategy was performed to generate a Pgbs0119-lacZ fusion using the primers 5′ATACGCCAGAATTCTCGGCGAC3′ and 5′CCTTGGATCCTTTGATGTGAAC3′, giving rise to plasmid pTCV-J21.
Mutagenesis and screening conditions
Random insertional mutagenesis was performed on S. agalactiae with pG+host8::ISS1 basically as described [69]. Both Pgbs1753-lacZ (reporter for gbs1753 transcription) and pG+host8::ISS1 plasmids were established in S. agalactiae. The strain was grown at 30°C with kanamycin for 2.5 h. The temperature was then shifted to 37°C for 2.5 h and plated on M17G with erythromycin, kanamycin and 80 µg/ml X-gal (5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-beta-D-galactopyranoside, BioMerieux), to obtain ∼100 CFU per plate. After 24 h incubation at 37°C, deep blue colonies were selected. Stable ISS1 mutants were isolated by growth at 30°C without erythromycin as described [70]. The flanking chromosomal DNA was sequenced using primer 5′AGGGCATGGAAACAATTCGAGG3′. From the 5000 mutants we screened, 7 were in the pefR locus. Stable ISS1 mutants were then retested for gbs1753 up-regulation.
Gbs1402 (PefR) overexpression and purification
The gbs1402 ORF was amplified by PCR from S. agalactiae NEM316 using primers 5′CACCATGGAGAATCCTCTTCAAAA3′ and 5′TAATCAAAATCTTCCATCGCC3′. This amplified fragment was cloned into the E. coli expression plasmid Champion pET100 directional TOPO vector (Invitrogen) and transformed into E. coli TOP10. After plasmid verification by sequencing, the plasmid pET100-J14 was electroporated in E. coli BL21 (DE3). Protein expression was induced at an OD600 = 0.6 by addition of 1 mM IPTG for 2 h. Cells were harvested by centrifugation at 6000 rpm for 10 min and resuspended in 10 ml binding buffer (Tris HCl 50 mM pH 8, NaCl 300 mM, Imidazole 50 mM). Cells were broken by shaking with glass beads in a Fast Prep apparatus (MP Biomedicals). The lysate was centrifuged at 14000 rpm for 15 min at 4°C. The recombinant His-tagged fusion protein was purified by nickel affinity chromatography using His-Select affinity (Sigma) equilibrated with binding buffer according to supplier's instructions. The elution was carried out with binding buffer containing 300 mM imidazole. All fractions were collected and analyzed by SDS-PAGE. Purified proteins were dialyzed against 50 mM Tris HCl pH 8, 80 mM NaCl and 6.25% glycerol. Protein concentrations were determined by the Lowry assay (Bio-Rad).
Immunoblotting analysis
Strains harboring PaphA-3-katA-His6 plasmid were incubated overnight under static conditions with or without 1 µM heme or PPIX. Cell growth was harvested by centrifugation at 6000×g during 10 min. Cells were broken by shaking with glass beads in a Fast Prep apparatus (MP Biomedicals). Immunoblotting analysis was done with rabbit anti-KatA antiserum as described, and kindly provided by Dr. L. Hederstedt [19]. Detection was performed using ECL Plus Western blotting detection reagents (GE Healthcare).
Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA)
A 281 bp DNA fragment containing the gbs1753 promoter region and a 248 bp DNA fragment containing the gbs1402 promoter region were generated by PCR from genomic DNA of S. agalactiae and purified using the PureLink PCR Purification Kit (Invitrogen). Binding assays with PefR were carried out using a binding buffer (5% glycerol, 20 mM Tris HCl pH 8, 50 mM KCl, 0.2 mM MgCl2, 1 mM EDTA, 0.2 mM DTT, 0.3 µM BSA) in a final volume of 15 µl at 37°C. Reaction mixtures were incubated at 37°C for 20 min, after which they were analyzed by gel electrophoresis on an 8% polyacrylamide gel in TBE 1× buffer, stained with ethidium bromide. Reactions were carried out in the presence of a 116 bp non-specific competitor DNA (internal coding gbs1753 sequence) where specified. Where tested, heme or PPIX were added 20 min after protein and DNA components. Gel shift experiments were performed with two independent batches of purified PefR.
Construction of Δgbs1753 (ΔpefA), Δgbs1752 (ΔpefB), Δgbs1401 Δgbs1400 (ΔpefCD) and Δgbs1402 (ΔpefR) mutants and ppefR plasmid construction
In-frame pefA, pefB, pefCD, and pefR deletion mutants were constructed using the strategy described below. Briefly, the two regions flanking the locus to be deleted were independently amplified by PCR (see Table S3 for primers). Amplified fragments were digested by HindIII or EcoRV enzyme and ligated to each other. The resulting fragments were amplified by PCR, digested by EcoRI enzyme and cloned into the thermosensitive shuttle plasmid pG+host5. Electroporation of S. agalactiae strains and allelic exchange were done as described [70]. In-frame deletions were confirmed by PCR and sequence analysis. The pefR gene was amplified (Table S3 for primers), and cloned using EcoRI and BamHI on fragment ends, onto plasmid pRC2 cut with the same enzymes; the resulting plasmid, pRC2-J14, is referred to as ppefR in Results.
PPIX and metalloporphyrin sensitivity tests
Stock solutions (10 mM) of PPIX, GaPPIX, ZnPPIX, and ZnMPIX (Frontier Scientific) were prepared in DMSO. PPIX sensitivity of S. agalactiae NEM316 and its derivatives was examined on early stationary growing cells (OD600 = 1.6). For PPIX light sensitivity tests, serial dilutions were spotted on plates and exposed to visible light for 0, 10 or 50 minutes. A 500 W halogen lamp with a glass lid placed at a distance of 55 cm was used as light source. Metalloporphyrin sensitivity tests on plates were performed as described [12]: Briefly, 1∶100 dilutions of stationary-phase cultures were prepared in M17G soft (0.7%) agar, and poured over M17G plates. Metalloporphyrin (heme, 5 µl of a 0.2 mM solution; GaPPIX, 5 µl of a 10 mM solution) was spotted onto the plates. All plates were incubated for 20 h at 37°C and then photographed.
Oxygen consumption.measurements
Oxygen consumption was determined as described [17]. Briefly, S. agalactiae WT and ΔpefR late exponential phase cultures, prepared in aerobic fermentation or respiration conditions, were washed twice with PBS at 4°C and resuspended in the same buffer to obtain a 1 ml bacterial suspension at OD600 = 1.0. Oxygen consumption was followed with a Clark-type oxygen electrode (Liquid-Phase Oxygen electrode unit DW1, Hansatech instruments). The maximum oxygen consumption rate was measured following the addition of 10 mM glucose.
Mouse virulence assay
Pathogen-free 6 week-old Swiss CD1 mice (Charles River laboratories) were infected intravenously with S. agalactiae NEM316 or derivatives. Groups of 7–8 mice were anesthetized with ketamine (100 µg/g, Merial) and xylazine (12 µg/g, Bayer) and were inoculated in the eye vein with 108 CFU. Bacterial counts were determined in parallel by plating serial dilutions in saline buffer on M17G. Cells were harvested from mid-log phase and washed in a solution of NaCl 0.9%. Mortality was observed over a 10-day period. Animal experiments were performed in triplicate.
Bioinformatics
To find the conserved sequence between pef promoter regions, sequence were aligned with ClustalW and manually refined. A search for the 23 bp consensus in S. agalactiae NEM316 genome was done by visual inspection, and using BlastN program with EXPECT threshold set at 100. Pef protein homologs were identified using Genome Region Comparison, http://cmr.jcvi.org/cgi-bin/CMR/CmrHomePage.cgi, and/or were retrieved from genomic Blast databases, http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi/, using BlastP program with an E-value threshold set at 0.01.
Supporting Information
Zdroje
1. MenseSM
ZhangL
2006 Heme: a versatile signaling molecule controlling the activities of diverse regulators ranging from transcription factors to MAP kinases. Cell Res 16 681 692
2. ShepherdM
HeathMD
PooleRK
2007 NikA binds heme: a new role for an Escherichia coli periplasmic nickel-binding protein. Biochemistry 46 5030 5037
3. Gilles-GonzalezMA
GonzalezG
2004 Signal transduction by heme-containing PAS-domain proteins. J Appl Physiol 96 774 783
4. KumarS
BandyopadhyayU
2005 Free heme toxicity and its detoxification systems in human. Toxicol Lett 157 175 188
5. LetoffeS
HeuckG
DelepelaireP
LangeN
WandersmanC
2009 Bacteria capture iron from heme by keeping tetrapyrrol skeleton intact. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
6. BaughnAD
MalamyMH
2004 The strict anaerobe Bacteroides fragilis grows in and benefits from nanomolar concentrations of oxygen. Nature 427 441 444
7. BrooijmansRJ
de VosWM
HugenholtzJ
2009 Lactobacillus plantarum WCFS1 electron transport chains. Appl Environ Microbiol 75 3580 3585
8. DuwatP
SouriceS
CesselinB
LamberetG
VidoK
2001 Respiration capacity of the fermenting bacterium Lactococcus lactis and its positive effects on growth and survival. J Bacteriol 183 4509 4516
9. GauduP
VidoK
CesselinB
KulakauskasS
TremblayJ
2002 Respiration capacity and consequences in Lactococcus lactis. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 82 263 269
10. HanYH
SmibertRM
KriegNR
1992 Cytochrome composition and oxygen-dependent respiration-driven proton translocation in Wolinella curva, Wolinella recta, Bacteroides ureolyticus, and Bacteroides gracilis. Can J Microbiol 38 104 110
11. HuyckeMM
MooreD
JoyceW
WiseP
ShepardL
2001 Extracellular superoxide production by Enterococcus faecalis requires demethylmenaquinone and is attenuated by functional terminal quinol oxidases. Mol Microbiol 42 729 740
12. PedersenMB
GarriguesC
TuphileK
BrunC
VidoK
2008 Impact of aeration and heme-activated respiration on Lactococcus lactis gene expression: identification of a heme-responsive operon. J Bacteriol 190 4903 4911
13. RezaikiL
CesselinB
YamamotoY
VidoK
van WestE
2004 Respiration metabolism reduces oxidative and acid stress to improve long-term survival of Lactococcus lactis. Mol Microbiol 53 1331 1342
14. RitcheyTW
SeeleyHW
1974 Cytochromes in Streptococcus faecalis var. zymogenes grown in a haematin-containing medium. J Gen Microbiol 85 220 228
15. SijpesteijnAK
1970 Induction of cytochrome formation and stimulation of oxidative dissimilation by hemin in Streptococcus lactis and Leuconostoc mesenteroides. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 36 335 348
16. WinstedtL
FrankenbergL
HederstedtL
von WachenfeldtC
2000 Enterococcus faecalis V583 contains a cytochrome bd-type respiratory oxidase. J Bacteriol 182 3863 3866
17. YamamotoY
PoyartC
Trieu-CuotP
LamberetG
GrussA
2005 Respiration metabolism of Group B Streptococcus is activated by environmental haem and quinone and contributes to virulence. Mol Microbiol 56 525 534
18. YamamotoY
PoyartC
Trieu-CuotP
LamberetG
GrussA
2006 Roles of environmental heme, and menaquinone, in Streptococcus agalactiae. Biometals 19 205 210
19. FrankenbergL
BrugnaM
HederstedtL
2002 Enterococcus faecalis heme-dependent catalase. J Bacteriol 184 6351 6356
20. AllenCE
SchmittMP
2009 HtaA is an iron-regulated hemin binding protein involved in the utilization of heme iron in Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J Bacteriol 191 2638 2648
21. AndrewsSC
RobinsonAK
Rodriguez-QuinonesF
2003 Bacterial iron homeostasis. FEMS Microbiol Rev 27 215 237
22. BibbLA
KunkleCA
SchmittMP
2007 The ChrA-ChrS and HrrA-HrrS signal transduction systems are required for activation of the hmuO promoter and repression of the hemA promoter in Corynebacterium diphtheriae. Infect Immun 75 2421 2431
23. CescauS
CwermanH
LetoffeS
DelepelaireP
WandersmanC
2007 Heme acquisition by hemophores. Biometals 20 603 613
24. KaurAP
LanskyIB
WilksA
2009 The role of the cytoplasmic heme-binding protein (PhuS) of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in intracellular heme trafficking and iron homeostasis. J Biol Chem 284 56 66
25. QiZ
HamzaI
O'BrianMR
1999 Heme is an effector molecule for iron-dependent degradation of the bacterial iron response regulator (Irr) protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96 13056 13061
26. StauffDL
BagaleyD
TorresVJ
JoyceR
AndersonKL
2008 Staphylococcus aureus HrtA is an ATPase required for protection against heme toxicity and prevention of a transcriptional heme stress response. J Bacteriol 190 3588 3596
27. TorresVJ
StauffDL
PishchanyG
BezbradicaJS
GordyLE
2007 A Staphylococcus aureus regulatory system that responds to host heme and modulates virulence. Cell Host Microbe 1 109 119
28. StauffDL
SkaarEP
2009 Bacillus anthracis HssRS signaling to HrtAB regulates heme resistance during infection. Mol Microbiol
29. DoranKS
NizetV
2004 Molecular pathogenesis of neonatal group B streptococcal infection: no longer in its infancy. Mol Microbiol 54 23 31
30. LindahlG
Stalhammar-CarlemalmM
AreschougT
2005 Surface proteins of Streptococcus agalactiae and related proteins in other bacterial pathogens. Clin Microbiol Rev 18 102 127
31. PaoSS
PaulsenIT
SaierMHJr
1998 Major facilitator superfamily. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62 1 34
32. PoyartC
Trieu-CuotP
1997 A broad-host-range mobilizable shuttle vector for the construction of transcriptional fusions to beta-galactosidase in gram-positive bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett 156 193 198
33. WilkinsonSP
GroveA
2006 Ligand-responsive transcriptional regulation by members of the MarR family of winged helix proteins. Curr Issues Mol Biol 8 51 62
34. ProvidentiMA
WyndhamRC
2001 Identification and functional characterization of CbaR, a MarR-like modulator of the cbaABC-encoded chlorobenzoate catabolism pathway. Appl Environ Microbiol 67 3530 3541
35. WilkinsonSP
GroveA
2004 HucR, a novel uric acid-responsive member of the MarR family of transcriptional regulators from Deinococcus radiodurans. J Biol Chem 279 51442 51450
36. KaatzGW
DeMarcoCE
SeoSM
2006 MepR, a repressor of the Staphylococcus aureus MATE family multidrug efflux pump MepA, is a substrate-responsive regulatory protein. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 50 1276 1281
37. FriedmanDB
StauffDL
PishchanyG
WhitwellCW
TorresVJ
2006 Staphylococcus aureus redirects central metabolism to increase iron availability. PLoS Pathog 2 e87 doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.0020087
38. EpeB
PflaumM
HaringM
HeglerJ
RudigerH
1993 Use of repair endonucleases to characterize DNA damage induced by reactive oxygen species in cellular and cell-free systems. Toxicol Lett 67 57 72
39. MalikZ
LadanH
NitzanY
EhrenbergB
1990 The bactericidal activity of a deuteroporphyrin-hemin mixture on gram-positive bacteria. A microbiological and spectroscopic study. J Photochem Photobiol B 6 419 430
40. EllisonDW
MillerVL
2006 Regulation of virulence by members of the MarR/SlyA family. Curr Opin Microbiol 9 153 159
41. AlekshunMN
LevySB
MealyTR
SeatonBA
HeadJF
2001 The crystal structure of MarR, a regulator of multiple antibiotic resistance, at 2.3 A resolution. Nat Struct Biol 8 710 714
42. LimD
PooleK
StrynadkaNC
2002 Crystal structure of the MexR repressor of the mexRAB-oprM multidrug efflux operon of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Biol Chem 277 29253 29259
43. BrochetM
CouveE
ZouineM
VallaeysT
RusniokC
2006 Genomic diversity and evolution within the species Streptococcus agalactiae. Microbes Infect 8 1227 1243
44. LeighJA
1999 Streptococcus uberis: a permanent barrier to the control of bovine mastitis? Vet J 157 225 238
45. WardPN
HoldenMT
LeighJA
LennardN
BignellA
2009 Evidence for niche adaptation in the genome of the bovine pathogen Streptococcus uberis. BMC Genomics 10 54
46. GorisJ
KonstantinidisKT
KlappenbachJA
CoenyeT
VandammeP
2007 DNA-DNA hybridization values and their relationship to whole-genome sequence similarities. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57 81 91
47. FiorentinoG
RoncaR
CannioR
RossiM
BartolucciS
2007 MarR-like transcriptional regulator involved in detoxification of aromatic compounds in Sulfolobus solfataricus. J Bacteriol 189 7351 7360
48. KaatzGW
McAleeseF
SeoSM
2005 Multidrug resistance in Staphylococcus aureus due to overexpression of a novel multidrug and toxin extrusion (MATE) transport protein. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49 1857 1864
49. LeeEH
Rouquette-LoughlinC
FolsterJP
ShaferWM
2003 FarR regulates the farAB-encoded efflux pump of Neisseria gonorrhoeae via an MtrR regulatory mechanism. J Bacteriol 185 7145 7152
50. PooleK
TetroK
ZhaoQ
NeshatS
HeinrichsDE
1996 Expression of the multidrug resistance operon mexA-mexB-oprM in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: mexR encodes a regulator of operon expression. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 40 2021 2028
51. SeoaneAS
LevySB
1995 Characterization of MarR, the repressor of the multiple antibiotic resistance (mar) operon in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 177 3414 3419
52. KeelSB
DotyRT
YangZ
QuigleyJG
ChenJ
2008 A heme export protein is required for red blood cell differentiation and iron homeostasis. Science 319 825 828
53. QuigleyJG
YangZ
WorthingtonMT
PhillipsJD
SaboKM
2004 Identification of a human heme exporter that is essential for erythropoiesis. Cell 118 757 766
54. KrishnamurthyP
RossDD
NakanishiT
Bailey-DellK
ZhouS
2004 The stem cell marker Bcrp/ABCG2 enhances hypoxic cell survival through interactions with heme. J Biol Chem 279 24218 24225
55. KrishnamurthyP
XieT
SchuetzJD
2007 The role of transporters in cellular heme and porphyrin homeostasis. Pharmacol Ther 114 345 358
56. TatsumiR
WachiM
2008 TolC-dependent exclusion of porphyrins in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 190 6228 6233
57. BlankLM
KoebmannBJ
MichelsenO
NielsenLK
JensenPR
2001 Hemin reconstitutes proton extrusion in an H(+)-ATPase-negative mutant of Lactococcus lactis. J Bacteriol 183 6707 6709
58. BrooijmansRJ
PoolmanB
Schuurman-WoltersGK
de VosWM
HugenholtzJ
2007 Generation of a membrane potential by Lactococcus lactis through aerobic electron transport. J Bacteriol 189 5203 5209
59. KleinAH
ShullaA
ReimannSA
KeatingDH
WolfeAJ
2007 The intracellular concentration of acetyl phosphate in Escherichia coli is sufficient for direct phosphorylation of two-component response regulators. J Bacteriol 189 5574 5581
60. KoebmannB
BlankLM
SolemC
PetranovicD
NielsenLK
2008 Increased biomass yield of Lactococcus lactis during energetically limited growth and respiratory conditions. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 50 25 33
61. WaySS
SallustioS
MagliozzoRS
GoldbergMB
1999 Impact of either elevated or decreased levels of cytochrome bd expression on Shigella flexneri virulence. J Bacteriol 181 1229 1237
62. EndleyS
McMurrayD
FichtTA
2001 Interruption of the cydB locus in Brucella abortus attenuates intracellular survival and virulence in the mouse model of infection. J Bacteriol 183 2454 2462
63. ProctorRA
von EiffC
KahlBC
BeckerK
McNamaraP
2006 Small colony variants: a pathogenic form of bacteria that facilitates persistent and recurrent infections. Nat Rev Microbiol 4 295 305
64. ShiL
SohaskeyCD
KanaBD
DawesS
NorthRJ
2005 Changes in energy metabolism of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in mouse lung and under in vitro conditions affecting aerobic respiration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102 15629 15634
65. GaillotO
PoyartC
BercheP
Trieu-CuotP
1997 Molecular characterization and expression analysis of the superoxide dismutase gene from Streptococcus agalactiae. Gene 204 213 218
66. LamyMC
ZouineM
FertJ
VergassolaM
CouveE
2004 CovS/CovR of group B streptococcus: a two-component global regulatory system involved in virulence. Mol Microbiol 54 1250 1268
67. ChomczynskiP
SacchiN
1987 Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162 156 159
68. SambrookJ
FritschE
ManiatisT
1989 Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual Cold Spring Harbor, New York Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press
69. MaguinE
PrevostH
EhrlichSD
GrussA
1996 Efficient insertional mutagenesis in lactococci and other gram-positive bacteria. J Bacteriol 178 931 935
70. BiswasI
GrussA
EhrlichSD
MaguinE
1993 High-efficiency gene inactivation and replacement system for gram-positive bacteria. J Bacteriol 175 3628 3635
71. LawJ
BuistG
HaandrikmanA
KokJ
VenemaG
1995 A system to generate chromosomal mutations in Lactococcus lactis which allows fast analysis of targeted genes. J Bacteriol 177 7011 7018
72. el KarouiM
EhrlichD
GrussA
1998 Identification of the lactococcal exonuclease/recombinase and its modulation by the putative Chi sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95 626 631
Štítky
Hygiena a epidemiológia Infekčné lekárstvo Laboratórium
Článek Suppression of mRNAs Encoding Tegument Tetraspanins from Results in Impaired Tegument TurnoverČlánek Novel Riboswitch Ligand Analogs as Selective Inhibitors of Guanine-Related Metabolic PathwaysČlánek The Physical Relationship between Infectivity and Prion Protein Aggregates Is Strain-DependentČlánek Rhomboid 4 (ROM4) Affects the Processing of Surface Adhesins and Facilitates Host Cell Invasion by
Článok vyšiel v časopisePLOS Pathogens
Najčítanejšie tento týždeň
2010 Číslo 4- Parazitičtí červi v terapii Crohnovy choroby a dalších zánětlivých autoimunitních onemocnění
- Očkování proti virové hemoragické horečce Ebola experimentální vakcínou rVSVDG-ZEBOV-GP
- Koronavirus hýbe světem: Víte jak se chránit a jak postupovat v případě podezření?
-
Všetky články tohto čísla
- Innate Recognition of Fungal Cell Walls
- Suppression of mRNAs Encoding Tegument Tetraspanins from Results in Impaired Tegument Turnover
- Junín Virus Infection of Human Hematopoietic Progenitors Impairs Proplatelet Formation and Platelet Release via a Bystander Effect Involving Type I IFN Signaling
- The Endosymbiotic Bacterium Induces Resistance to Dengue Virus in
- Natural Regulatory T Cells in Malaria: Host or Parasite Allies?
- Keratinocytes Determine Th1 Immunity during Early Experimental Leishmaniasis
- Spatial and Temporal Association of Outbreaks of H5N1 Influenza Virus Infection in Wild Birds with the 0°C Isotherm
- Novel Riboswitch Ligand Analogs as Selective Inhibitors of Guanine-Related Metabolic Pathways
- RNA Polymerase Activity and Specific RNA Structure Are Required for Efficient HCV Replication in Cultured Cells
- The Physical Relationship between Infectivity and Prion Protein Aggregates Is Strain-Dependent
- Inadequate Clearance of Translocated Bacterial Products in HIV-Infected Humanized Mice
- Topology and Organization of the Type III Secretion Needle Complex Components
- Temperature Modulates Plant Defense Responses through NB-LRR Proteins
- Peptide Inhibitors of Dengue-Virus Entry Target a Late-Stage Fusion Intermediate
- Identification of Host-Dependent Survival Factors for Intracellular through an siRNA Screen
- Exposure to HIV-1 Directly Impairs Mucosal Epithelial Barrier Integrity Allowing Microbial Translocation
- Increased Asymmetric Dimethylarginine in Severe Falciparum Malaria: Association with Impaired Nitric Oxide Bioavailability and Fatal Outcome
- Reconstitution of SARS-Coronavirus mRNA Cap Methylation
- Induces Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cell Detachment from the Matrix and Cleavage of Occludin: A Role for MMP-8
- Two Coregulated Efflux Transporters Modulate Intracellular Heme and Protoporphyrin IX Availability in
- The Type I NADH Dehydrogenase of Counters Phagosomal NOX2 Activity to Inhibit TNF-α-Mediated Host Cell Apoptosis
- Rhomboid 4 (ROM4) Affects the Processing of Surface Adhesins and Facilitates Host Cell Invasion by
- Increased Monocyte Turnover from Bone Marrow Correlates with Severity of SIV Encephalitis and CD163 Levels in Plasma
- The RING-CH Ligase K5 Antagonizes Restriction of KSHV and HIV-1 Particle Release by Mediating Ubiquitin-Dependent Endosomal Degradation of Tetherin
- Molecular Mechanisms of Ethanol-Induced Pathogenesis Revealed by RNA-Sequencing
- Highly Frequent Mutations in Negative Regulators of Multiple Virulence Genes in Group A Streptococcal Toxic Shock Syndrome Isolates
- Emergence and Pathogenicity of Highly Virulent Genotypes in the Northwest United States
- Structural and Functional Analysis of Viral siRNAs
- Prion Shedding from Olfactory Neurons into Nasal Secretions
- a GATA Transcription Factor That Directs Disparate Fates in Including Morphogenesis and Siderophore Biosynthesis
- Three Members of the 6-cys Protein Family of Play a Role in Gamete Fertility
- Complement as an Endogenous Adjuvant for Dendritic Cell-Mediated Induction of Retrovirus-Specific CTLs
- A Genomic Survey of Positive Selection in Provides Insights into the Evolution of Accidental Virulence
- Overcomes Stress of Azole Drugs by Formation of Disomy in Specific Multiple Chromosomes
- Blood Fluke Exploitation of Non-Cognate CD4 T Cell Help to Facilitate Parasite Development
- Antagonism of Tetherin Restriction of HIV-1 Release by Vpu Involves Binding and Sequestration of the Restriction Factor in a Perinuclear Compartment
- The Development of Therapeutic Antibodies That Neutralize Homologous and Heterologous Genotypes of Dengue Virus Type 1
- Deficiencies in Jasmonate-Mediated Plant Defense Reveal Quantitative Variation in Pathogenesis
- Interactions with Bacteria in the Context of Human Health and Disease
- Viral Capsid Is a Pathogen-Associated Molecular Pattern in Adenovirus Keratitis
- Electron Tomography Reveals the Steps in Filovirus Budding
- Selective Condensation Drives Partitioning and Sequential Secretion of Cyst Wall Proteins in Differentiating
- The Effect of Vaccination on the Evolution and Population Dynamics of Avian Paramyxovirus-1
- A Timescale for Evolution, Population Expansion, and Spatial Spread of an Emerging Clone of Methicillin-Resistant
- VacA Toxin/Subunit p34: Targeting of an Anion Channel to the Inner Mitochondrial Membrane
- Production of Extracellular Traps against and in Infected Lung Tissue Is Dependent on Invading Neutrophils and Influenced by Hydrophobin RodA
- A Differential Role for Macropinocytosis in Mediating Entry of the Two Forms of Vaccinia Virus into Dendritic Cells
- Impaired Innate Immunity in Mice but Preserved CD8 T Cell Responses against in -, -, - or -Deficient Mice
- SARS-CoV Pathogenesis Is Regulated by a STAT1 Dependent but a Type I, II and III Interferon Receptor Independent Mechanism
- Proteolysis of Human Thrombin Generates Novel Host Defense Peptides
- Multilayered Mechanism of CD4 Downregulation by HIV-1 Vpu Involving Distinct ER Retention and ERAD Targeting Steps
- PLOS Pathogens
- Archív čísel
- Aktuálne číslo
- Informácie o časopise
Najčítanejšie v tomto čísle- The Effect of Vaccination on the Evolution and Population Dynamics of Avian Paramyxovirus-1
- Reconstitution of SARS-Coronavirus mRNA Cap Methylation
- Deficiencies in Jasmonate-Mediated Plant Defense Reveal Quantitative Variation in Pathogenesis
- A Timescale for Evolution, Population Expansion, and Spatial Spread of an Emerging Clone of Methicillin-Resistant
Prihlásenie#ADS_BOTTOM_SCRIPTS#Zabudnuté hesloZadajte e-mailovú adresu, s ktorou ste vytvárali účet. Budú Vám na ňu zasielané informácie k nastaveniu nového hesla.
- Časopisy



